- Home
- UTC Development
- Bispecific ADC Development
- Biparatopic Receptor based Bispecific ADC Development
- Biparatopic c-MET-targeted Bispecific ADC Development
Biparatopic c-MET-targeted Bispecific ADC Development Service
Bispecific antibodies (bsAbs) are artificially engineered monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) that consist of two distinct binding sites and are capable of binding two different antigens noncovalently, which is one of the fastest growing class of investigational drugs. Currently, over a hundred different formats of bsAbs are in the pipeline. As a novel and effective modality in cancer therapeutics, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) take advantage of the specificity provided by monoclonal antibodies to achieve targeted delivery of the cytotoxic drug to cancer cells. There are eight approved ADCs available for cancer treatment. Recent research found that the combination of bsAbs and ADCs to form bispecific ADCs can be more effective in cancer treatment.
As a global leader in delivering customer-centric solutions of ADCs development, Creative Biolabs has world-class facilities and highly experienced scientist team. We offer integrated services from conjugation development to clinical and commercial ADC GMP batch manufacturing. Now we provide comprehensive bispecific biparatopic ADCs development services targeting different targets including c-MET biomarker.
Introduction of c-MET
c-Met (tyrosine-protein kinase Met or hepatocyte growth factor receptor (HGFR)) is the membrane receptor for hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), which is encoded by the MET gene in humans. It is a single-pass heterodimer composed of an extracellular alpha subunit containing three functional domains (the semaphorin, plexin-semaphorin-integrin, and immunoglobulin-plexin-transcription domains) linked to a transmembrane beta subunit by a disulphide bond. The transmembrane and intracellular subunits contain three portions regulating the kinase activity. HGF is mainly expressed by cells of mesenchymal origin and mainly functions in regulating epithelial growth and morphogenesis. HGF/MET signaling has been found to facilitate tumorigenesis in human cancers. Normally, c-MET is expressed by epithelial cells, which allow these cells to grow invasively to generate new tissues in an embryo or regenerate damaged tissues of an adult. However, cancer stem cells can hijack the normal stem cells to express MET, and thus become the cause of cancer persistence and spread to other sites in the body. It is highly expressed on tumor cells in a wide range of human malignancies, including gastric, lung, breast, ovary, colon, kidney, thyroid, liver carcinomas, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Thus, c-MET is regarded as a drug target currently under clinical investigation.
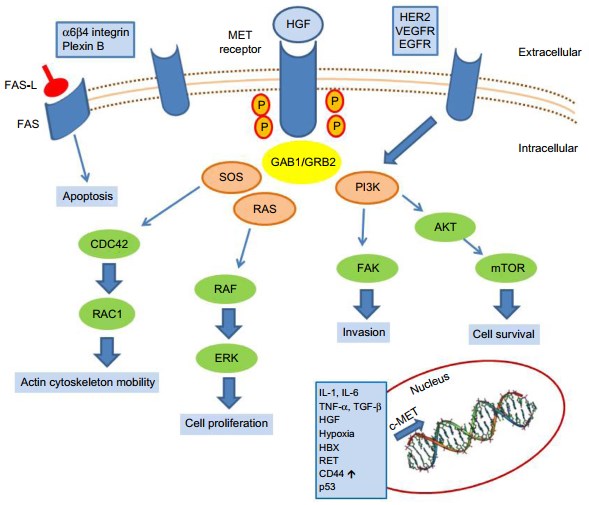 Fig.1 c-MET activation signaling pathways. (Granito, 2015)
Fig.1 c-MET activation signaling pathways. (Granito, 2015)
Biparatopic c-MET-targeted Bispecific Antibody
Bispecific biparatopic antibody can increase internalization and trafficking to the lysosomes by simultaneously targeting two different epitopes on the same antigen with a bispecific entity. It can increase selectivity towards cancer cells and lead to enhanced internalization and trafficking to the lysosome through inducing clustering and cross-linking of receptors. Thus, this approach is now used in the ADC field.
A biparatopic IgG1 antibody targeting two distinct, HGF-competing, non-overlapping epitopes on the extracellular region of the c-MET receptor has been developed. Study results indicated that the antibody can simultaneously target the two epitopes of c-MET recognized by the parental monoclonal antibodies. Besides, the biparatopic antibody present improved MET-inhibitory activity compared with the parental monoclonal antibodies in a tumor xenograft mouse model. Thus, the novel and native-format anti-MET biparatopic antibody shows superior biological activity over the parental monospecific antibodies both in vitro and in vivo.
Current bispecific biparatopic antibody against c-MET showing more potent anti-tumor activity, the bispecific biparatopic ADC equipped with the biparatopic anti-c-MET antibody could be a potential therapeutic strategy for cancer treatment.
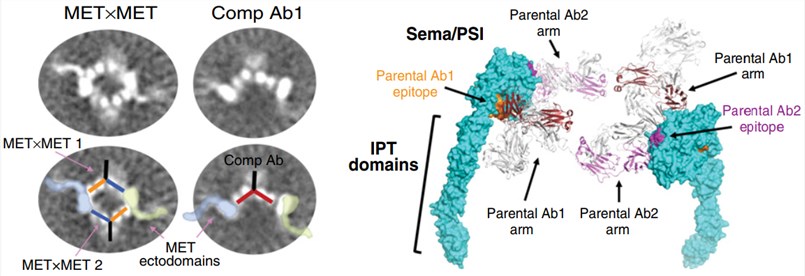 Fig.2 Biparatopic MET antibody forms a 2:2 complex with MET. (DaSilva, 2020)
Fig.2 Biparatopic MET antibody forms a 2:2 complex with MET. (DaSilva, 2020)
What Can We Do for You?
Creative Biolabs has extensive experience in providing services related to the development and characterization of ADCs as well as other bioconjugates. We have worked with various highly potent payloads, as well as plenty of cleavable and non-cleavable linkers and spacers. At present, we provide a bispecific biparatopic ADC construction service targeting the c-MET protein. Our ADC development services include ADC Antibody Screening, DrugLnk™ Custom Synthesis, Antibody Design and Conjugation, ADC in vitro Analysis, and ADC in vivo Analysis.
If you're requiring custom ADCs construction, please contact us for more information.
References
- Granito, A.; et al. c-MET receptor tyrosine kinase as a molecular target in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Journal of hepatocellular carcinoma. 2015, 2, 29.
- DaSilva, J. O.; et al. A Biparatopic Antibody That Modulates MET Trafficking Exhibits Enhanced Efficacy Compared with Parental Antibodies in MET-Driven Tumor Models. Clinical Cancer Research, 26(6). 2020, 1408-1419.
For Research Use Only. NOT FOR CLINICAL USE.

Online Inquiry
Welcome! For price inquiries, please feel free to contact us through the form on the left side. We will get back to you as soon as possible.
