Diagnostic Applications of Exosomes
Overview Services Features FAQs
Exosomes carrying stable bioactive molecules, such as nucleic acids and proteins, are highly effective liquid biopsy biomarkers that can provide dynamic insights into the diagnosis and prognosis of various diseases. Creative Biolabs provides services related to the discovery and research of exosome markers to advance the disease diagnostic applications of exosomes.
Diagnostic Advantages of Exosomes
Exosomes and their components have become promising markers for diagnostic and prognostic applications in diseases. Liquid biopsies with exosomes as markers not only break through several limitations of traditional solid biopsies but also demonstrate superiority over other sources of liquid biopsies, including
|
Advantages
|
Details
|
-
Sample source diversity and easy storage
|
Exosomes are more readily available from virtually all body fluids than circulating tumor cells. Similar exosomal markers are observed for these samples in the fresh state, stored at 4°C for 24 hours and at -80°C for long-term storage, and the higher biological stability greatly reduces the cost and difficulty of their preservation and transportation.
|
-
Convenient sampling operability facilitates dynamic monitoring
|
Liquid biopsies overcome the limitations of traditional tissue biopsies, resulting in non-invasive, non-destructive results. This allows multiple sampling for continuous and dynamic monitoring based on liquid biopsies.
|
-
Clearer analytical methods and more reliable predictive accuracy
|
Exosomes prefer to be isolated with classical extraction methods by ultracentrifugation and continuously innovative methods under development. Subsequently, established sequencing and histological analysis techniques are used to achieve a clear analysis of exosome-associated disease markers, possessing a more reliable diagnostic accuracy than traditional serum-based biomarkers such as a carcinoembryonic antigen.
|
-
Richer biological information
|
Exosomes are more representative than cell-free DNA (cfDNA) derived from necrotic and apoptotic processes. On the one hand, exosomes appear with the same surface proteins as their parental cells or even target cells, contributing to exosome isolation of specific origin and predicting metastasis to specific organs. On the other hand, most plasma cfDNA in advanced plasmacytic ovarian cancer and mitochondrial DNA are higher than the plasma and peripheral blood copy numbers located in exosomes, showing the sensitivity and specificity of nucleic acid mutation frequency detection of exosomes over cfDNA.
|
The diseases involved in the discovery and study of exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers include, but are not limited to:
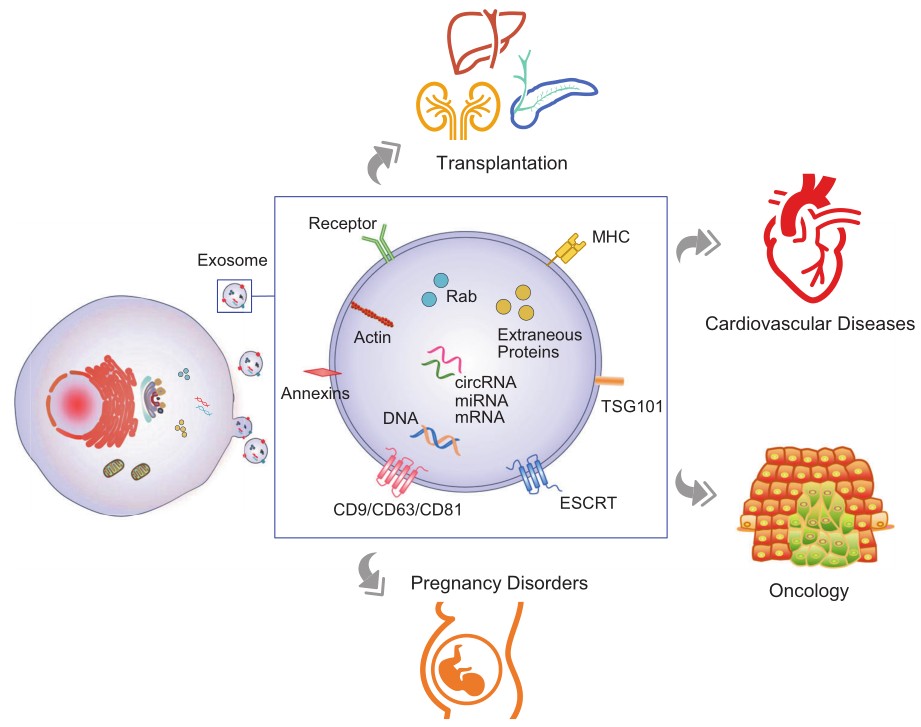 Fig.1 Biogenesis, secretion, composition, and application of exosomes as liquid biopsy.1, 3
Fig.1 Biogenesis, secretion, composition, and application of exosomes as liquid biopsy.1, 3
Procedures for Diagnosis at Creative Biolabs
The general procedure for exosome diagnosis at Creative Biolabs is divided into the following key steps:
|
1. Exosome isolation and purification from biofluidic samples.
|
At Creative Biolabs, various sample sources are available for exosome isolation, including cell cultures, plasma, serum, urine, cerebrospinal fluid, saliva, ascites, follicular fluid, and breast milk. We offer a wide selection of methods for exosome isolation and purification by ultracentrifugation, size-exclusion chromatography, tangential flow filtration, affinity-based capture, and combinations of the above methods.
|
|
2. Exosome contents extraction and profiling.
|
Creative Biolabs has established a comprehensive platform for exosome content profiling. For exosomal RNA sequencing, Creative Biolabs has equipped several powerful technologies including PCR, qPCR, and NGS. With these technologies, we offer a wide range of exosomal RNA analysis services, including whole transcriptome sequencing and miRNA sequencing. Exosomal proteomic analysis is performed by mass spectrometry to identify and analyze exosomal protein composition data. Chemical isotope labeling and nLC-MS-based technologies are available for exosomal lipidomics and metabolomics analysis services.
|
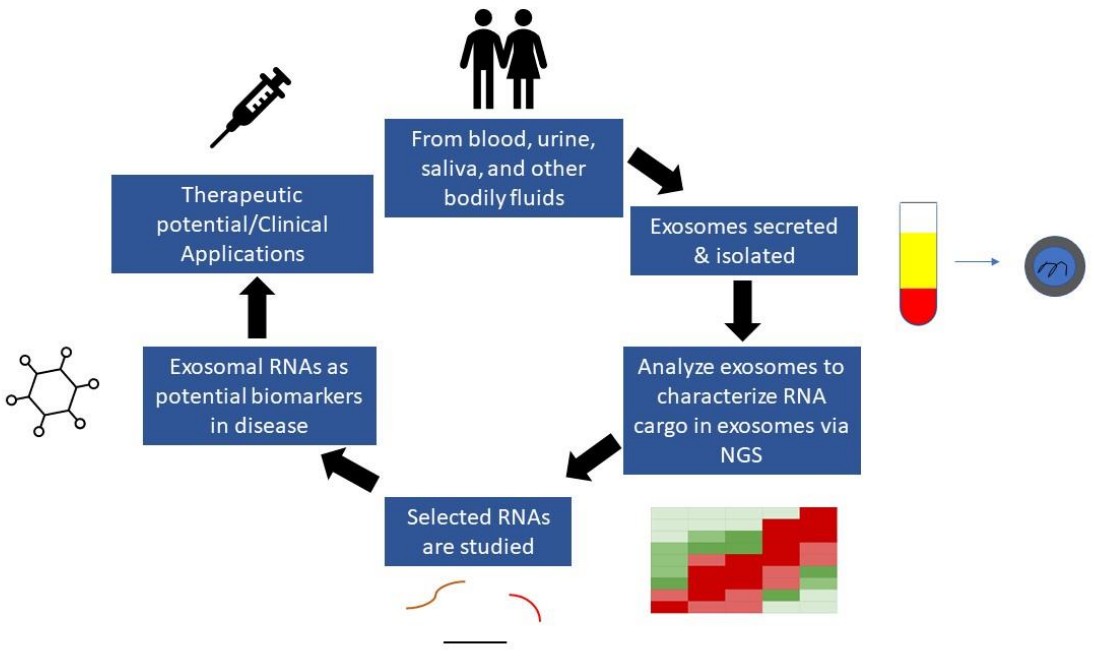 Fig.2 Schematic representation detailing the discovery of biomarkers from exosomes.2, 3
Fig.2 Schematic representation detailing the discovery of biomarkers from exosomes.2, 3
Features of Exosome-based Diagnostic
-
Diverse Applications: From cancer detection to infectious disease monitoring, exosome diagnostics are versatile tools capable of detecting a wide range of conditions.
-
Non-invasive Sampling: Exosome isolation provides a non-invasive method for diagnostic testing, reducing patient discomfort.
-
Potential for Early Detection: Exosome biomarkers can indicate disease presence at early stages, facilitating timely intervention and treatment.
-
High Sensitivity and Specificity: Exosome-based diagnostics offer unparalleled sensitivity and specificity due to their ability to carry disease-specific biomarkers.
-
Personalized Solution: The molecular cargo of exosomes reflects the unique molecular profile of the individual, enabling personalized strategies.
Drawing on the multiple active cargoes carried by exosomes that can be used as liquid biopsy biomarker candidates, Creative Biolabs provides exosome marker discovery services in diagnostic applications and comprehensive research analysis services, improving the research of disease prognosis and diagnosis. Please contact us with your interest.
FAQs
Q: What types of diseases are involved in the research of exosome diagnostic applications?
A: Exosome diagnostics can identify various illnesses, such as infectious infections, cancer, heart problems, and neurological conditions. They are especially helpful in cases where bodily fluids contain biomarkers.
Q: How can exosome diagnostics contribute to personalized strategies?
A: Exosome diagnostics can provide information about an individual molecular profile, allowing for tailored treatment plans based on particular characteristics and responses.
Q: What is the future outlook for exosome-based diagnostics?
A: The field of exosome-based diagnostics is rapidly evolving, with ongoing research focusing on improving detection methods, expanding applications, and validating preclinical utility across different diseases.
References
-
Zhou, Biting, et al. "Application of exosomes as liquid biopsy in clinical diagnosis." Signal transduction and targeted therapy 5.1 (2020): 144.
-
Elkommos-Zakhary, Marina, Neeraja Rajesh, and Vladimir Beljanski. "Exosome RNA sequencing as a tool in the search for cancer biomarkers." Non-coding RNA 8.6 (2022): 75.
-
Under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Biogenesis, secretion, composition, and application of exosomes as liquid biopsy.1, 3
Fig.1 Biogenesis, secretion, composition, and application of exosomes as liquid biopsy.1, 3
 Fig.2 Schematic representation detailing the discovery of biomarkers from exosomes.2, 3
Fig.2 Schematic representation detailing the discovery of biomarkers from exosomes.2, 3









