Therapeutic Exosomes for Neurological Diseases
Neurological Diseases (NDs) are one of the leading causes of death and disability worldwide. Drug delivery to the brain has been a hurdle in the treatment of NDs due to the limitations of the Blood–Brain Barrier (BBB). Numerous studies have shown that exosomes can be used as drug delivery vehicles to treat NDs through the BBB. Creative Biolabs is the world's leading exosome service provider, which can provide customers with the best one-stop service.
Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB)
NDs are organic diseases of the peripheral nervous system. Symptoms of NDs generally include pain, numbness, weakness, and paralysis. The BBB is a defensive barrier composed of brain capillary endothelial cells, basement membranes, pericytes, and astrocyte ends. The BBB separates the brain from the peripheral circulation containing inflammatory mediators and immune cells to defend against foreign pathogens in the blood and maintain brain homeostasis. However, the properties of the BBB prevent almost all drugs from entering the brain. Excitingly, studies have found that the use of exosomes can safely and effectively deliver drugs to the brain to treat NDs.
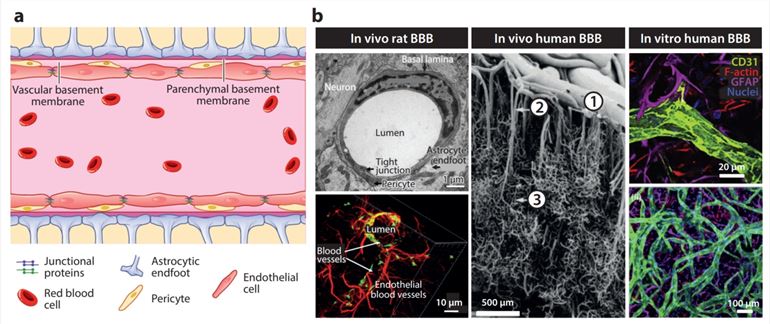 Fig.1 Schematic representation of the BBB.1,2
Fig.1 Schematic representation of the BBB.1,2
Therapeutic Exosomes Capable of Penetrating the BBB
Although natural exosomes can be delivered to the brain through their surface ligands. However, studies have found that intravenously injected exosomes are mainly distributed in the liver or spleen, and the distribution in the brain is relatively low. Therefore, exosomes need to be modified to enhance their ability to target brain tissue. At present, a large number of studies have been using exosomal signal peptides to construct brain-targeting proteins on the surface of exosomes. For example, lysosome‑associated membrane glycoprotein 2b (Lamp2b) is an exosomal membrane protein with a signal peptide. A plasmid expressing the rabies virus glycoprotein (RVG)-Lamp2b fusion protein can be formed by modifying the plasmid expressing Lamp2b and fusing it with the neuron-specific RVG gene. After the RVG-Lamp2b plasmid is transferred into the donor cells, the exosomes released by the donor cells can be loaded with nucleic acids or drugs. Furthermore, the engineered exosomes can be targeted to brain tissue to release drugs to treat NDs by binding to α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors.
In addition, intranasal administration (IA) is a non-invasive mode of drug delivery that bypasses the BBB. IA delivers drugs directly to the brain via the olfactory or trigeminal pathways. Many studies have found that engineered exosomes can reach brain nerves through IA and significantly improve NDs. A nasal spray used to treat epilepsy has been approved by the FDA (Food and Drug Administration). The current research on the use of exosomes as drug delivery vehicles for the treatment of NDs mainly focuses on the following aspects.
Creative Biolabs has been upgrading its talent pool and equipment. We can provide customers with the most comprehensive technical services related to exosome drugs. If you have any idea about NDs-related exosome drug research, please feel free to contact us.
References
-
Hajal, C.; et al. Biology and Models of the Blood-Brain Barrier. Annual Review Biomedical Engineering. 2021, 23:359-384.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Schematic representation of the BBB.1,2
Fig.1 Schematic representation of the BBB.1,2









