NAA Services for Rheumatoid Factor (RF)
Rheumatoid factors are a family of autoantibodies produced in rheumatoid arthritis by B cells, which have been researched as natural autoantibody (NAA) biomarkers in both animal models and clinical tests. We Creative Biolabs can provide a full range of rheumatoid factor (RF) marker services for diseases diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring. Our professional team is optimized to help you get a milestone development in your NAA project.
Background of Rheumatoid Factors
RF is an autoantibody produced by the immune system that can attack healthy tissue in the human body. It was the first autoantibody described in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) by Waaler in 1940, and also can be detected in other autoimmune diseases, infectious diseases as well as healthy individuals. RF is a group of autoantibodies with specificity against constant regions of the heavy chain in the IgG Fc fragment. Different RF can recognize different parts of the IgG-Fc. Majority of RF are identified as IgM isotype and can be detected by ELISA in 60-80% of RA patients. A higher level RF has been observed in many immune system-related diseases, such as rheumatic diseases, systemic lupus erythematosus, sjögren's syndrome, malaria, and AIDS. Evidence indicates that RFs are one of the most useful diagnostic disease biomarkers of RA. Anti-RFs are a family of autoantibodies directed to the Fc portion of IgG, which has proven to be the most useful disease marker of rheumatoid arthritis.
The Role of Anti-Rheumatoid Factor in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
SLE is a kind of autoimmune multisystem disease which is characterized by multiple autoantibodies involves many parts of the body. Clinical and laboratory tests showed that all IgM, IgG and IgA RF could be determined in patients with SLE. Recent studies have suggested that IgA RF is the definition of SLE patients subgroup characterized by distinct autoimmune phenomena and high disease activity in the absence of nephritis. It can be developed as one of the useful biomarkers in the clinical diagnosis of SLE.
The Role of Anti-Rheumatoid Factor in Rheumatic Diseases
Rheumatic diseases are parts of autoimmune diseases that characterized by inflammation that affects the connecting or supporting structures of the body - most commonly the joints, but also sometimes the tendons, ligaments, bones, and muscles. RA refers to one of the rheumatic disorder that affects the joints, which mainly caused by the presence of various autoantibodies in serum and synovial fluid. The first identified NAA in RA was RF, which was considered to be one of the criteria for the classification of RA in American College of Rheumatology due to detection in the sera of approximately 75% of RA patients. Moreover, affinity maturation is a distinction of RFs in RA patients from those in healthy individuals. Although new powerful biomarkers for the early stage of RA have been investigated, RF is still one of the most reliable diagnostic biomarkers for RA especially in the case of early RA.
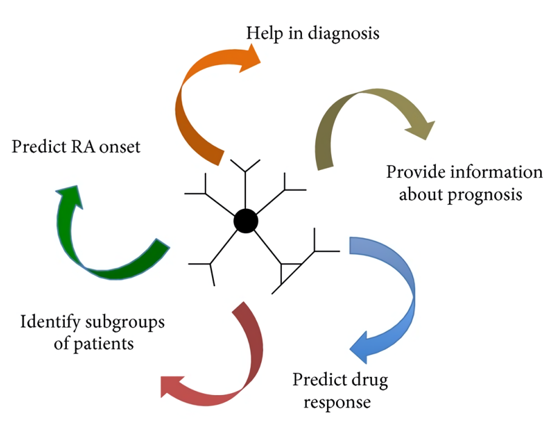 Fig.1 Role of rheumatoid factors in the management of rheumatoid arthritis patients. (Ingegnoli, 2013)
Fig.1 Role of rheumatoid factors in the management of rheumatoid arthritis patients. (Ingegnoli, 2013)
The Role of Anti-Rheumatoid Factor in Sjögren's Syndrome (SS)
SS is a chronic systemic autoimmune disorder characterized by lachrymal and salivary gland dysfunction presenting as dry mouth and dry eyes. SS is one of the most common autoimmune diseases that mainly affect elder females accompanying other immune system disorders, such as RA and SLE. Although the pathogenesis of SS still remains unclear, evidence showed that autoreactive lymphocytes and autoantibodies make a great contribution to this pathogenic process. In 1992, it was reported that IgA RF has been found both in serum and saliva of patients with SS. Together with anti-SS-B/La, RF have been regarded as useful markers of SS in clinical.
The Role of Anti-Rheumatoid Factor in Malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease caused by parasitic single-celled microorganisms and transmitted by the bite of infected mosquitoes. Once infected, the parasites multiply in the host's liver before infecting and destroying red blood cells. At the early malaria infection, the parasites habitat in the host and can develop escape mechanisms to resist the host immune system. This escape can lead to a generation of autoantibodies by the immune system, including RF. And IgM isotype of the RF could cause interference in immunoassays in individuals affected by malaria.
The Role of Anti-Rheumatoid Factor in AIDS
Human acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) is a type of infection immune system attack by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). The association between AIDS and autoimmunity has attracted lots of attention from clinical and pathophysiological perspectives. One of the hallmarks of autoimmunity is the presence of high levels of circulating autoantibodies. HIV-infected patients presented higher overall frequency of autoantibodies (including anti-RF), which is associated with lower CD4+ cell counts. Furthermore, with the infection process, the incidence of autoantibodies is increased, and IgA RF isotype is significantly raised in both AIDS and AIDS-related complex.
Creative Biolabs is committed to providing extensively custom NAA products, applications, and services about NAA to promote the progress of your projects. Please contact us for more information and a detailed quote.
Reference:
- Ingegnoli, F.; et al. Rheumatoid Factors: Clinical Applications. Disease markers. 2013, 35(6): 727-734.
Related Services:
- NAA Services for Anti-Nuclear Antibody (ANA)
- NAA Services for Anti-Double-Stranded DNA (dsDNA)
- NAA Services for Anti-Smith
- NAA Services for Anti-Ribonucleoprotein (RNP)
- NAA Services for Anti-Ro Autoantibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-La Autoantibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-C3
- NAA Services for Anti-C4
- NAA Services for Anti-C1q

