Antigen Microarray Detection Service for Coronavirus-Associated Autoimmunity
Creative Biolabs is pleased to provide services of antigen microarray detection for coronavirus-associated autoimmunity to our global clients. With years of accumulation and exploration, we have established a reliable platform for autoantigen microarray detection services, which supports both functional and analytical assays, ready to assist you in the investigation of preselected proteins, as well as the identification of novel targets of coronavirus-associated autoantibodies in various disease conditions.
Background
Introduction of Coronavirus-Associated Autoimmunity
- SARS-CoV
In the winter of 2002-2003, severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) emerged in China and subsequently spread throughout the world. SARS is caused by a novel species of coronavirus that has been named SARS-CoV. Several studies have suggested that autoimmunity may also be involved in the pathogenesis of SARS. Indeed, there are cross-reactive epitopes on domain 2 of the SARS-CoV spike protein (S2) with human lung epithelial cell proteins. Anti-SARS-CoV spike antibodies enhance the adherence of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells to A549 cells. Thus, the autoimmune responses in SARS-CoV infection may contribute to the pathogenesis of the disease.
- SARS-CoV-2
It has been suggested that the shared pathogenetic mechanisms and clinical-radiological aspects between the hyper-inflammatory diseases and Covid-19 may suggest that SARS-CoV-2 could act as a triggering factor for the development of a rapid autoimmune and/or autoinflammatory dysregulation, leading to the severe interstitial pneumonia, in genetically predisposed individuals. Furthermore, in an online pre-published study, the authors studied prospectively a group of 22 patients for the possible role of autoimmunity in SARS-CoV-2-associated respiratory failure. Based on serological, radiological, and histomorphological similarities between Covid-19-associated ARDS and acute exacerbation of connective tissue disease-induced interstitial lung disease, the authors suggest that SARS-CoV-2 infection might trigger or simulate a form of organ-specific autoimmunity in predisposed patients. In a similar retrospective study from China of 21 patients with critical SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia, the authors showed a prevalence of between 20% and 50% of autoimmune disease-related autoantibodies, suggesting the rationale for immunosuppression in such cases of Covid-19.
Antigen Microarray Detection for Coronavirus-Associated Autoimmunity
Antibody microarrays, or so-called antigen microarrays, belong to the category of protein microarrays with unique capabilities and take advantage of a novel promising proteomic technology performing high throughput, multiplex, and miniaturized tests to target low-abundant analytes in the samples. Antigen arrays are not only tools to investigate limited sets of preselected proteins. They can rather serve as discovery tools to identify novel targets of coronavirus-associated autoantibodies in various disease conditions. Using antigen arrays, both analytical and functional assays can be performed. In a functional assay format, the arrayed antigens are utilized to decipher various binding activities such as protein-protein, protein-drug, protein-peptide, or protein-nucleic acid interactions. Protein microarrays provide a proteome-wide characterization of the present antibodies in response to SARS-CoV-2 antigens. This strategy is preferred for profiling antibodies by enabling antibody screening using some or all of the proteins present in SARS-CoV-2 particles with a high resolution.
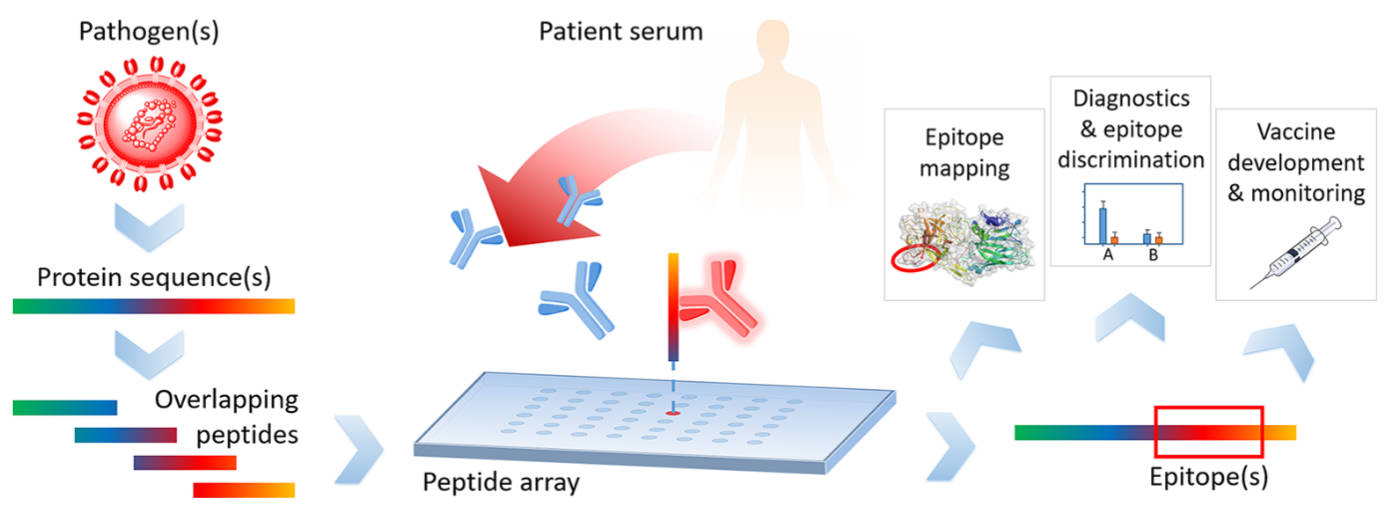 Fig.1 The typical workflow of a peptide microarray experiment.1
Fig.1 The typical workflow of a peptide microarray experiment.1
Our Service
With the global pandemic of COVID-19, coronavirus has attracted the attention of global researchers. With the deepening of study, the importance of coronavirus-associated autoimmunity has also been gradually revealed. As we mentioned above, antigen microarray detection has advantages in many aspects in this context. Due to our effort in this field for years, Creative Biolabs has grown a professional in autoantibodies studies. We are confident in offering quality-assured antigen microarray detection services with autoantigens from coronavirus to global customers.
| SERVICE | SAMPLE TYPE | DELIVERY | LEAD TIME |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antigen Microarray Detection for Coronavirus-associated Autoimmunity | Plasma, serum, antibody, cerebrospinal fluid, urine, and saliva | Project Report; Experiment Data; Heatmap | 2-3 week |
If you are interested in our services or you have any other requirements for antigen microarray detection, please feel free to contact us for more information.
Highlight
- High throughput, multiplex, and miniaturized tests.
- High sensitivity for low-abundant analytes in the samples.
- Availability for multiple sample types.
- Short turnaround time of 2-3 weeks.
FAQs
-
Q1: How can antigen arrays help in my project of drug development?
A: Arrayed antigens can be used to analyze various binding activities of protein-protein, protein-nucleic acid, protein-peptide, or protein-drug interactions, providing proteome-wide characterizations of the presently known antibodies in response to your target virus particles and enabling high-resolution antibody screening. -
Q2: What kind of samples can be tested here?
A: Our platform is suitable for various sample types, including plasma, serum, antibody, cerebrospinal fluid, urine, and saliva.
Resource
Reference
- Heiss, Kirsten, et al. "Rapid response to pandemic threats: immunogenic epitope detection of pandemic pathogens for diagnostics and vaccine development using peptide microarrays." Journal of proteome research 19.11 (2020): 4339-4354.
Related Services:
- Autoantigens General Survey Detection
- Brain and Central Nervous System Disorders Detection
- Cancer and Neoplasms Detection
- Common Allergens Detection
- Autoimmunity, Allergy, and Infection Detection
- SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus Detection

