Exosome Communication between Tissues Advance Summary
Exosomes can be released by almost all cells and circulated in body fluids. Exosomes produced by various cell types in certain tissues have the capacity to influence disease development as well as regulate the tissue microenvironment in which they are positioned and preserve tissue homeostasis. Exosomes can also enter the body fluid circulation and travel to different organs and tissues all throughout the body to take part in the control of the body physiological functions. Exosomes released from specific tissues into body fluids can interact with target cell receptors in target tissues through ligands on their surface (such as transmembrane proteins, integrins, intercellular adhesion molecules, etc.). In this way, the signal released by the parent tissue is transmitted to the target tissue to complete the remote communication and regulation between the tissues. This is one of the important mechanisms for the cooperation between distant tissues to maintain the homeostasis of the body. Creative Biolabs aims to explore the exosome communication mechanism that can better reflect the real state of the body and can provide customers with the most efficient exosome communication research program between tissues and a one-stop service.
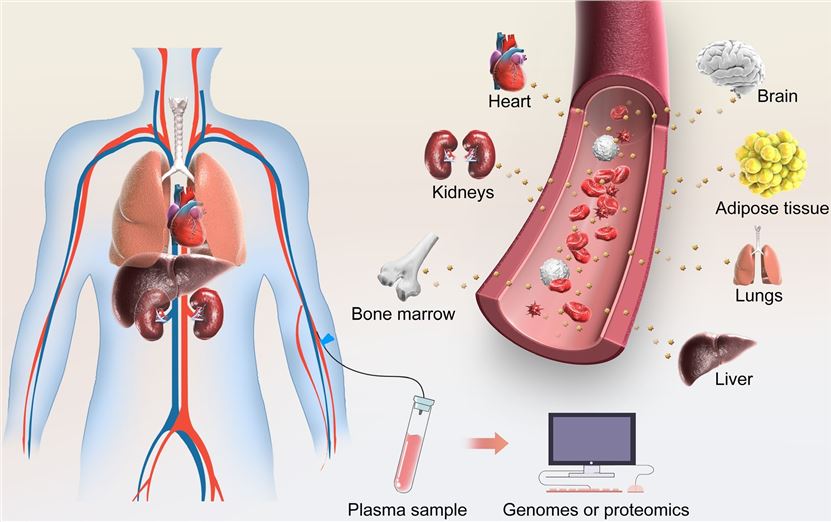 Fig.1 Exosomes could mediate biological effect at distant sites.1,2
Fig.1 Exosomes could mediate biological effect at distant sites.1,2
Research progress on the Exosome Communication mechanism between Tissues
The human body is like a complex and precise machine, and its normal operation depends on the coordinated and orderly work of various organs or tissues. One of the important mechanisms to keep the operation going is the signaling in the circulation of body fluids. Once a disease develops in one tissue, it releases regulatory signals to affect other tissues. Different tissues and different types of cells in the human body can secrete exosomes. Due to their small size (30-150nm), strong encapsulation, and good biocompatibility, exosomes can carry out long-distance transport through body fluids and transfer the signals from the donor cells to the recipient cells in distant target tissues. At present, it has been found in various health and disease models that exosomes can transmit the substances and signals they carry to recipient cells and change their biological functions by fusing with cell membranes. Because of this, a large number of researchers have transformed exosomes into carriers for drug delivery or gene therapy or screened exosomes for disease diagnostic markers through high-throughput sequencing. However, these studies are based on exosomes derived from cell supernatants or body fluids in vitro, and cannot more truly reflect the exosome communication mechanism between two tissues in vivo. Excitingly, direct extraction of tissue-specific exosomes to study the mechanism of exosomes between two tissues has been reported in recent years. Creative Biolabs has been constantly summarizing and updating the following related reports to help customers understand the latest ideas in exosome research.
Heart-Brain Exosome Communication
Lung-Bone Exosome Communication
Muscle-Bone Exosome Communication
Brain-Adipose Exosome Communication
Heart-Adipose Exosome Communication
Colon-Adipose Exosome Communication
Bone-Vascular Tissue Exosome Communication
Atherosclerotic Plaque Tissue-Vascular Tissue Exosome Communication
Muscle-Liver Exosome Communication
Liver-Vascular Tissue Exosome Communication
Creative Biolabs has been committed to the research on the mechanism of exosomes in long-distance communication between cells, hoping to help customers discover the exosome regulation mechanism of lesion sites affecting other tissues in the body. With years of project experience, continuously upgraded technology and equipment, and a professional technical team, we can provide global customers with the most comprehensive one-stop service for tissue exosome research, including exosome isolation, exosome identification, exosome profiling, exosome proteomics, exosome RNA sequencing, exosome lipidomics and metabolomics and tissue exosome related services. If you want to have a more comprehensive and realistic understanding of how the lesion affects other tissues or even the whole body, please contact us and put forward your specific ideas. We will get in touch with you immediately and provide the most rigorous research program on the long-distance transport mechanism of exosomes.
References
-
Zhang, J.; et al. Small but significant: Insights and new perspectives of exosomes in cardiovascular disease. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine. 2020, 24(15):8291-8303.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Exosomes could mediate biological effect at distant sites.1,2
Fig.1 Exosomes could mediate biological effect at distant sites.1,2









