NAA Affinity Measurement
As a pioneer in the field of natural autoantibody, Creative Biolabs is dedicated to providing reliable services of comprehensive NAA detection, NAA profiling, and NAA affinity measurement, to assist our worldwide customers in investigating interactions between autoantigens and autoantibodies. With well-designed experimental schemes and unique technology platforms, our team of experienced scientists offers the most professional customized plans, and the largest portfolio of premade or custom NAA products and services to significantly advance your projects.
Background
Introduction of Antibody Affinity
Antibody affinity, which means the strength with which an antibody binds to its cognate antigen, is an equilibrium dissociation constant (KD), that is regulated by two kinetic constants, i.e., the rates of association (kon or ka) and dissociation (koff or kd). The rate of association is defined by the time required for the antibody to bind with its antigen. The dissociation rate, which is usually given as a half-life constant, defines the time the antibody-antigen complex remains intact. Several methods have been developed to measure these kinetic constants, which can be used to estimate antibody affinity. Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) is the most widely used method today.
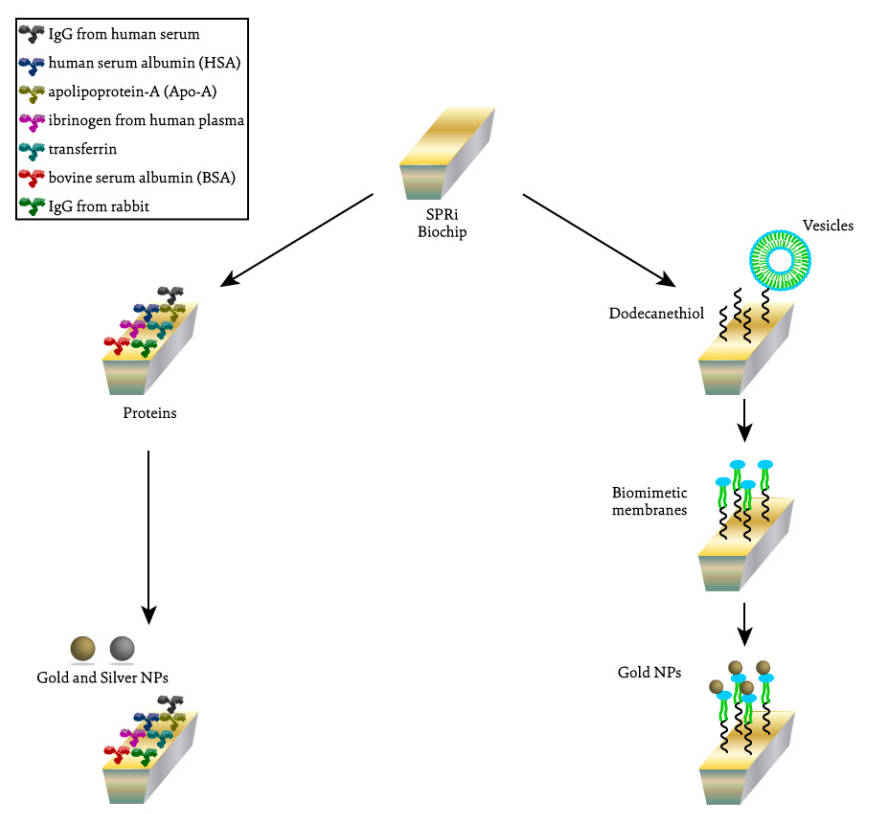 Fig.1 Schematic representation of the different SPRi assays performed to evaluate the interaction between silver and gold NPs and proteins (on the left) and between gold NPs and lipidic membranes (on the right).1
Fig.1 Schematic representation of the different SPRi assays performed to evaluate the interaction between silver and gold NPs and proteins (on the left) and between gold NPs and lipidic membranes (on the right).1
NAA Affinity Measurement
NAA affinity measurement can be performed using the common detection method-Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR). SPR is an extremely sensitive method for the detection of molecular interactions by tracking the changes of signal via sensor chips. SPR signal is established as refractive index changes, meaning that the response unit (RU) is approximately equivalent to a surface concentration of protein at 1pg/mm2. Plotting the SPR signal over time during the interaction between two molecules can obtain a sensorgram, which could be visualized in real time. Generally, the binding response consists of three phases: association, equilibrium, and dissociation; fitting these sensorgram data with a mathematic model allows scientists to calculate the association (ka) and dissociation (kd) rate constants and ultimately determine the binding affinity (KD). The measurement of antibody binding affinity based on equilibrium point is different from isothermal calorimetry (ITC) method, SPR could obtain full kinetic parameters to evaluate all the effects of association and dissociation as well as antibody affinity.
Workflow
Workflow of NAA Affinity Measurement
- First, the autoantibodies of serum or other body fluids to be analyzed are captured by high-affinity anti-IgG antibody immobilized on the sensor chip surface.
- Then different concentrations antigens are sequentially added across the surface. We can rank the antibodies based on the sensorgram curve and kinetic parameters. In addition, according to the bivalent analyte model, we can identify autoantibodies binding to two distinct antigen epitopes.
- A generic anti-antibody is covalently attached to the chip surface, and then the first antibody is captured by the generic antibody previously attached.
- After the blocking of unbound sites, the injected antigen will be combined by the first antibody with the formation of Ab-Ag complex.
- Followed by the implementation of a second monoclonal antibody which is applied to evaluate the binding affinity, a unique sensorgram curve will be observed if the second antibody binds to a distinct separate epitope.
Our Service
Creative Biolabs offers comprehensive NAA services to help you detect NAA-associated immune diseases and new NAA biomarkers using autoantibody microarray in a timely and cost-effective manner. Our tailored services and high-quality products will contribute greatly to the success of your projects. Please contact us for more information and a detailed quote.

Highlight
- Determination of direct NAA-antigen interactions.
- High throughput analysis.
- Full kinetics analysis, such as detailed binding kinetic data.
- Timely and cost-effective services.
FAQs
-
Q1: Which method is applied here for NAA affinity measurement?
A: We use Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) in our NAA affinity measurement service, which enables real-time monitoring and label-free detection with high sensitivity. -
Q2: What kind of results can I get from this service?
A: You will receive an exhaustive and rigorous project report with full kinetics analysis, including detailed binding kinetic data.
Resource
Reference
- de Macedo, Erenildo Ferreira, et al. "Interaction between Nanoparticles, Membranes and Proteins: A Surface Plasmon Resonance Study." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24.1 (2022): 591.

