Selection Strategies of Internal and External Parameters in Exosomal RNA Detection
Exosomes are rich in a variety of disease-related RNA molecules, such as miRNA, mRNA, lncRNA, etc. The detection of target RNA abundance in exosomes by fluorescent qPCR (quantitative PCR) has proven to be a promising liquid biopsy tool. The selection of appropriate internal and external parameters in qPCR is the key to ensuring authentic and valid data. Creative Biolabs understands the uniqueness of exosomal samples from respective projects and has mastered the strategy of professional internal and external parameters selection in exosomal RNA assays to provide reliable exosome research services.
Significance of Internal and External Parameters Selection
qPCR is an effective means to detect low-abundance RNA, assisting in the identification of potential exosomal RNA biomarkers. Exosomal samples from different sources and treatments differ significantly in RNA quality, yield, and reverse transcription efficiency, which affects the reliability of results for differential expression of target genes. The selection of specific internal parameters to correct and standardize the results while detecting the target gene facilitates quality control of the RNA extraction and PCR process. In addition, to overcome the limitation of the lack of recognized watcher genes with constant expression as internal parameters, the selection of external referent genes is also feasible. The standardized external parameters are exogenous substances added to the samples to be tested during the exosomal RNA assay, which can accurately reflect the bias in the assay process of different samples.
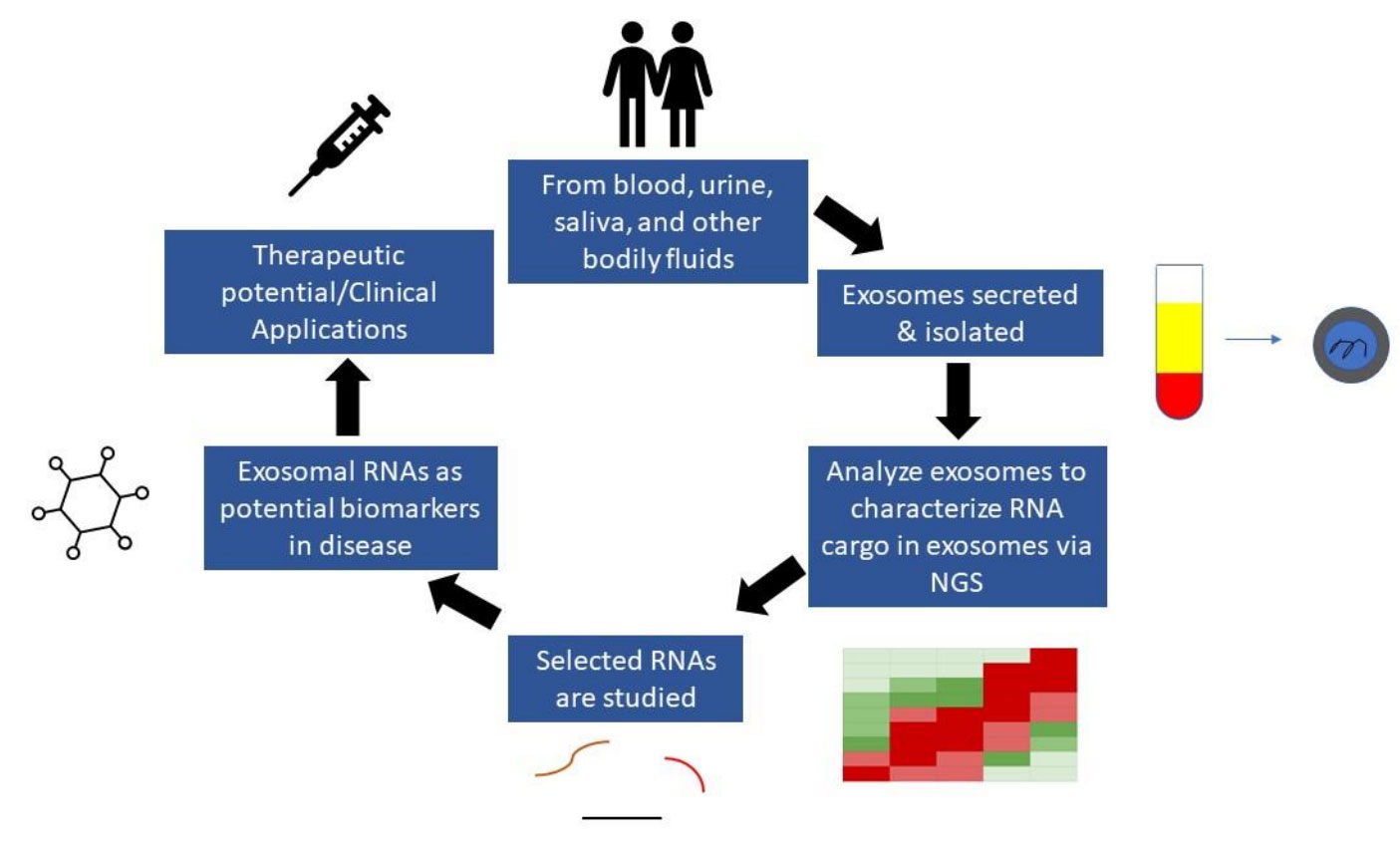 Fig.1 RNA biomarker discovery from exosomes. (Elkommos-Zakhary, 2022)
Fig.1 RNA biomarker discovery from exosomes. (Elkommos-Zakhary, 2022)
Selection of Internal Parameters for Exosomal RNA Detection
Currently, research work on exosomal RNA detection is performed with internal parameters that are heavily used in classical cell biology studies for PCR, such as GAPDH, ACTIN, 18S for long-stranded RNA, and U6 for miRNA, while a single internal parameter is often used for normalized correction of different genes to be tested. There are obvious limitations of this approach, which are mainly reflected in the following points.
-
Large data have shown that internal parameters genes, which are constantly expressed in different human samples, are significantly different in pathological-physiological states, and even in the same state, there are significant expression differences between different individuals.
-
A single internal parameter for normalized correction of target genes with different levels of expression results in different levels of accuracy in the quantification of genes with different expression abundance. The closer the expression is to the RNA of the internal parameters gene, the better the correction is.
-
If the selected internal parameter genes are not exosome-specific in body fluids but exist in both free form and vesicle-encapsulated form, the expression of the internal parameter genes will be severely affected by the extraction process of that exosome, and thus losing the essential value of the internal parameter. In brief, internal parameter genes and target genes may have different distribution patterns in exosome samples and behave differently during the experiment.
Therefore, a uniform internal parameter for all sample types of exosomal RNA is not available at this stage. The correct and reasonable choice of internal parameters depends heavily on the type of sample under study. Moreover, even for the same body fluid type, a single internal parameter gene cannot simply be applied between different exosome extraction methods. Also, PCR correction of exosomal RNA using multiple internal parameter genes with different expression abundance is worth considering. The selection of internal parameter genes should meet the following basic requirements.
-
The expression abundance is close between samples without significant differences.
-
Its expression level is comparable to that of the target gene to be tested and should not be too far apart.
-
It is not affected by the treatment measures during the experiment.
Selection of External Parameters for Exosomal RNA Detection
The exosomal RNA assay based on the external parameter method still applies the model of total RNA assay in the liquid biopsy field. That is, after exosome extraction and before RNA extraction, an equal amount of free exogenous RNA is added to normalize the quality of the sample, the efficiency of the RNA extraction, and the reverse transcription process. The ideal exosomal RNA external parameter should theoretically meet the following characteristics.
-
It is present in the same form as the target RNA to be examined in the sample, i.e., present in the vesicle-encapsulated state.
-
It has the same kinetic behavior as the exosomal RNA to be examined during exosome isolation and enrichment.
-
The same efficiency as the target gene in the process of exosome RNA extraction and PCR detection, which can completely simulate the kinetic changes of the target gene in the whole liquid biopsy process.
Screening internal and external parameters that fit the system based on stable sample types and exosome extraction methods helps to improve the fit between sequencing data and PCR results, and ensures consistent and reproducible PCR results. At Creative Biolabs, we understand the uniqueness of different exosomal samples and can provide high-quality exosomal RNA detection services with appropriate internal and external parameters selected for the correction process. Please contact us for further information.
Reference
-
Elkommos-Zakhary, M.; et al. Exosome RNA sequencing as a tool in the search for cancer biomarkers. Noncoding RNA. 2022, 8(6): 75.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 RNA biomarker discovery from exosomes. (Elkommos-Zakhary, 2022)
Fig.1 RNA biomarker discovery from exosomes. (Elkommos-Zakhary, 2022)









