Bacteria-derived Exosome Research and Applications
Bacteria are a type of single-celled organisms in the field of microbiology, characterized by simple cell structures including cell walls, cell membranes, and ribosomes. Bacteria are widely distributed in various environments on Earth, some of which are beneficial, while others are pathogens that can cause infectious diseases. Numerous studies in recent years have shown that bacteria can also release exosomes. As a specialized provider of exosome research, Creative Biolabs supports research on bacteria-derived exosomes, offering opportunities for a deeper understanding of bacterial biology, the development of new biomedical applications, and the formulation of therapeutic strategies.
The Relationship Between Bacteria and Human Health
There are complex interactions between bacteria and human health:
-
On one hand, the human body harbors numerous normal bacterial communities, such as the gut microbiota, which are crucial for our health. They assist in food digestion, immune system regulation, and more.
-
On the other hand, certain bacteria can cause infections, leading to various infectious diseases such as bacterial pneumonia, urinary tract infections, food poisoning, and more. Additionally, the emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria poses a global health challenge.
Summary of Bacteria-Derived Exosome Research
Both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria can produce exosomes, but they exhibit some differences, resulting in unique characteristics and potential biomedical applications:
Gram-Positive Bacteria-derived Exosome
-
Composition: The cell wall of Gram-positive bacteria is primarily composed of thick layers of peptidoglycan, a major component of the cell envelope. Consequently, exosomes derived from Gram-positive bacteria typically contain these peptidoglycans.
-
Release Mechanism: Exosomes from Gram-positive bacteria are typically released via the secretion systems in the cell wall, such as the Sec system or other secretion mechanisms.
-
Applications: Exosomes from Gram-positive bacteria have been studied as vaccine carriers, drug delivery systems, and subjects of research on antibiotic resistance transmission.
Gram-Negative Bacteria-derived Exosome
-
Composition: The outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria contains lipopolysaccharides (LPS), a major component of their cell envelope. Therefore, exosomes derived from Gram-negative bacteria typically contain LPS.
-
Release Mechanism: Exosomes from Gram-negative bacteria are typically released via secretion systems like outer membrane vesicle formation (OMV formation) or other secretion pathways.
-
Applications: Exosomes from Gram-negative bacteria have also been studied as vaccine carriers, drug delivery systems, and subjects of research on antibiotic resistance transmission. Additionally, due to their rich content of LPS, they may have different impacts on the immune system compared to exosomes from Gram-positive bacteria, potentially having applications in immunotherapy.
Research Directions for Bacteria-Derived Exosomes
-
Information Transfer: Bacteria-derived exosomes can transfer DNA, RNA, proteins, and other biomolecules, facilitating information and gene transfer between bacteria.
-
Antibiotic Resistance: Bacteria-derived exosomes can transfer antibiotic resistance-related genes, promoting the spread of antibiotic resistance.
-
Vaccines and Immunotherapy: Bacteria-derived exosomes are being researched as vaccine carriers for preventing infectious diseases or as tools for immunotherapy.
-
Drug Delivery: Bacteria-derived exosomes can be used as part of drug delivery systems to precisely deliver drugs or therapeutic agents to specific bacterial infection sites or cancer cells.
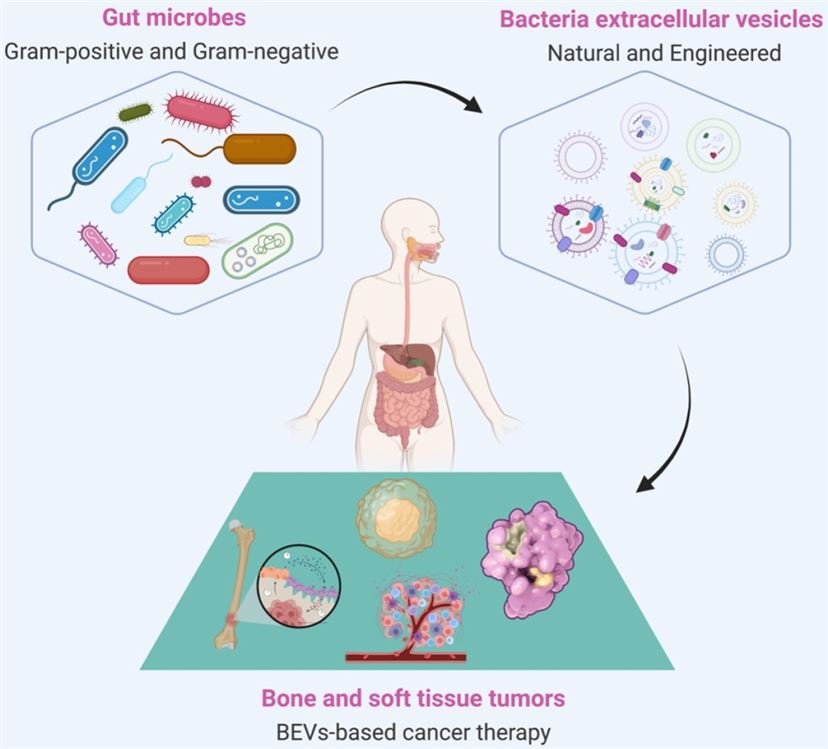 Fig.1 BEVs-based cancer therapy is of great significance.1,2
Fig.1 BEVs-based cancer therapy is of great significance.1,2
Bacteria-Derived Exosome Research Services
Creative Biolabs is committed to providing excellent services for the extraction and development of bacteria-derived exosomes and bacteria-derived exosome extraction kits to meet various research needs. Our professional team has extensive experience in the field of bacterial exosomes and can offer comprehensive support and customized solutions for your projects.
Bacteria-derived Exosome Isolation and Identification
In Vitro Functional Discovery of Bacteria-derived Exosomes
In Vivo Functional Discovery of Bacteria-derived Exosomes
If you are looking for a professional partner in bacteria-derived exosome research, please feel free to contact us to explore the potential applications of bacteria-derived exosomes together.
References
-
Liu, H.; et al. Bacterial extracellular vesicles-based therapeutic strategies for bone and soft tissue tumors therapy. Theranostics. 2022, 12(15):6576-6594.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 BEVs-based cancer therapy is of great significance.1,2
Fig.1 BEVs-based cancer therapy is of great significance.1,2









