Support
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) is a technique to measure the presence and concentration of antigens in biological samples, which is based on the solid phase and the enzymatic labeling of antigens and antibodies. Since being invented in the 1970s, ELISA has quickly become the most convenient method to quantitatively measure the level of various biomarkers, especially in antibodies, because of its low-cost, simplicity, and rapidity. After half a century of development, the great potential of ELISA has been realized to be used in almost every field in biotechnology including natural-autoantibody (NAA) research. Indeed, before the role of NAA in the immune response was understood, scientists began to measure NAA levels in various cases via ELISA and realized the relationship between NAA and different health situations. Nowadays, despite the rapid development of biotechnology, ELISA is still one of the most important techniques in antibody research. As an advanced biotech company, Creative Biolabs established mature ELISA platforms and launched related one-stop services to our clients all over the world.
The Principle of ELISA
ELISA is a typical approach in quantitative detection of immune responses using the specific binding of antigens and antibodies. While immobilized antibodies or antigens still retain binding activities, the enzymes labeled on the antibodies are also functional. Therefore, after adding substrate catalyzed by the enzyme into colored products, the accurate amount of biomarkers is intuitively reflected by the gradation of color, which can be quantified by a microplate reader. ELISA is widely suitable for lots of biomarkers and without the requirement of a strict experimental environment.
The Classes of ELISA
Although using similar principles, there are still many classes of ELISA depending on the type of substance to be tested. While the direct ELISA is simple and inexpensive, the high background limits its accuracy. Therefore, indirect ELISA and sandwich ELISA are most commonly used in the measurement of antigens and antibodies, respectively. Competitive ELISA is relatively rare in the use of antibodies detection. However, competitive ELISA is widely used in the test of small molecule compounds or a small amount of antibody which is not enough in other methods.
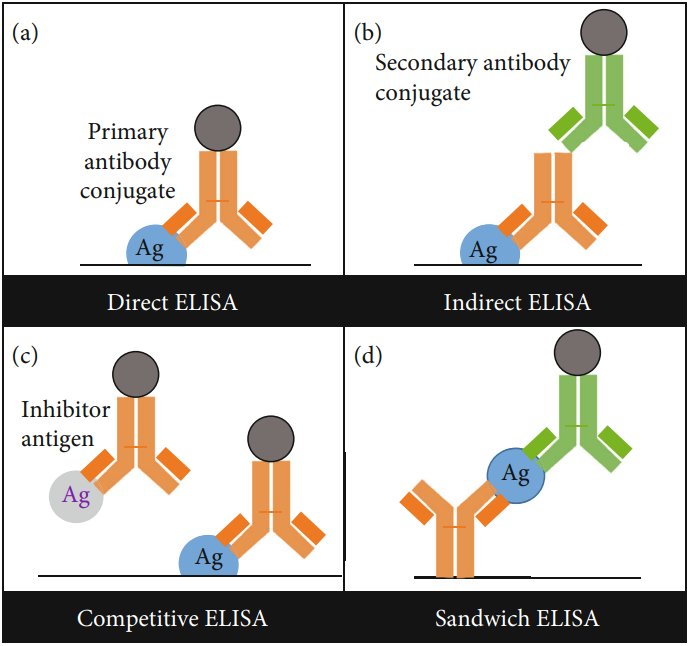 Fig.1 The four types of ELISA.1
Fig.1 The four types of ELISA.1
| Advantages | Disadvantages | Application | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct ELISA |
|
|
|
| Indirect ELISA |
|
|
|
| Sandwich ELISA |
|
|
|
In the development of NAA, ELISA has always been one of the most important techniques. Creative Biolabs has built a strong technology platform to provide a full range of NAA services and NAA Detection Kits. Our mature and competitive ELISA platform will accelerate your NAA research process. Please feel free to contact us or click follow key words.
Reference
- Japp, Nicole C., et al. "Tumor biomarker in-solution quantification, standard production, and multiplex detection." Journal of Immunology Research 2021 (2021).
Related Services:
- Western Blot
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
- Cryogenic Electron Microscopy (Cryo-EM)
- Site-Directed Mutagenesis Mapping

