Approaches Utilized for Drug Loading into Exosomes
After years of hard working in exploring application of exosomes, Creative Biolabs has got all the necessary experience and technologies of exosome engineering. The most usually used approaches are loading naïve exosomes isolated from parental cells ex vitro, loading parental cells with a drug, and transfecting/infecting parental cells with DNA encoding therapeutically active compounds. We will respectively give a brief introduction to each of them.
Advantages of Exosomes as Drug Carriers
Exosomes offer distinct advantages that uniquely position them as highly effective drug carriers. Comprised of cellular membranes with multiple adhesive proteins on their surface, exosomes are famous to specialize in cell-cell communications and provide an exclusive approach for the delivery of various therapeutic agents to target cells. In addition, exosomes can be amended through their parental cells to express a targeting moiety on their surface, or supplemented with desired biological activity. Development and validation of exosome-based drug delivery systems have been searched for a long time. Different techniques of exosome isolation, characterization, drug loading, and applications in experimental disease models and clinic are discovered now. Exosome-based drug formulations may be applied to a wide variety of disorders such as cancer, various infectious, cardiovascular, and neurodegenerative disorders. Overall, exosomes combine benefits of both synthetic nanocarriers and cell-mediated drug delivery systems while avoiding their limitations.
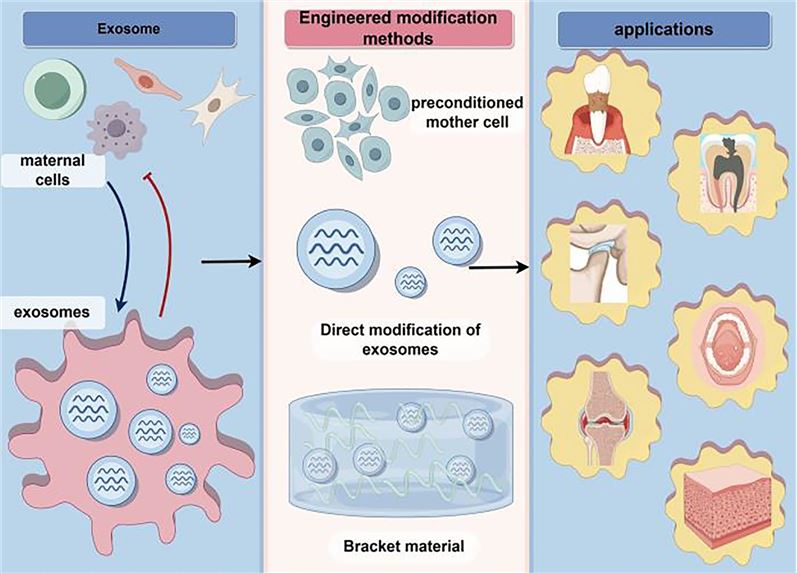 Fig.1 Exosome-based engineering strategies for the diagnosis and treatment of oral and maxillofacial diseases.1,2
Fig.1 Exosome-based engineering strategies for the diagnosis and treatment of oral and maxillofacial diseases.1,2
Approaches Utilized for Drug Loading into Exosomes
-
Loading Naïve Exosomes Isolated from Parental Cells Ex Vitro
In most cases, small molecules are passively loaded into exosomes by co-incubation with exosomes or exosome-like vesicles. Carriers for nucleic acids normally used are electroporation of purified exosomes, and elevated temperature has been reported to improve siRNA loading into exosomes by electroporation. Exosomes can also deliver different proteins. The extensive reformation, reshaping of exosomes upon sonication and extrusion procedures, and treatment with saponin all acheive high loading efficiency of exosomal carriers, which can be applied to other therapeutic and imaging agents. This approach seems to be the most appropriate, as it allows obtaining large amounts of exosomes combined from several isolations, and then loading them with the therapeutic cargo.
-
Loading Parental Cells with a Drug
Another approach is loading parental cells with a drug compound, which will then be released in exosome. If a protein is loaded, catalase should be involved followed by isolation of drug-loaded exosomes from conditioned media. To preserve the therapeutic protein against degradation in host cells and increase loading capacity, catalase is incorporated into a polymer-based nanocontainer before the loading. Importantly, the formulation design of this polymer-based nanocontainer is different from the commonly held approach, where a drug nanoformulation is prepared for systemic administration. The cross-linking of polymer-based nanoparticles with an excess of a non-biodegradable linker ensures low cytotoxicity of the nanoformulation and efficient catalase protection in the parental cells.
-
Transfecting/Infecting Parental Cells with DNA Encoding Therapeutically Active Compounds
Isolation of drug-loaded exosomes secreted from genetically-modified parental cells has been suggested as a third way of manufacturing exosome-based formulations. For example, we have developed a new drug delivery system for different therapeutic proteins, where macrophages are transfected with plasmid DNA (pDNA) encoding therapeutic proteins, catalase, or glial cell-line derived neurotropic factor (GDNF) to treat neurodegenerative disorders. Another interesting approach for the incorporation of adeno-associated virus (AAV) capsids into extracellular vesicles to diminish their immunogenicity and improve gene delivery is also suggested. It is found that during production, a fraction of released AAV vectors are associated with exosomes, termed exosomes (vector-exosomes), which outperforms conventionally purified AAV vectors in transduction efficiency in vitro.
With the help of our advanced technologies and skillful scientists, Creative Biolabs can provide service to separate, expand and identify exosomes. It’s our pleasure to offer various kinds of research and industrial customers. If you have any questions, please feel free to contact us for more information, we will get back to you as soon as possible.
References
-
Ren, J.; et al. Exosome-based engineering strategies for the diagnosis and treatment of oral and maxillofacial diseases. Journal of Nanobiotechnology. 2023, 21(1):501
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Exosome-based engineering strategies for the diagnosis and treatment of oral and maxillofacial diseases.1,2
Fig.1 Exosome-based engineering strategies for the diagnosis and treatment of oral and maxillofacial diseases.1,2









