- Home
- UTC Development
- Antibody-Enzyme Conjugate Development
- Antibody-directed Enzyme Prodrug Therapy (ADEPT) Development
- Antibody-β-Lactamase Conjugate Development
Antibody-β-Lactamase Conjugate Development Services
Creative Biolabs provides comprehensive customized antibody-directed enzyme prodrug therapy (ADEPT) development services using antibody-β-lactamase conjugate for targeted immunotherapy to meet customers' requirements.
β-lactamase
β-lactamase is a type of enzyme secreted by bacteria (normally are Gram-positive bacteria). It harbors multi-resistance to many antibiotics that contain β-lactam, such as penicillins, cephalosporins, cephamycins, and carbapenems (ertapenem), except carbapenems which are relatively resistant to β-lactamase. β-lactamase displays antibiotic resistance via breaking the antibiotics' structure. These antibiotics consist of a common four-atom ring known as a β-lactam in their molecular structure. The lactamase enzyme can break the β-lactam ring, after hydrolysis, inactivating the molecule's antibacterial functions. β-lactamase is a bacterial enzyme that hydrolyzes the β-lactam (C-N) bond in β-lactam antibiotics. Owing to its broad substrate specificity, it has been widely used to catalyze a wide range of prodrugs that contain the β-lactam ring.
MOA of β-lactamase
β-lactamase catalyzes the hydrolytic cleavage of prodrug containing a β-lactam ring open such as cephalosporin mustards, C-DOX, CM, and so on, yielding the parent drug mitomycin C, Doxorubicin, Phenylenediamine mustard and Taxol, respectively. Thus, β-lactamase ADEPT systems have been demonstrated as ideal chemical conjugates and fusion proteins with a variety of antibody formats to target carcinomas and melanomas. For example, β-lactamase was fused with a 'sdAb' to target carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA).
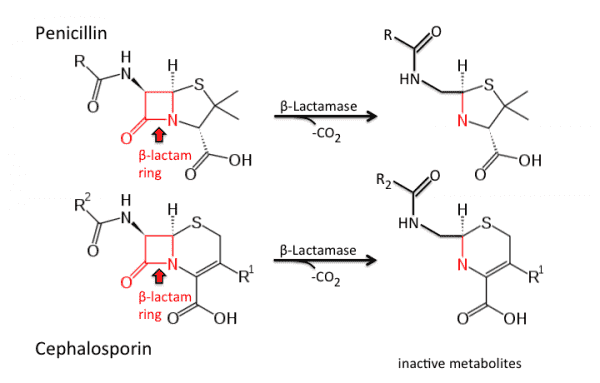 Fig.1 β-lactam resistant bacteria generally evade these antibiotics through two paths: restriction of entry of the antibiotic into the bacterial cell and secretion of β-lactamase enzymes, which neutralize the antibiotic outside of the cell.1,2
Fig.1 β-lactam resistant bacteria generally evade these antibiotics through two paths: restriction of entry of the antibiotic into the bacterial cell and secretion of β-lactamase enzymes, which neutralize the antibiotic outside of the cell.1,2
Antibody-β-lactamase Conjugate-based ADEPT
It has been demonstrated that chemical conjugates and fusion proteins with a variety of antibody formats in β-lactamase ADEPT systems have targeted carcinomas and melanomas successfully. For example, β-lactamase was fused with a 'sdAb' to target carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA). The sdAbs are single-domain VHH antibody fragments found in camels with the absence of a light chain. This is the smallest antibody that has been used in ADEPT. The sdAb-β-lactamase protein in colorectal carcinoma xenograft mouse models therapy studies revealed tumor regressions, with some complete cures upon enzymatic activation of the cephalosporin nitrogen mustard and other prodrugs.
Creative Biolabs is dedicated to helping you develop antibody-β-lactamase conjugate using readily available or customized linkers or direct antibody-enzyme fusion proteins. Please contact us for more information and a detailed quote.
References
- Nagshetty, Kavita, et al. "An overview of extended spectrum beta lactamases and metallo beta lactamases." Advances in Microbiology 11.01 (2021): 37.
- Distributed under Open Access License CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. NOT FOR CLINICAL USE.

Online Inquiry
Welcome! For price inquiries, please feel free to contact us through the form on the left side. We will get back to you as soon as possible.
