NAA Service for Infectious Diseases
Natural autoantibody (NAA) represents a substantial proportion of the normal antibodies, and contributes to the stimulation of primitive innate immune system. Using NAA biomarkers to achieve early diagnosis of infectious disease is promising and can reflect clinical responses to immunotherapy. Empowered by our advanced high-resolution analytical platforms and experienced technical personnel, Creative Biolabs offers a comprehensive set of NAA services to assist our clients in disease diagnosis and provide a guideline for project progression.
The Relationship Between NAA and Infectious Diseases
NAA can target highly conserved epitopes and often binds to ligands of varying chemical composition with low affinity. The functional abilities of NAA are not very clear but it is generally accepted that they may participate in a variety of activities, such as resistance to infections, regulation of the immune response, maintenance of immune homeostasis, transport and functional modulation of biologically active molecules. Besides, specific adaptive immune responses through high-affinity, class-switched IgG autoantibodies, which bind self-proteins, can cause tissue damage or malfunctions, inducing autoimmune diseases. The most widely studied function of NAA is the ability to provide protection against bacterial, viral, and fungal infections, such as influenza virus, sepsis, S. pneumoniae, Borrelia hermsii, Listeria monocytogenes, and Pneumocystis murina.
 Fig.1 NAA secretion during different infections of atypical/autoimmune B cells.1
Fig.1 NAA secretion during different infections of atypical/autoimmune B cells.1
NAA Targets in Infectious Diseases
NAA can be detected with higher levels among individuals exposed to viral, bacterial and parasitic infections. The association between various infections and the presence of autoantibodies has generated interest for a long time. NAA Associated Malaria and NAA Associated AIDS are no exception. The detection of NAA against self-proteins is important for the diagnosis of a variety of associated diseases, such as autoimmune disorders, infection diseases, and neurological diseases. For certain targets, autoantibodies can play a direct role in the pathogenesis. Several technologies such as immunosensors, ELISA, luciferase immunoprecipitation systems (LIPS), antigen arrays, and bead arrays have been applied to the detection of autoantibodies against a wide range of different infectious agents. Anti-nuclear antibodies, anti-rheumatoid factor autoantibodies both have been identified in malaria and AIDS. Besides, anti-fluorescent anti-nuclear antibodies, anti-smooth muscle autoantibodies, anti-dsDNA autoantibodies, anti-mitochondrial autoantibodies and anti-native DNA autoantibodies, anti-denatured DNA autoantibodies, anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies, anti-cardiolipin autoantibodies have also been identified in malaria and AIDS respectively.
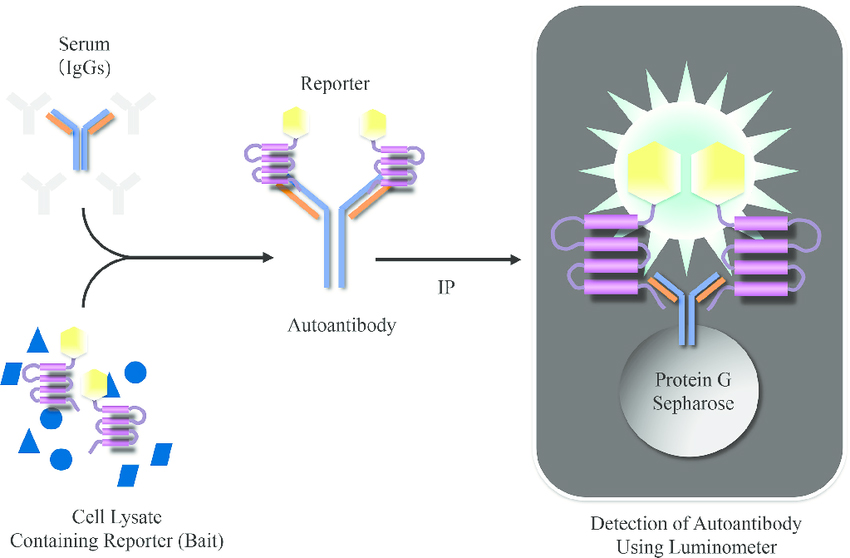 Fig.2 Schematic illustration of LIPS in the detection of autoantibody. (Nakane, 2015)
Fig.2 Schematic illustration of LIPS in the detection of autoantibody. (Nakane, 2015)
Technologies and Features in Creative Biolabs
- ELISA / WB / Dot Blot / LIPS
- Protein array / peptide array
- Multiple affinity protein profiling (MAPPing)
- Low cost
- Best after-sale services
NAA can directly target intracellular structures or intracellular enzymes. With Ph.D. level scientists and rich experience in antigen-antibody interaction and antibody detection fields, Creative Biolabs is dedicated to serving the unique needs of our clients in NAA development projects by providing customized services that are tailored to meet your R&D timeline and budget. If the infectious disease you concerned is not mentioned, please do not hesitate to contact us for more information.
References
- Rivera-Correa, Juan, and Ana Rodriguez. "Autoantibodies during infectious diseases: Lessons from malaria applied to COVID-19 and other infections." Frontiers in Immunology 13 (2022): 938011.
- Nakane, Shunya, et al. "Clinical features of autoimmune autonomic ganglionopathy and the detection of subunit-specific autoantibodies to the ganglionic acetylcholine receptor in Japanese patients." PLoS One 10.3 (2015): e0118312.
Choosing natural autoantibody (NAA) microarray to profile autoantibody repertoire and reveal novel disease's marker.
Related Services:
- Autoimmune Disorders
- Neurological Diseases
- Cardiovascular Diseases
- Endocrine Diseases
- Hematological Diseases
- Nephropathy
- Pulmonary Diseases
- Cancers

