Hematological Diseases
Creative Biolabs can offer various NAA services to help our customers obtain more precise hematological diseases diagnosis, and promote drug discovery and treatment design. Our technical scientists can not only save valuable time but also provide highly stable and qualified services for our clients all over the world.
Introduction of Hematological Disease
Hematological diseases are a kind of disease that the constituents of blood have been changed by a diverse range of conditions. This includes disorders of the blood cells (red cells, white cells and platelets) and cancerous conditions impacting these blood cells.
Types of Haematological Diseases
1. Myeloid Disorders
Hemoglobinopathies (congenital abnormality of the hemoglobin molecule or of the rate of hemoglobin synthesis); Anemias (lack of red blood cells or hemoglobin); Decreased numbers of cells; Myeloproliferative disorders (increased numbers of cells); Coagulopathies (disorders of bleeding and coagulation).
2. Hematological Malignancies
Hematological malignancies (Lymphomas, Myelomas, Leukemias increased WBC).
3. Miscellaneous Disorders
Hemochromatosis; Asplenia; Hypersplenism; Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance; Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis; Tempi syndrome.
4. Hematological Changes Secondary to Non-Hematological Disorders
Anemia of chronic disease; Infectious mononucleosis; AIDS; Malaria; Leishmaniasis.
Hemoglobinopathy
Hemoglobinopathy is a kind of genetic defect disease that leads to the abnormal structure of one of the globin chains of the hemoglobin molecule. Hemoglobinopathy can be inherited via single-gene disorders; in most cases, they are inherited as autosomal co-dominant traits. Common hemoglobinopathies include sickle-cell disease. Hemoglobinopathy is one of the most common diseases and about 7% of the world's population (420 million) are carriers in the world. NAA Associated Thalassemia, in contrast, usually manifests insufficient of normal globin proteins often along with mutations in regulatory genes. The two types of symptoms may overlap, namely, due to some conditions which cause abnormalities in globin proteins (hemoglobinopathy) also affect their production (thalassemia).
Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia is a condition with abnormally low levels of thrombocytes (platelets) in the blood. Normally, a healthy human harbors 150,000 to 450,000 platelets per microliter of blood. When the platelets count is below 50,000 per microliter, it can be regarded as thrombocytopenia required emergency treatment. Thrombocytopenia usually with no significant symptoms, sometimes some thrombocytopenia individuals may arise external bleeding such as nosebleeds, and/or bleeding gums. Some women may experience heavier or longer periods or breakthrough bleeding.
There are many reasons for thrombocytopenia. One of the most common causes of low platelets is a condition called immune thrombocytopenia purpura (ITP). Although currently don't know what causes ITP, people believe it happens when your immune system defense against disease abnormally. In fact, body’s antibodies destroy your platelets mistakenly, which are supposed to attack infections instead. Thrombocytopenia can happen in families, but you can also get it from many medical conditions. Treatment of the medical condition may improve ITP. Some other causes may also induce thrombocytopenia: viral infections (such as chickenpox, parvovirus, hepatitis C, Epstein-Barr, and HIV), medication side effects, including drugs for heart problems, seizures, and infections and chemotherapy and so on.
NAA Detection Associated with Hematological Diseases
In the sera of healthy individuals, there exist some antibodies that react with a variety of endogenous and exogenous antigens, are considered as NAA. Those NAA play a role of protector (IgM isotype natural autoantibodies) contributing to the enhancement of innate functions and preventing pathogenic processes and maintaining or restoring health status, or destructor (pathogenic IgG autoantibodies) binding self-proteins and frequently causing autoimmune diseases. In addition, some data show strong evidence that NAA and NAA B cells can suppress autoimmune diseases and suggest several potential mechanisms, which reminds us the NAA detection is so important in medicine development and diseases diagnosis and appropriate therapeutic intervention in autoimmune and malignant diseases.
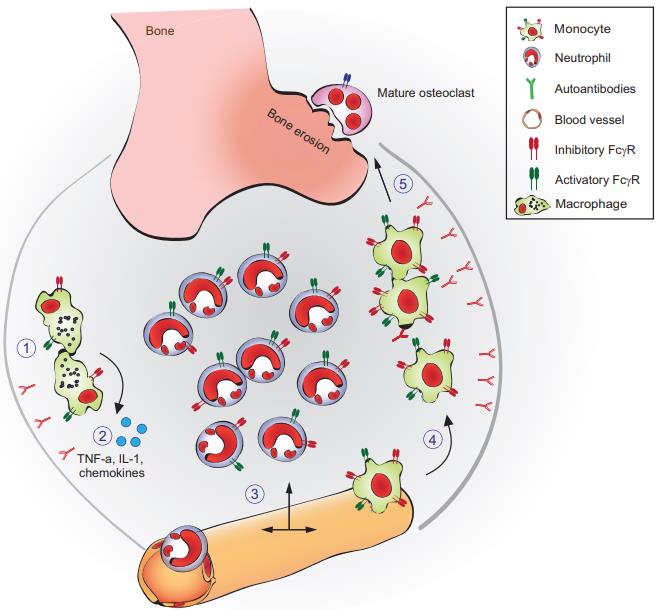 Fig.1 The autoantibody-driven processes that contribute to inflammation and bone destruction in inflammatory arthritis.1
Fig.1 The autoantibody-driven processes that contribute to inflammation and bone destruction in inflammatory arthritis.1
Features of Our Services
- Extensive experience in antibody design, analysis and modification services
- Providing NAA profiling analysis aided by our advanced technical platforms
- Excellent scientists are committed to providing high-quality NAA affinity measurement
- Epitope mapping and paratope mapping timely and cost-effective
As a leading service provider that focuses on novel therapeutics antibody design, analysis and development for over a decade, Creative Biolabs has the ability to provide NAA services associated with all kinds of hematological diseases by our state-of-art technical platform and rich expertise. We succeed with excellence and confidence to meet your demands for antibody related services, which are efficient and cost-effectively. Please feel free to contact us for more information and a detailed quote.
Reference
- Ludwig, Ralf J., et al. "Mechanisms of autoantibody-induced pathology." Frontiers in immunology 8 (2017): 603.
Choosing natural autoantibody (NAA) microarray to profile autoantibody repertoire and reveal novel disease's marker.
Related Services:
- Autoimmune Disorders
- Infectious Diseases
- Neurological Diseases
- Cardiovascular Diseases
- Endocrine Diseases
- Nephropathy
- Pulmonary Diseases
- Cancers

