Autoantigen Microarray
Creative Biolabs is glad to provide natural autoantibodies (NAA) detection and analysis services for our client all over the world. Here, we have developed a mature platform for NAA services, which can facilitate the diagnosis and treatment of the interested disease. In addition, NAA detection and profiling would be useful for your drug design and development projects. Autoantigen microarray with high load and high accuracy is one of the high-throughput methods we now provide to benefit all our clients.
Background
Background of Autoantigens
Autoantigens consist of intracellular organelles, nuclear or cytoplasm, which are useful in disease diagnosis. Examples include centromere or Scl-70 autoantigens which occur in scleroderma, ribonucleoprotein autoantigens in lupus-related diseases, and mitochondrial autoantigens in primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC). Generally, some conditions need to be fulfilled if autoantigens become pathogenic. One requirement would be that the autoantigen can translocate to the cell surface, which may suggest autoimmunity may influence the intracellular transport of molecules between nucleus, cytoplasmic organelles, and cell membranes. The other condition is that autoantibodies with the capacity to penetrate the membrane of intact cells access intracellular organelles.
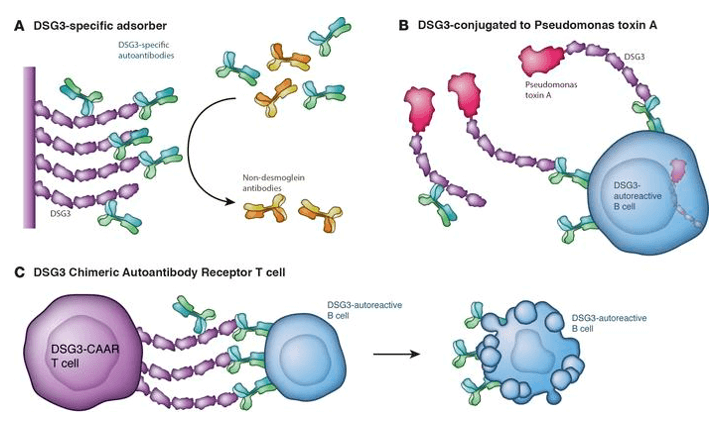 Fig.1 Autoantigen-based targeted therapies in pemphigus. (Ellebrecht, 2017)
Fig.1 Autoantigen-based targeted therapies in pemphigus. (Ellebrecht, 2017)
Autoantigen Microarray
Autoantigen microarray technology is a high throughput approach in autoantibody profiling, in which auto-epitopes (recombinant proteins or peptides) are spotted on microarrays and tested for immunoglobulins binding with test sera. The capacity of microarray (bearing multiple autoantigens on the same slide and the minute volume of sera needed) make it a very attractive method for autoantibody profiling and mapping of epitopes. Autoimmune disease-specific arrays inclusive of self-antigens, recombinant proteins, viral proteins, peptides, and bacterial antigens have been validated for several autoimmune diseases including experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, primary biliary cirrhosis, scleroderma, and systemic lupus erythematosus. The potential applications of autoantigen microarrays are diverse and are not limited to the identification of “autoantibody signatures” associated with disease state or outcome, the profiling of autoantibodies during the natural course of diseases and monitoring change in the autoantibody profiles of patients in response to therapeutic intervention. Future clinical applications of autoantigen microarray will depend on the standardization and automation of this promising high throughput technology.
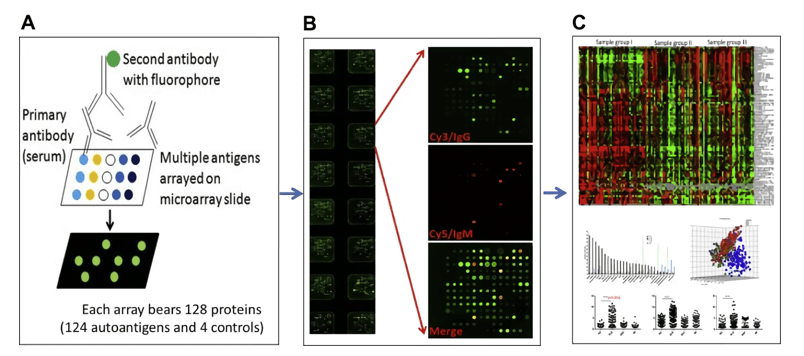 Fig.2 Autoantigen microarray for high-throughput autoantibody screening. (Zhu, 2015)
Fig.2 Autoantigen microarray for high-throughput autoantibody screening. (Zhu, 2015)
Our Service
| Services | Sample type | Delivery | Lead time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antigen Microarray Detection for Autoantigens General Survey | Plasma, serum, antibody, cerebrospinal fluid, urine and saliva | Project Report; Experiment Data; Heatmap | 2-3 week |
| Antigen Microarray Detection for Brain and Central Nervous System Disorders | |||
| Antigen Microarray Detection for Cancer and Neoplasms | |||
| Antigen Microarray Detection for Common Allergens | |||
| Antigen Microarray Detection for Autoimmunity, Allergy, and Infection | |||
| Antigen Microarray Detection for Coronavirus-associated Autoimmunity | |||
| Antigen Microarray Detection for SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus |
Highlights
- High throughput and high load. Each slide can process up to 15 samples in parallel.
- High sensitivity, 100-fold more sensitive than ELISA.
- Timely and cost-effective, get the data as little as 2 weeks.
- Small sample volume. As little as 10ul of serum is needed for detection.
FAQs
-
Q1: What should I do if I want to inquire about Creative Biolabs' other NAA-related services?
A: You can contact our expert team directly. If you have specific and detailed service needs, you can directly request a quote. If not, you can send us a request and we will provide you with a customized solution.
Published Data
Title: Autoantigen Microarray for High-throughput Autoantibody Profiling in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Journal: GENOMICS, PROTEOMICS & BIOINFORMATICS
Authors: Honglin Zhu, Hui Luo, Mei Yan, Xiaoxia Zuo, Quan-Zhen Li
Abstract: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a complex autoimmune disease characterized by the production of autoantibodies to a broad range of self-antigens. Profiling the autoantibody repertoire using array-based technology has emerged as a powerful tool for the identification of biomarkers in SLE and other autoimmune diseases. Proteomic microarray has the capacity to hold large number of self-antigens on a solid surface and serve as a high-throughput screening method for the determination of autoantibody specificities. The autoantigen arrays carrying a wide variety of self-antigens, such as cell nuclear components (nucleic acids and associated proteins), cytoplasmic proteins, phospholipid proteins, cell matrix proteins, mucosal/secreted proteins, glomeruli, and other tissue-specific proteins, have been used for screening of autoantibody specificities associated with different manifestations of SLE. Arrays containing synthetic peptides and molecular modified proteins are also being utilized for identification of autoantibodies targeting to special antigenic epitopes. Different isotypes of autoantibodies, including IgG, IgM, IgA, and IgE, as well as other Ig subtypes, can be detected simultaneously with multi-color labeled secondary antibodies. Serum and plasma are the most common biologic materials for autoantibody detection, but other body fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid, synovial fluid, and saliva can also be a source of autoantibody detection. Proteomic microarray as a multiplexed high-throughput screening platform is playing an increasingly-important role in autoantibody diagnostics. In this article, we highlight the use of autoantigen microarrays for autoantibody exploration in SLE.
 Autoantigen microarray for high-throughput autoantibody screening.
Autoantigen microarray for high-throughput autoantibody screening.
Resource
Creative Biolabs is committed to offering NAA services to help you detect NAA associated diseases and new biomarkers using autoantigen microarray in a timely and cost-effective manner. Our high-quality products and services will contribute greatly to the success of your projects. Please feel free to contact us for more information and a detailed quote.
References:
- Ellebrecht, C.T.; Payne, A.S. Setting the target for pemphigus vulgaris therapy. Jci Insight. 2017, 2(5): e92021.
- Zhu, H.; et al. Autoantigen microarray for high-throughput autoantibody profiling in systemic lupus erythematosus. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2015, 13(4): 210-218.
Choosing natural autoantibody (NAA) microarray to profile autoantibody repertoire and reveal novel disease's marker.
- Autoantigens General Survey Detection
- Brain and Central Nervous System Disorders Detection
- Cancer and Neoplasms Detection
- Common Allergens Detection
- Autoimmunity, Allergy, and Infection Detection
- Coronavirus-Associated Autoimmunity Detection
- SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus Detection

