Therapeutic Exosomes for Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurological disorder characterized by a high risk of disease associated with advanced age. In the global trend of aging, timely treatment of PD is of great public health importance. Creative Biolabs provides customized services for PD-related exosome extraction, purification and functional evaluation to help clients better decipher PD pathology and develop therapeutic strategies.
Pathogenesis of PD
The pathogenesis of PD is mainly the abnormal neurotransmitter signaling of the downstream substantia nigra (SN)-striatal pathway caused by massive loss of dopaminergic neurons in the SN lesion area. As a result, patients clinically present with motor symptoms such as bradykinesia, postural instability and gait freezing, along with non-motor symptoms such as cognitive impairment and autonomic dysfunction. Although the pathogenesis of PD is still not fully understood due to the combination of genetic and environmental factors, Lewy's pathology, which consists of mutations and excessive aggregation of α-synuclein (α-syn), is currently recognized as the pathological feature of PD. Nineteen pathogenic genes such as α-Syn encoding gene (SNCA), leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2), vacuolar protein sorting 35 (VPS35) and environmental factors such as MPTP, paraquat, rotenone, iron and manganese have been shown to increase the risk of developing PD. The pathogenic process of PD essentially involves neuronal cell death in brain regions induced by responses such as oxidative stress, inflammatory damage, dysregulation of autophagy and immune dysfunction.
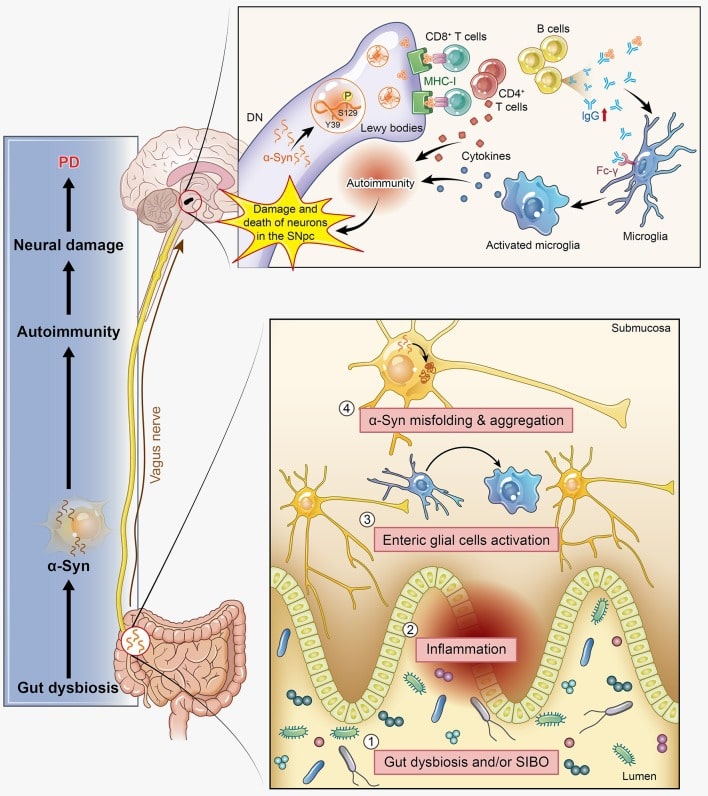 Fig.1 α-Syn participates in autoimmunity and is involved in the pathological progression of PD. (Jiang, 2018)
Fig.1 α-Syn participates in autoimmunity and is involved in the pathological progression of PD. (Jiang, 2018)
Challenges of PD Treatment
Current PD pharmacological approaches based on supplementation with dopamine precursors and dopamine agonists have shown significant weakness, challenged mainly by low delivery rates across the blood-brain barrier and the emergence of drug resistance. As disruptions in neurological signaling and movement disorders worsen, there is a concomitant need for increased doses of dopamine analogs. At the same time, a combination of medication for specific nonmotor symptoms such as depression, fatigue, dementia, and psychiatric abnormalities has triggered the emergence of drug tolerance and adverse reactions to toxic side effects in patients. In addition, the long-term efficacy of surgical treatments such as deep brain stimulation and nucleus accumbens destruction is unpredictable, and the downside risks of focal area destruction are difficult to control. In conclusion, PD as a neurodegenerative disease with progressive enlargement of the lesion area, the existing treatments cannot eradicate PD, but only delay the deterioration of PD.
Therapeutic Exosomes for PD
Exosomes as delivery vehicles not only improve drug stability in long circulation, but also overcome difficulties such as immune response, blood-brain barrier obstruction and random distribution in non-focal areas, showing good biocompatibility, drug therapeutic activity and target enrichment. As one of the promising therapeutic strategies for PD, preclinical experiments have shown the therapeutic potential of exosomes after successful loading of mRNAs, siRNAs, enzymes and multiple chemotherapeutic agents. For example, antioxidants such as peroxidase and its mRNA, glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) loaded exosomes can reduce the levels of pro-inflammatory factors in nigrostriatal neurons and microglia, alleviating neurotoxicity and neuroinflammatory responses in PD mice. In addition, siRNAs that interfere with α-syn expression and autophagy modulators that reduce toxic α-syn fibers have also shown efficient neuroprotective effects in preclinical studies when used in combination with exosome delivery platforms, and these exosome-based drug systems are less toxic than their free forms.
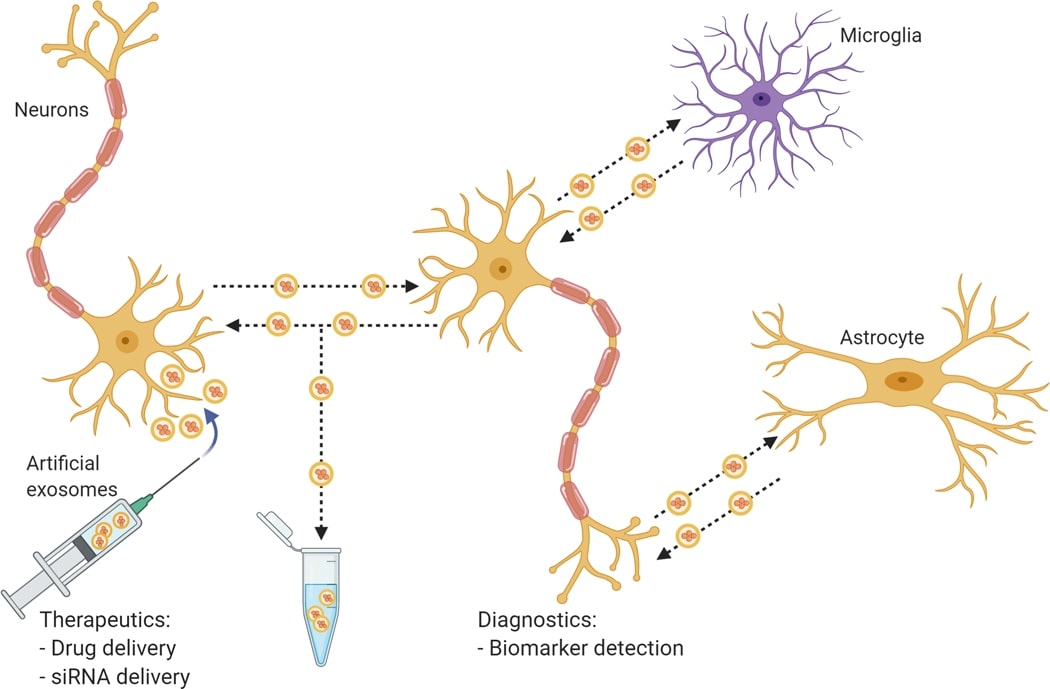 Fig.3 Potential roles of exosomes in neuropathology and clinical applications. (Pinnell, 2021)
Fig.3 Potential roles of exosomes in neuropathology and clinical applications. (Pinnell, 2021)
Future studies of exosomal therapeutics for PD are highly desirable to develop a standard procedure to ensure high loading efficiency, targeting and purity of exosomes. Creative Biolabs has accumulated experience in research services for a variety of neurological disease-related exosomes, including exosome extraction, identification, biomarker and drug development. We are committed to continuously providing better PD-related exosome research services. Please feel free to contact us.
References
-
Jiang, T.; et al. The challenge of the pathogenesis of PD: is autoimmunity the culprit? Front Immunol. 2018, 9: 2047.
-
Pinnell, J.R.; et al. Exosomes in Parkinson disease. J Neurochem. 2021, 157(3): 413-428.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 α-Syn participates in autoimmunity and is involved in the pathological progression of PD. (Jiang, 2018)
Fig.1 α-Syn participates in autoimmunity and is involved in the pathological progression of PD. (Jiang, 2018)
 Fig.3 Potential roles of exosomes in neuropathology and clinical applications. (Pinnell, 2021)
Fig.3 Potential roles of exosomes in neuropathology and clinical applications. (Pinnell, 2021)









