NAA Associated Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a unique cancer of head and neck, commonly arising from the epithelial lining of the lateral wall of the nasopharynx, especially at the fossa of Rosenmüller and superior posterior wall. NPC is prevalent in Southern China and Southeast Asia, and natural autoantibodies (NAAs) signatures may improve early detection of NPC. Creative Biolabs has over a decade of working experience in cancer therapy and disease diagnosis. The science team at Creative Biolabs can provide customers with comprehensive NAA services for PLC to promote your project progress.
Introduction of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
The incidence of NPC reaches 20 to 30 per 100,000 men and 15 to 20 per 100,000 women. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) classification, the pathological type of NPC is classified into keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma (type I, known as well differentiated), differentiated nonkeratinizing carcinoma (type II, known as moderately differentiated), and undifferentiated carcinoma (type III, known as poorly differentiated). In fact, in the areas with high incidence, at least 95% of NPC patients are of the poorly differentiated (types II and III) pathological types and are thus sensitive to radiotherapy and chemotherapy. NPC is usually caused by the combined effects of three etiology factors.
➢ The first one is environmental carcinogens which include cigarette smoke, Cantonese-style salted fish, preserved foods.
➢ The second one is genetic susceptibility which includes mutations in one or more genes, genetic polymorphism, and family history of NPC.
➢ The last one is the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) which belongs to the herpes family and infects epithelial cells and B cells of the immune system.
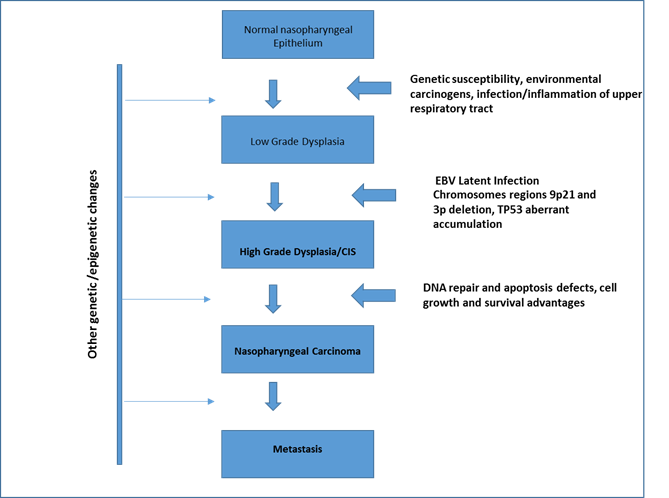 Fig.1 Etiology and pathogenesis of NPC. (Saad, 2014)
Fig.1 Etiology and pathogenesis of NPC. (Saad, 2014)
Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Diagnosis
Since patients with early-stage disease are often lacking clinically specific symptoms, NPC tends to present at an advanced stage at diagnosis. Therefore, it highlights the need to improve the early diagnosis rate of NPC through a screening protocol. EBV infection is closely related to NPC development, so detection of EBV-DNA and viral capsid antigen immunoglobulin A (VCA-IgA) has been the most commonly used method for screening the disease. However, NPC screening by EBV-related detection cannot completely meet the requirements of effective and accurate diagnostic markers.
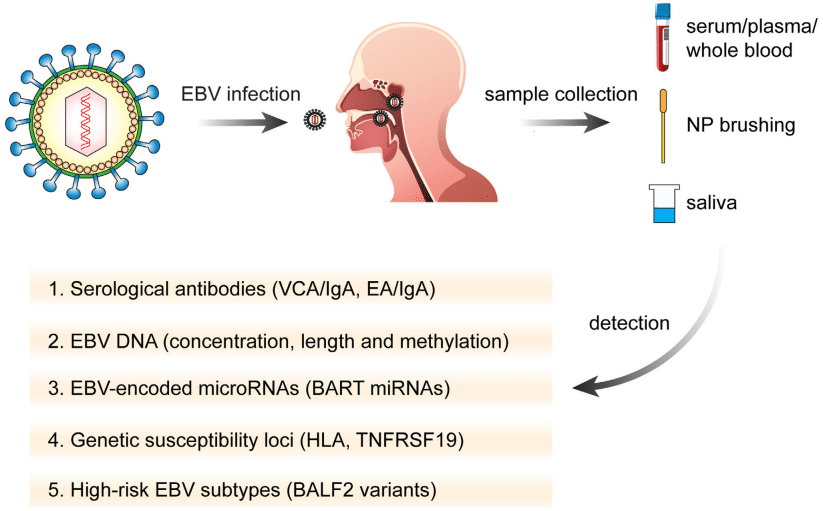 Fig.2 Strategies for the screening of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.2
Fig.2 Strategies for the screening of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.2
The Association Between NAA and Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
NAAs have attracted more attention as possible biomarkers in recent years. Numerous studies describe the presence of NAAs against tumor-associated antigens (TAA) in serum samples from patients with a variety of cancers, including NPC. NAAs seem to appear months to years before the clinical diagnosis of a tumor, which makes the measurement of NAAs is suitable for early-stage cancer diagnosis. Several TAAs have been identified as biomarkers in NPC diagnosis. Here show the common targets in NPC that have already been developed to offer services by us.
| Natural Autoantibodies Targets in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma | |||
| Anti-MAGE | Anti-Fibronectin | Anti-CD44 | Anti-HSP 70 |
| Anti-EBNA-1 | Anti-NY-ESO-1 | Anti-PRDX2/3 | Anti-BMI-1 |
NAAs could serve as promising biomarkers for early detection of NPC. Equipped with advanced research and excellent technical team with rich experience in autoantibody research, Creative Biolabs is dedicated to helping our clients to make progress in NAA research using our featured services. With expertise and dedication, Creative Biolabs will be your best companion in NAA detection and profiling, as well as NPC-related projects. If the disease and related targets you interested is not mentioned above, please do not hesitate to contact us for more information and a detailed quote.
References
- Saad, S., and T. J. C. Wang. "Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Current treatment options and future directions." J Nasopharyng Carcinoma 16 (2014): 1-16.
- Zhu, Qian‐Ying, et al. "Advances in pathogenesis and precision medicine for nasopharyngeal carcinoma." MedComm 2.2 (2021): 175-206.
Choosing natural autoantibody (NAA) microarray to profile autoantibody repertoire and reveal novel disease's marker.
- NAA Services for Anti-MAGE
- NAA Services for Anti-Fibronectin Antibody
- NAA Services for Anti-CD44 Antibody
- NAA Services for Anti-BMI-1 Antibody
- NAA Services for Anti-EBNA-1 Antibody
- NAA Services for Anti-NY-ESO-1 Antibody
- NAA Services for Anti-PRDX2/3 Antibody
Related Services:
- NAA Associated Primary Liver Cancer
- NAA Associated Lung Cancer
- NAA Associated Gastric Cancer
- NAA Associated Pancreatic Cancer

