Antigen Microarray Detection Service for Cancer and Neoplasms
With advanced platforms and rich experience, Creative Biolabs has developed many types of antigen microarrays that can track numerous types of proteins, enabling diagnostic and therapeutic studies on a variety of diseases. Our antigen microarray detection services can effectively detect autoantibodies that may be produced in cancer patients, in addition to helping to screen and identify new tumor biomarkers for cancer treatment or prevention.
Background
Overview of Autoantibodies for Cancer and Neoplasms
The mechanisms underlying T cell-mediated humoral immune responses to cancer-associated antigens are not completely understood and are the subject of intensive studies. Immunogenicity of the overwhelming majority of tumor-associated antigens is related to their aberrant regulation and/or tumor-specific modifications generated by oncogenic processes in tumor cells. From this standpoint, serum autoantibodies to cancer-associated antigens can be regarded as specific “reporters” of carcinogenesis. However, the majority of currently known cancer-associated B-cell antigens have a serious disadvantage—low detection frequency of respective autoantibodies and, as a consequence, low diagnostic sensitivity in revealing cancer, the most critical parameter from the clinical standpoint. To overcome this problem, it was suggested to combine candidate antigens into arrays in order to optimize diagnostic sensitivity and specificity parameters.
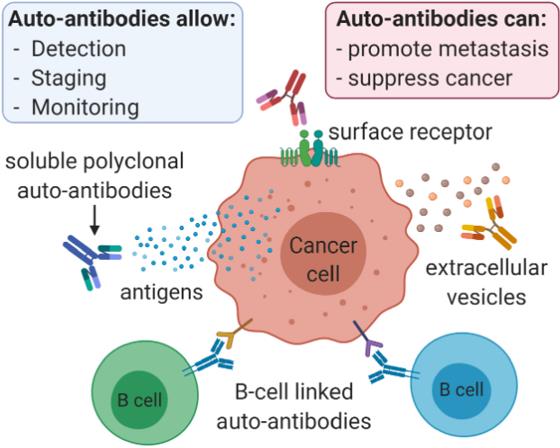 Fig.1 The role of autoantibody in cancer.1
Fig.1 The role of autoantibody in cancer.1
Serum autoantibodies to cancer-associated antigens represent a relatively new class of serological biomarkers and have a number of advantages over conventional protein oncomarkers. Their main characteristics are as follows:
- High specificity in cancer detection;
- Lack of specific requirements for biomaterials and sampling
- High stability in blood, serum, and plasma samples;
- Long half-life;
- Minimum concentration variations (e.g., diurnal, food and drug intake, physical activity, menstrual cycle phases, checkup procedures, etc.).
Application
Antigen Microarray and Detection for Cancer
Low sensitivity in cancer detection is the main disadvantage of virtually all (excluding ECPKA) cancer-associated B-cell antigens, while high diagnostic sensitivity is the main requirement for virtually all clinical applications of tumor biomarkers. The use of antigen arrays allows the identification of so-called “autoantibody signatures” of various diseases; the latter represent combinations of reactive antigens able to discriminate between pathology and a normal state. The association of antigens into arrays allows one to select a combination of antigens whose respective antibodies are strictly specific for the given pathology (~100%). The sensitivity (i.e., detection frequency of antibodies to at least one antigen) of such arrays also can reach 100%.
Antigen microarrays also allow for high-throughput and scalable analysis, and they are effective tools for screening the immune response in cancer patients to identify autoantibodies and tumor-associated antigens.
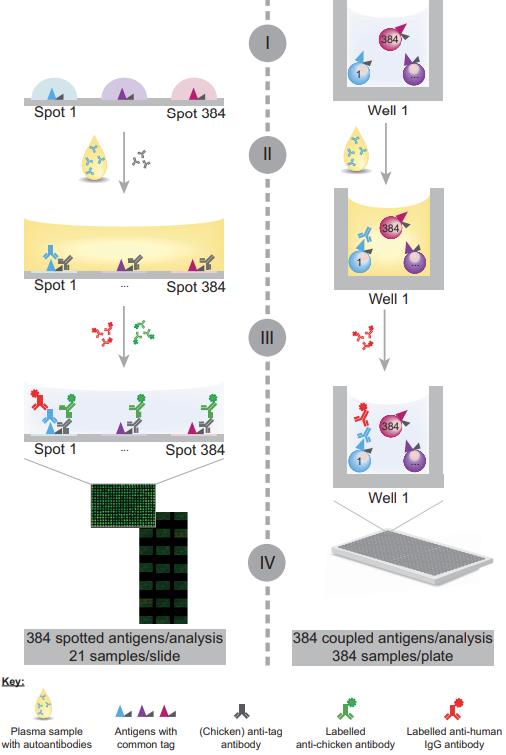 Fig.2 The assay workflow on planar and bead-based antigen arrays for profiling autoantibody responses.2
Fig.2 The assay workflow on planar and bead-based antigen arrays for profiling autoantibody responses.2
Our Service
Services at Creative Biolabs
As the important roles autoantigen plays in cancer and neoplasms has been gradually revealed, detection of autoantigens has also attracted a lot of sight from researchers. With high throughput and accurate detection results, antigen microarray shows outstanding capabilities in this field. Creative Biolabs has been focusing on autoantibodies and relevant research over years. With extensive experience accumulated from practice, we are confident in offering high-quality cancer and neoplasms array detection services to global clients to help accelerate the research of autoantibodies in cancer and neoplasms.
Highlight
- High-throughput and scalable analyses.
- High sensitivity, overcoming the challenge of recognizing important low-abundance proteins in complicated biological fluids.
- Strict specificity (~100%).
- Instant data availability.
FAQs
-
Q1: How to ensure experimental reproducibility?
A: First, ensure that the analyte and antibody concentrations match the affinity constants, which ensures that the antibody-antigen affinity is in the linear range. Secondly, the array of capture antibodies or protein antigens on the slide's surface, the consistency of binding to the array surface, and the variation in background noise between slides can all cause differences, so we will develop protocols to promote consistency and include standards samples or calibrators to ensure that results are standardized between slides. Finally, integration of data from other techniques (e.g., ELISA) will also be considered. -
Q2: Is it personalized customer service?
A: We are focused on providing customized services to our clients. We will design detection plans according to your study requirements, including the selection of different analysis types and sample dilution ratios, etc.
Resource
If you are interested in antigen microarray detection services, or you have any other questions about autoantibodies, please feel free to contact us for more information.
References
- de Jonge, Hugo, et al. "Anti-cancer auto-antibodies: Roles, applications and open issues." Cancers 13.4 (2021): 813.
- Ayoglu, Burcu, et al. "Autoantibody profiling in multiple sclerosis using arrays of human protein fragments." Molecular & Cellular Proteomics 12.9 (2013): 2657-2672.
Related Services:
- Autoantigens General Survey Detection
- Brain and Central Nervous System Disorders Detection
- Common Allergens Detection
- Autoimmunity, Allergy, and Infection Detection
- Coronavirus-Associated Autoimmunity Detection
- SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus Detection

