NAA Services for Anti-GluR3 Antibody
It is well known that natural autoantibodies (NAAs) can be valuable markers of disease activity and severity, an effective aid for disease classification and a guide for therapy. Since anti-glutamate receptor 3 (GluR3) autoantibodies are highly specific for epilepsy, based on years of extensive experience in disease diagnosis and NAA research, Creative Biolabs now offers a full range of high-quality antibody services against GluR3 marker for epilepsy research.
Background of Anti-GluR3 Antibody
Glutamate receptors (GluR) are the predominant excitatory neurotransmitter receptors in the mammalian brain and are activated in a variety of normal neurophysiologic processes. NAAs to the "B" peptide (372-395 aa) of GluR3 are found in serum and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of some patients with different types of epilepsy. Anti-GluR3B antibodies are produced primarily in the periphery due to specific/non-specific "irritation" of the immune system. Once they reach the brain via a leaky blood-brain barrier (BBB) they may cause neuronal/glial damage and facilitate the outburst of epilepsy and additional neurological abnormalities. Anti-GluR3 antibodies are “active” and potentially pathogenic molecules since they display a glutamate-like activity and thus induce glutamate receptor-mediated ion currents.
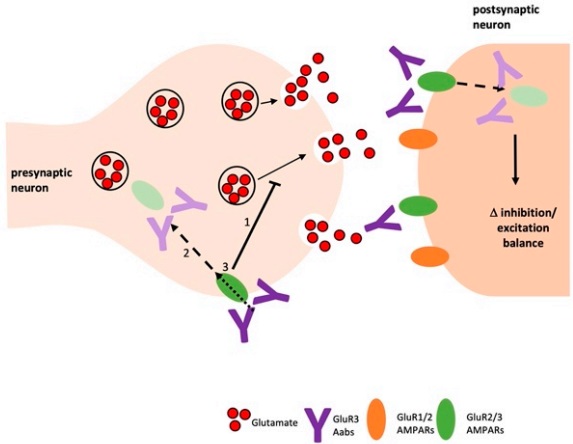 Fig.1 Schematic of potential mechanisms of anti-GluR3 antibody.1
Fig.1 Schematic of potential mechanisms of anti-GluR3 antibody.1
The Role of Anti-GluR3 Antibody in Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a major health problem, affecting almost 1-2% of the world population. Both the GluR-activating and the neuronal-killing potential of anti-GluR3 antibody suggest that they may contribute to epilepsy. Since such anti-GluR3B antibodies can activate and/or kill neurons in vitro and in vivo, they may contribute to epilepsy. Yet, more recent data clearly show that anti-GluR3 antibodies are neither specific nor restricted to Rasmussen’ s encephalitis (RE), as they are found in some patients with other types of epilepsy. Numerous cases proved that the presence of anti-GluR3 antibodies was highly specific for epilepsy compared to healthy controls.
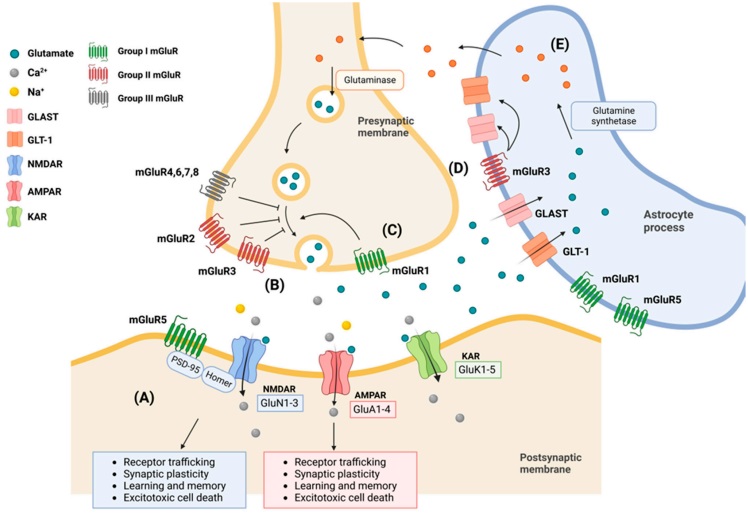 Fig.2 The role of GluR3 and associated proteins in Epilepsy.2
Fig.2 The role of GluR3 and associated proteins in Epilepsy.2
What We Can Do about NAA?
Aided by our well-established platforms and experienced scientists, we can provide comprehensive NAA services, from NAA detection, NAA profiling, to NAA epitope mapping. Our customized services can cover every step of your project. In addition, a wide spectrum of NAA products is available for your choice.
Features of our Anti-GluR3 Services Including but Not Limited to
- Different NAA detection methods with high accuracy and high specificity
- One-stop pipeline to save your energy and time
- High efficiency without large-scale repeats
- Best after-sale service
Detection and analysis of anti-GluR3 autoantibodies may have important diagnostic and therapeutic implications. With the help of our professional scientists, Creative Biolabs is confident in providing unique NAA services about GluR3 biomarker to meet every customer's requirements. If you are interested in the service we provide, please feel free to contact us for more detail and information.
References
- Day, Charlotte, et al. "Anti-AMPA receptor autoantibodies reduce excitatory currents in rat hippocampal neurons." Pharmaceuticals 16.1 (2023): 77.
- Chen, Tsang-Shan, et al. "The Role of Glutamate Receptors in Epilepsy." Biomedicines 11.3 (2023): 783.

