Therapeutic Exosomes for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Exosomes are nanovesicles found in human biological fluids that can be successfully loaded with therapeutic drugs for the targeted delivery of therapeutics. Several drug-loaded exosomes are promising for the treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC). Creative Biolabs has optimized our technology platform with advanced equipment and experienced experts to help our customers accelerate the research of exosome drugs for HCC through efficient and high-quality exosome experimental services.
Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) and Exosome
Liver cancer is ranked as the sixth most common malignancy worldwide, with HCC accounting for approximately 80% of primary liver cancer cases. Most HCC is caused by hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), aflatoxin, heavy alcohol consumption, obesity, smoking, and type 2 diabetes. The 5-year overall survival rate for HCC patients remains less than 25%. In HCC, numerous pieces of evidence suggest that microRNAs (miRNAs) in exosomes that regulate various oncogenes and tumor suppressors play an important role in carcinogenesis, remodeling of the tumor microenvironment, HCC cell proliferation and metastasis, angiogenesis, and drug resistance effect. However, the intrinsic properties of low immunogenicity and high stability make exosomes an ideal vehicle for targeted drug delivery for the treatment of HCC.
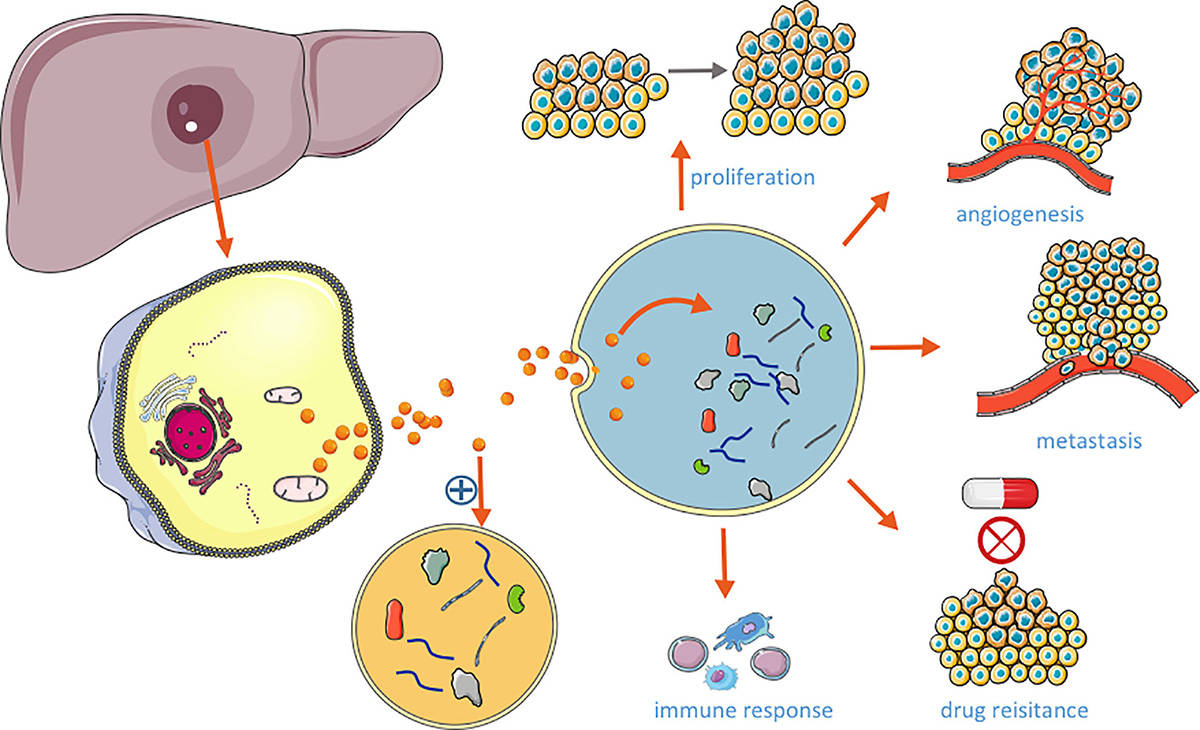 Fig.1 Role of HCC-derived exosomes in HCC.1,2
Fig.1 Role of HCC-derived exosomes in HCC.1,2
Exosome Cargo and the Therapy of HCC
miRNAs play important regulatory roles in RNA silencing and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression by targeting specific mRNAs for degradation or translational repression. miRNAs encapsulated in exosomes with targeting peptides can be protected from inactivation or degradation caused by in vivo circulation and can be targeted for accumulation at tumor sites. Several research groups have loaded miR-335-5p, miR-26a, and miR-31 into exosomes targeting HCC cells, respectively. These therapeutic exosomes have been found to inhibit HCC cell proliferation and invasion in vitro and induce HCC tumor shrinkage in vivo.
Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMS), can promote tumor development. Currently, multiple therapeutic exosomes have been found to reprogram TAMs into M1-like macrophages, suggesting that exosome-related cancer immunotherapy is very promising. For HCC, STAT6 silencing induced apoptosis and growth inhibition of HCC-derived cells by reducing the expression of RANKL. Therefore STAT6 is a promising target for the treatment of HCC. In HCC models, researchers have found that therapeutic exosomes loaded with nucleic acids that inhibit STAT6 expression can significantly reduce STAT6 mRNA levels in mice and significantly promote the number of M1-like macrophages. Furthermore, this therapeutic exosome could slow down HCC growth and induce complete remission of HCC. At present, the therapeutic exosome has entered clinical phase I.
Creative Biolabs can provide various forms of exosome loading services and related one-stop exosome drug research services. If you are looking for a partner to assist you with your exosome drug research, please feel free to contact us for more information.
References
-
Li, S.; Chen, L. Exosomes in Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Frontiers in Oncology. 2022, 12:793432.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Role of HCC-derived exosomes in HCC.1,2
Fig.1 Role of HCC-derived exosomes in HCC.1,2









