NAA Services for Anti-TERF1 Antibody
Autoantibody against TERF1 has been an attractive non-invasive biomarker for detection of gastric cancer due to its inherently stable in serum. It attracts increased interest because of its potential as an effective biomarker for disease diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring. Based on our first-class natural autoantibodies (NAA) platform, Creative Biolabs offers a comprehensive range of NAA services characterized by quality, predictability, delivery, and customization.
Background of TERF1
Telomeric repeat-binding factor 1 (TERF1), also known as TRF1 or TRBF1, is a telomere specific protein which is a component of the telomere nucleoprotein complex. The structure of TERF1 is characterized by a conserved N-terminal homodimerization domain (TRFH), which is involved in homodimer assembly and in the recruitment of other proteins; and a C-terminal DNA binding domain connected by a long loop region. It has been documented that the N terminus of TERF1 comprises the binding site for tankyrase 1.
The major function of TERF1 is to function as a negative regulator in telomere protection and telomere length regulation. TERF1 is important both to prevent telomere fusions as well as for the replication of telomeric regions. TERF1 abrogation results in the induction of senescence and multi-telomeric signals. In addition, high-level TERF1 has been recently proposed to induce and maintain pluripotency. In particular, recent studies have shown that TERF1 may be a potential anti-cancer target, and both genetic and chemical inhibition of TERF1 levels at telomeres has an anti-tumoral effect.
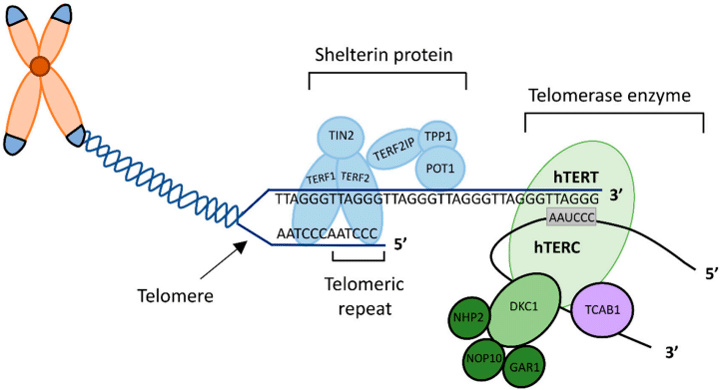 Fig.1 The structure of the human telomere and telomerase.1
Fig.1 The structure of the human telomere and telomerase.1
The Role of Anti-TERF1 Antibody in Gastric Cancer
Gastric cancer (GC) is a lethal disease with high mortality and poor survival rate because patients are often diagnosed with advanced disease. So, it is important to discover novel biomarkers for carcinoma accurate diagnosis and novel therapeutic targets. Natural autoantibody-based biomarkers attract particular interests because of the early and abundant occurrence before the cancer onset.
In human GC, anti-TERF1 is one of the identified serum autoantibodies with potential for diagnosis and prognosis. Anti-TERF1 autoantibodies test can improve the diagnosis, treatment, prognosis, and prevention of GC. TERF1 changes can result in telomere dysfunction, such as telomere shortening and telomerase activation, which is the main possible reason for chromosome instability. While, chromosome instability may activate cellular carcinogenesis, which leads to the activation of oncogenes, the loss of tumor suppressor genes and multiple mutations, finally, lead to gastric cancer formation. Given the importance of TERF1 for organismal viability and tissue homeostasis, it is urgent to study the potential therapeutic effects of TERF1 in GC.
What Can We Do?
Creative Biolabs can offer anti-TERF1 autoantibodies detection and identification services for the early diagnosis and prognosis of GC. Based on well-established platforms and experienced scientists in NAA research, we can offer the optimized methods, including but not limited to basic immunochemical methods (ELISA, LIPS, WB and dot blot) and high throughput methods (autoantigen/autoantibody array, peptide array) with high flux and accuracy. Besides, our one-stop NAA services (NAA detection, NAA profiling, NAA epitope mapping, etc.) and premade NAA products are also available for your choice.
Features of Our Services
- Advanced technologies and experienced scientists
- High accuracy without numerous repeated trials
- One-stop pipeline to save your time
- Cost-effective and best after-sale service
In human GC, identification and detection of anti-TERF1 autoantibodies are of great clinical significance for the early diagnosis and immunotherapy. Creative Biolabs is dedicated to providing the largest portfolio of NAA products and services. Besides, we also provide custom services to meet the clients' specific demands. Please contact us for more information.
Reference
- Button, Lucy, et al. "Telomere and telomerase-associated proteins in endometrial carcinogenesis and cancer-associated survival." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23.2 (2022): 626.
Related Services:
- NAA Services for Anti-HCC-22-5
- NAA Services for Anti-Peroxiredoxin VI
- NAA Services for Anti-KM-HN-1
- NAA Services for Anti-p90
- NAA Services for Anti-NT5E Antibody
- NAA Services for Anti-MAGEA4
- NAA Services for Anti-COPS2 Antibody
- NAA Services for Anti-CTSF Antibody

