Lung-Bone Exosome Communication Research Introduction
Evidence that lung tumors can remotely activate osteoblasts in bone and induce Siglec-F high expression in neutrophils suggests potential communication between lung and bone organs. This is inextricably linked to the mediating role of tissue exosomes therein. Creative Biolabs has accumulated experience in tissue exosome research services to provide valuable insights for exploring the physiological characteristics and mediating role of tissue exosomes in lung-bone remote communication.
Tissue Exosome Extraction and Traceability
The acquisition of high-purity tissue exosomes facilitates the reliability of subsequent omics sequencing and mass spectrometry analysis data. Specifically, tissues are processed into suspensions by protease and DNA enzymes and shaken to fully dissociate the tissues. Then, supernatants should be collected and high-purity tissue-derived exosomes should be obtained by ultracentrifugation and density gradient ultracentrifugation. The expression abundance of the corresponding genes encoding tissue exosome proteins is examined by co-analysis of tissue exosome protein profiling data with public scRNA-seq data to determine the extent to which different cell clusters in the tissues contribute to exosomes.
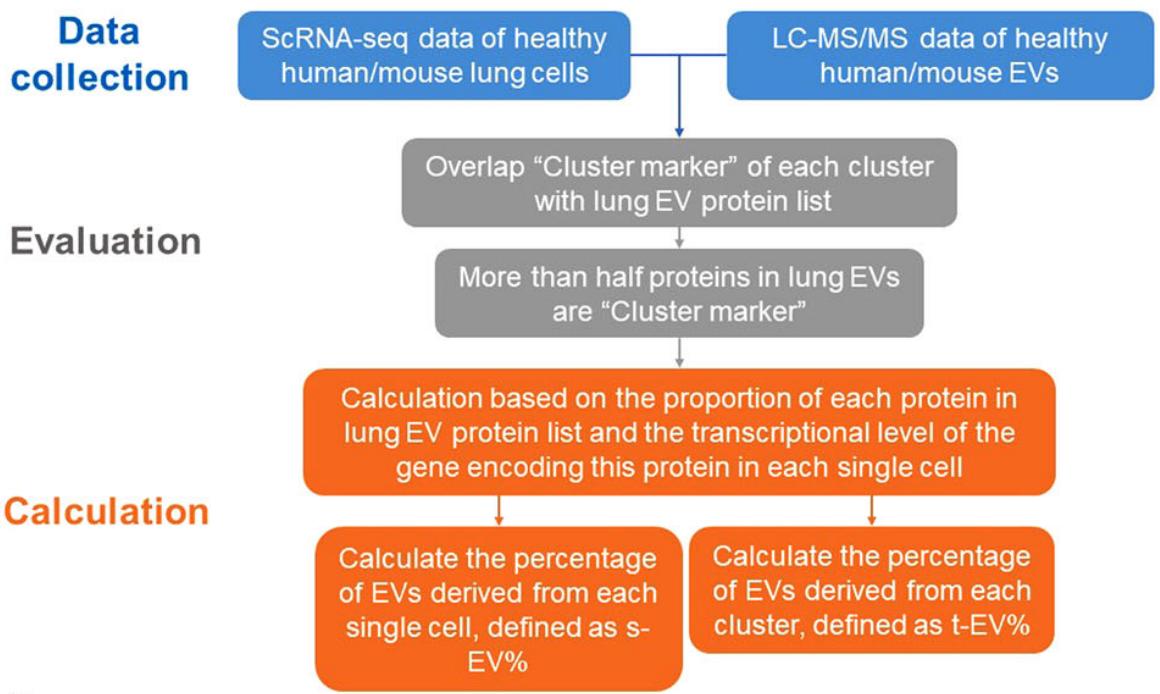 Fig.1 Lung tissue EVs origin assessment. (Liu, 2022)
Fig.1 Lung tissue EVs origin assessment. (Liu, 2022)
Detection of Tissue Exosome Mediating Lung-Bone Communication
Analysis of lung tissue exosome proteomics and single-cell RNA sequencing data have shown that type II alveolar epithelial cells are the predominant source of lung tissue exosomes. It was also demonstrated that lung tissue exosomes accumulate in the bone marrow and enhance neutrophil recruitment under inflammatory conditions. In this case, mice injected with fluorescently labeled lung tissue exosomes were observed to present hyperfluorescent signals in the lower extremities. It was further confirmed by flow cytometry that there was a more fluorescent signal of lung tissue exosomes in the bone marrow and that bone marrow neutrophils were the most represented among the bone marrow cells with the positive signaling, thus indicating that lung tissue exosomes can mediate communication between the lung and bone marrow.
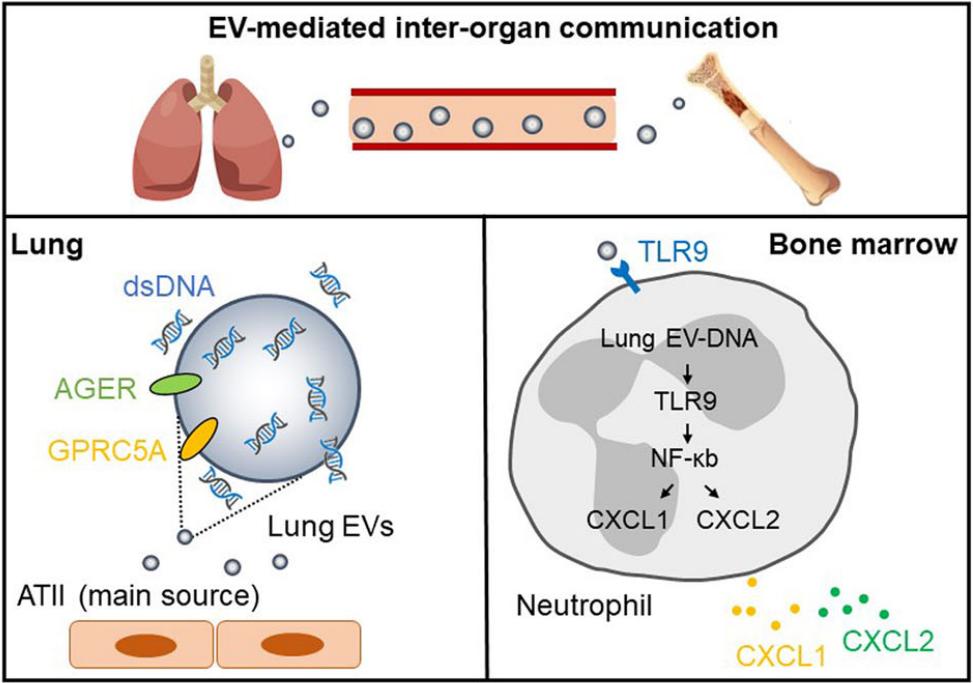 Fig.2 Lung EVs enhance the recruitment of neutrophils. (Liu, 2022)
Fig.2 Lung EVs enhance the recruitment of neutrophils. (Liu, 2022)
Key Functional Molecules for Lung-Bone Exosome Communication
The discovery and validation of functional molecules of tissue exosomes should be rigorous. By setting up different experimental conditions and focus, performing omics sequencing of tissue exosomes, comparing the difference analysis between experimental and control groups, and finally doing relevant validation to screen key functional molecules of tissue exosomes. For example, it has been shown that lung tissue exosome contains dsDNA both internally and externally which acts in enhancing the immune response of the host after bacterial infection. The dsDNA from lung tissue exosomes can be sensed by Toll-like receptors and stimulate the expression of neutrophil chemokines in the bone marrow via DNA-TLR9 signaling, thereby enhancing chemotaxis.
Creative Biolabs has established a high-quality tissue exosome isolation and purification system to provide accurate profiling of exosome molecular composition, underlying a better understanding of exosome-mediated long-distance lung-bone communication. You are welcome to contact us.
Reference
-
Liu, B.; et al. Extracellular vesicles from lung tissue drive bone marrow neutrophil recruitment in inflammation. J Extracell Vesicles. 2022, 11(5): e12223.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Lung tissue EVs origin assessment. (Liu, 2022)
Fig.1 Lung tissue EVs origin assessment. (Liu, 2022)
 Fig.2 Lung EVs enhance the recruitment of neutrophils. (Liu, 2022)
Fig.2 Lung EVs enhance the recruitment of neutrophils. (Liu, 2022)









