NAA Services for Anti-NY-ESO-1 Antibody
With abundant experience and high-end technologies in NAA (natural autoantibodies) research, Creative Biolabs has developed a series of innovative and diversified NAA platforms, which enable us to successfully explore a wide range of NAA associated biomarkers for diseases diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring. Anti-NY-ESO-1 is one of the autoantibodies serving as potential biomarkers for the screening and diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Now, we are proud to offer fast and convenient NAA services for our worldwide customers. Our professional team is optimized to help you get a milestone development in your NAA project.
Background of NY-ESO-1
Natural autoantibodies (NAA) have been found to precede manifestations of symptomatic cancers, including nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), which is one of the most common malignant tumors and its early detection remains a challenge. NY-ESO-1 is a human tumor antigen of the cancer-testis antigens (CTAs) and is highly expressed in various poor-prognosis multiple myelomas. CTAs are widely explored as both a diagnostic marker and a therapeutic target in malignant lesions. Since the original discovery in esophageal cancer, NY-ESO-1 antigen has been observed in a variety of neoplasms. It is documented that NY-ESO-1 antigen can elicit both humoral and cellular immune responses, resulting in the production of autoantibodies. Data have shown that anti-NY-ESO-1 autoantibodies are present in a broad variety of cancer types, such as lung, breast, prostate and nasopharyngeal cancer, providing a possibility of early detection. Because of the high correlation, NY-ESO-1 antigen has become a target for some experimental engineered T-cell therapies for myeloma and it is being studied as a possible target for a cancer vaccine or immunotherapy.
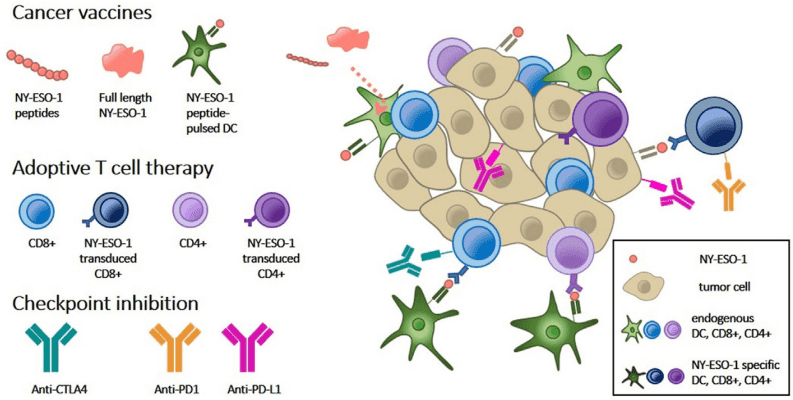 Fig.1 Overview of NY-ESO-1 targeted strategies to cancer immunotherapy.1
Fig.1 Overview of NY-ESO-1 targeted strategies to cancer immunotherapy.1
The Role of Anti-NY-ESO-1 Antibody in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is one of the most common cancers in Southern China and Southeast Asia, where the incidence rate is approximately 100-fold higher than that in the Western world. The majority of cases of NPC often present at an advanced stage at the time of diagnosis, because of its deep location and vague symptoms. Therefore, a screening and early detection of indicators for the early diagnosis of NPC is urgently required and may contribute to improving the treatment outcome.
Now, a large number of studies describe the presence of anti-NY-ESO-1 autoantibodies in serum samples from NPC patients, suggesting its potential role as an ideal biomarker and immunological hallmark of NPC with superior diagnostic accuracy. In addition, serum anti-NY-ESO-1 autoantibodies are positively correlated with tumor differentiation, lymphatic metastasis, cTNM stage and abdominal pain. So, the identification and detection of predictive and prognostic anti-NY-ESO-1 autoantibodies are of great clinical importance to the improvement of the curative rate and survival rate of NPC patients.
The Role of Anti-NY-ESO-1 Antibodies in Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is a condition that causes cells to divide uncontrollably in the lungs and is the leading cause of cancer death worldwide. Small-cell lung carcinoma (SCLC) and non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) are the two main types. The cancer-associated antigen NY-ESO-1 is an autoantigen expressed in lung tumor and a number of malignancies of different histological type. Patients with NY-ESO-1 positive tumors have been detected to bear circulating autoantibodies against this antigen. Previous studies suggested that the incidence of autoantibodies was significantly higher in patients suffering from NSCLC (23%) as compared to those with SCLC (9%). In non-small cell lung cancer, NY-ESO-1 tumor expression is associated with a higher risk of recurrence, poorer treatment response, and shorter survival. Thus, NY-ESO-1 antibody could be a useful tumour marker for detecting advanced or prognostic lung cancer and inferring the post-treatment tumour load in seropositive patients.
Anti-NY-ESO-1 Autoantibody Detection
There are a series of tests for the detection of anti-NY-ESO-1 autoantibodies, among which, the most common tests used for screening are Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) and immunofluorescence. Based on years of extensive experience in NAA research, we can provide a whole set of anti-NY-ESO-1 autoantibodies detection and analysis services with different approaches, including but not limited to autoantigen/autoantibody array, peptide array, ELISA, LIPS, WB and dot blot.
What We Can Do About NAA?
Aided by our well-established platforms and experienced scientists, we can provide comprehensive NAA services, from NAA detection, NAA profiling, to NAA epitope mapping. A wide spectrum of NAA products is also available for your choice.
Features of Our Services
- Seasoned technology and experienced scientists
- One-stop pipeline
- High efficiency without a lot of repeated trials
- Best after-sale service
The analysis of serum anti-NY-ESO-1 autoantibodies is used for screening, predicting response, and postoperative surveillance of malignancies including NPC. Creative Biolabs is well-positioned to deliver the largest portfolio of products and services about NAA. Our proven and optimized platforms can help you quickly get satisfactory results without repeated trials. We also provide custom services based on the requirements of the clients to meet their specific demand. Please contact us for more information.
Reference
- Thomas, Remy, et al. "NY-ESO-1 based immunotherapy of cancer: current perspectives." Frontiers in immunology 9 (2018): 947.
Related Services:
- NAA Services for Anti-MAGE
- NAA Services for Anti-Fibronectin Antibody
- NAA Services for Anti-CD44 Antibody
- NAA Services for Anti-BMI-1 Antibody
- NAA Services for Anti-EBNA-1 Antibody
- NAA Services for Anti-PRDX2/3 Antibody

