NAA Services for Anti-MUC1 Antibody
Numerous anti-mucin 1 (anti-MUC1) antibodies recognize O-glycan core structures and are ideal for immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence experiments. At present, Creative Biolabs provides a full range of anti-MUC1 marker services for diseases diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring. With years of experience and high-end technologies in NAA (natural autoantibodies) research, we developed a series of innovative and diversified NAA platforms to provide fast and convenient services for our worldwide customers. Our professional team is optimized to help you get a milestone development in your NAA project.
Background of Anti-MUC1 Antibody
Mucin 1 (MUC1) is a heavily glycosylated large protein found on the apical surface of a variety of glandular epithelial cells. This transmembrane protein is composed of two fragments: a longer extracellular N-terminal subunit (MUC1-N, 250-500 kDa), and a shorter transmembrane C-terminal subunit (MUC1-C, 17-25 kDa). In healthy tissues, MUC1 is found on the luminal surface of many epithelial cells in duct tissue and its negatively charged sugar branches form a physical barrier with anti-adhesive and protective properties towards pathogens, changes in pH, desiccation, and microbes. In cancer cells, the aberrantly glycosylated MUC1 can be found overexpressed in most human epithelial tumor cells. The deregulation of the glycosyltransferase machinery leads to hypo-glycosylated and less polar structures which impact the stability and localization of MUC1. One direct consequence of the cell polarity loss implies the redistribution of cell surface growth factors receptors in the basolateral surface of epithelial cells, which subsequently results in the alteration of signal transduction and their local microenvironment. Recently, the overexpressed MUC1 represents a clinical marker for the detection of several types of cancer.
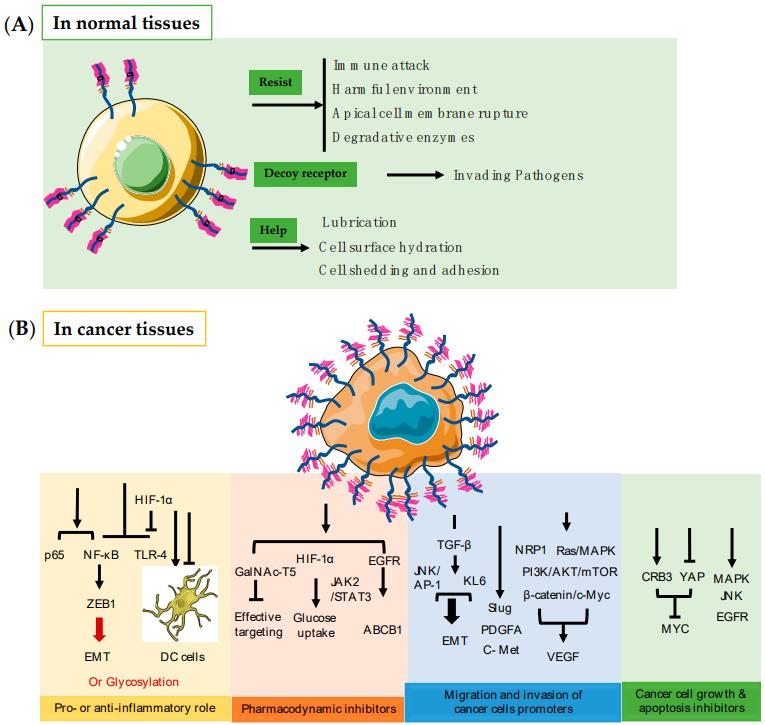 Fig.1 Different function of MUC1 in health or cancer tissues.1
Fig.1 Different function of MUC1 in health or cancer tissues.1
The Role of Anti-MUC1 Antibody in Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is a malignant tumor that severely threatens human health, and is characterized by high morbidity and mortality rates. Furthermore, lung cancer accounts for the highest incidence of male cancer and the mortality rate of all malignant tumors in males, and the second-highest in females worldwide. The high morbidity and mortality of lung cancer are closely associated with the alterations observed in the biological behavior of lung cancer cells. Adenocarcinoma (ADC) and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) are the two types of lung cancer.
In addition to their anti-adhesion functions, mucins can affect the transcriptional profile of various gene products involved in cancer cell invasion and metastasis by mediating signal transduction. MUC1 greatly contributes to the growth and metastasis of various cancers, including lung cancer, and MUC1 gene length polymorphisms are associated with susceptibility to lung cancer and its prognosis. A novel classification of MUC1 expression pattern was correlated with tumor differentiation and postoperative survival in ADC, of which MCU1 serves a key role as an oncogene in the tumorigenesis of various human ADCs. Thus, the utility potential of MUC1 as a diagnostic biomarker and/or therapeutic target in lung cancer is broad.
Creative Biolabs offers the largest, diversiform and extensive portfolio of innovative research products and services of NAA. Our proven and optimized platforms can help you quickly get satisfactory results without repeated trials. We also provide custom services based on the requirements of the clients to meet the specific demand. Please contact us for more details.
Reference
- Chen, Wenqing, et al. "MUC1: structure, function, and clinic application in epithelial cancers." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22.12 (2021): 6567.
Related Services:
- NAA Services for Anti-p53
- NAA Services for Anti-CAGE
- NAA Services for Anti-HER2
- NAA Services for Anti-c-Myc Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-GBU4-5

