Exosomes for Plastic and Cosmetic
Exosomes are a subpopulation of extracellular vesicles ranging in size from 40 nm to 200 nm that contain proteins, nucleic acids and lipids specific to the donor cell type. Adipose stem cells have the potential for multidirectional differentiation, and the study and application of the specific bioactivities of adipose stem cell-derived exosomes holds the promise of providing insights and support for the development of new therapeutic strategies targeting tissue regeneration in plastic and cosmetic surgery. Creative Biolabs can provide high purity customized exosome products, functional validation of exosomes and research services designed to help customers conduct studies on the functional potential of exosomes in plastic and cosmetic surgery.
Biological Properties of Exosomes
Exosomes are found in many body fluids such as blood, urine, saliva, cerebrospinal fluid, lymph, bile and breast milk and serve as key mediators of cellular communication and material delivery, carrying specific proteins (tetramembrane proteins, cytoskeletal proteins, enzymes), nucleic acids (DNA, RNA) and lipid functional molecules that can potentially regulate recipient cell proliferation, migration, angiogenesis, inflammation and immune response, among other specific activities.
Adipose stem cells (ASCs) are one of the important stem cell types isolated from the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of adipose tissue, the other two being mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), and pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). Adipose tissue is mainly composed of adipocytes that store fat and SVF, which is one of the cell sources that determine the multidirectional differentiation potential of adipose tissue. A heterogeneous cell population consisting of endothelial cells, ASCs, tissue-type macrophages and non-characteristic stromal erythrocytes can be easily isolated by enzymatic digestion. Therefore, ASCs are not only easy to isolate, but also have the potential to differentiate into multiple lines of epithelial cells, osteoblasts, chondrocytes, myocytes, and neuronal cells due to their low differentiation and high plasticity, and are capable of high-frequency proliferation and self-renewal. The platelet-derived growth factor AA (PDGF-AA) secreted by ASCs can activate the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway to promote collagen synthesis in the human dermis, which has potential for cosmetic anti-aging skin applications. Similar to the properties of donor cells, exosomes derived from ASCs via the paracrine pathway (ASCs-EXO) also carry multiple trophic factors that activate the paracrine signaling pathway and exert pro-survival effects on target cells and tissues. Furthermore, thanks to the lack of MHC-II in ASCs, ASCs-EXO induces pro-lymphangiogenic activity and higher levels of anti-inflammatory macrophages and has emerged as a prominent candidate for a tissue engineering product.
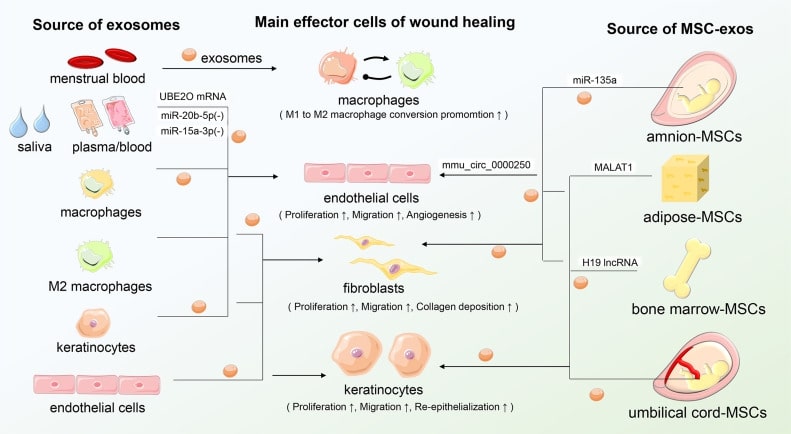 Fig.1 Characterization of exosomes derived from multiple sources. (Xiong, 2021)
Fig.1 Characterization of exosomes derived from multiple sources. (Xiong, 2021)
Exosomes for Plastic and Cosmetic
Several research methods and techniques such as biomaterials, nanotechnology, microsurgery, composite tissue allografts and cell biology have been widely used in plastic and cosmetic surgery, so that the repair of congenital or acquired defects, both morphological and functional, is a therapeutic procedure closely related to tissue regeneration. Tissue regeneration is primarily a repair activity of defective tissue involving progenitor cells and immune cells, in addition to the regulatory role of growth factors, inflammatory cytokines and proteases. The use of autologous adipose tissue in cosmetic surgery for skin care, wound repair and contouring have been explored extensively, however, given the individual variability and efficacy instability of adipose tissue, there is still a lack of reliable and accepted mechanisms for its efficacy and safety. ASCs-EXO, derived from adipose tissue ASCs, is able to maintain a high degree of cargo stability in the circulation and can mimic the pro-regenerative effect of ASCs for cell-free therapy, avoiding cell therapy defects such as immune rejection potency and genetic instability. In addition, ASCs-EXO can be sterile filtered and frozen during preparation, storage and delivery without the need for cryopreservation and maintenance of cell viability, and has shown therapeutic potential and safety in many clinical applications related to tissue transplantation and reconstruction. For example, researchers found that ASCs-EXO may play an active role in inhibiting HaCaT cell apoptosis and alleviating skin tissue damage by delivering lncRNA MALAT1 targeting miR-124 and activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Protein array analysis of a fat graft nude mouse model showed that ASCs-EXO induced high levels of expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein MCP2/4, VEGF and its receptor VEGF-R2/3 in transplanted tissues by regulating VEGF/VEGF-R signaling and promoted peritissue neovascularization. Thus, the above results show that the study of stem cell-derived exosomes can provide new insights and understanding for the exploration of therapeutic strategies in the field of plastic and cosmetic surgery.
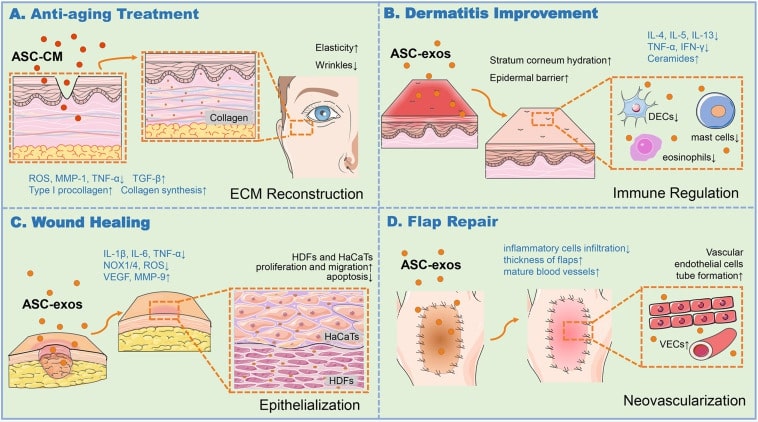 Fig.2 ASCs-EXO function in various skin associated applications. (Xiong, 2020)
Fig.2 ASCs-EXO function in various skin associated applications. (Xiong, 2020)
Exosomes are ideal biomaterials obtained from stem cell sources, containing a wide range of stem cell-like surface markers and active components, with positive and efficient bioactivities in tissue transplantation, repair, regeneration and immunosuppression, promising to be attractive therapeutic candidates. Creative Biolabs has successfully provided a variety of customized services including Exosome Isolation, Exosome Purification, Exosome Characterization, In Vitro and In Vivo Function of Exosomes, and would be delighted to assist you with your plastic and cosmetic related exosome studies. Please contact us and let us know your needs.
References
-
Xiong, M.; et al. The novel mechanisms and applications of exosomes in dermatology and cutaneous medical aesthetics. Pharmacol Res. 2021, 166: 105490.
-
Xiong, M.; et al. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells: the emerging roles and applications in tissue regeneration of plastic and cosmetic Surgery. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020, 8: 574223.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Characterization of exosomes derived from multiple sources. (Xiong, 2021)
Fig.1 Characterization of exosomes derived from multiple sources. (Xiong, 2021)
 Fig.2 ASCs-EXO function in various skin associated applications. (Xiong, 2020)
Fig.2 ASCs-EXO function in various skin associated applications. (Xiong, 2020)









