Food-derived Exosome-based Delivery Vehicle Feature Summary
Food-derived exosomes, mainly milk-derived exosomes and edible plant-derived exosomes, benefit from a special vesicular structure and rich compositions which allow them to tolerate the specific environment of the gastrointestinal tract for convenient oral delivery routes in disease interventions and therapies, especially in digestive diseases, acting as stable drug carriers. Creative Biolabs supports research projects and applications of food-derived exosomes through innovative technology platforms and the most advanced insights into exosomes that can provide exosome isolation, profiling, and functional investigation services related to food-derived exosomes.
Milk-Derived Exosomes as Drug Vehicles Summary
-
Function: As an abundant component of milk, milk-derived exosomes have gained attention and research for their promise in translational medicine and nutrition as drug and therapeutic nucleic acid carriers. Milk exosomes mediate communication processes and immune responses between mammary cells and are capable of transferring their substances to recipient cells. Proteomic analysis of milk exosomes revealed that milk exosomes influence the mechanism of immune-related molecule formation in milk, which is valuable for applying exosomal immune-related functions to the immune regulation of diseases. The lipid membrane of milk exosomes contributes to protecting their RNAs from degradation by ribonucleases and digestive enzymes, thus protecting the vital function of milk exosomes in loading RNAs and drugs as a carrier platform. In in vitro simulated gastric acid experiments, human lacto-exosomes can be protected from digestion in the GI tract and taken up by human intestinal cells. Significantly, as compared to other exosomes, milk exosomes can transport their contents to the progeny or even other species, thus enabling interspecies communication.
-
Preparation: Isolation of milk-derived exosomes is easily and inexpensively obtained from milk, with the removal of interference from casein, the most abundant protein in milk, contributing to greater subsequent purification. It is mainly achieved by pretreatment of milk with acids such as sodium citrate or EDTA to precipitate and remove casein, followed by the preparation of milk-derived exosomes by centrifugation or affinity capture, according to different experimental needs.
-
Advantages: Since absorption from the gastrointestinal tract occurs through the neonatal Fc receptor, milk exosomes are potentially scalable as drug carriers, showing the potential to enhance the bioavailability of orally administered drugs by crossing the human intestinal epithelial barrier with intact particles. Thus, milk-derived exosomes offer superior carrier performance compared to cell-derived exosomes for both mass production and oral drug delivery.
Edible Plant-Derived Exosome as Drug Vehicles Properties
Another source of food-derived exosomes is a wide variety of edible plants, including ginger, carrots, grapes, strawberries, and herbal plants. Exosomes of edible plant origin have unique morphological and compositional characteristics of natural nanocarriers. They are rich in bioactive lipids, proteins, RNA, and other pharmacologically active molecules, which play anti-inflammatory, antiviral, anti-fibrotic, and anti-tumor properties and are involved in the defense response to pathogenic attacks. For example, ginger-derived exosomes can be taken up by intestinal bacteria and readily absorbed by Lactobacillus. The miRNAs contained can directly regulate the gene expression and metabolites of specific bacteria, thus affecting the flora composition and host physiology, enhancing the host intestinal barrier function to alleviate colitis in mice, as well as preventing ethanol-induced liver damage. The exosomes isolated from crushed grapes, after consumed by mice, evaded hydrolysis from various digestive enzymes and eventually reached the intestine and accelerated intestinal epithelial proliferation to promote colitis recovery. Herbal exosomes serve as a combination therapy for precision drugs and provide an effective oral route for the delivery of pharmacologically active molecules. Honeysuckle-derived exosomes with active components targeting influenza viruses are highly stable in tonics, with continuous drinking or gavage administration inhibiting viral replication in peripheral blood and lung tissue of mice, providing a new strategy for the effective mitigation of viral infections.
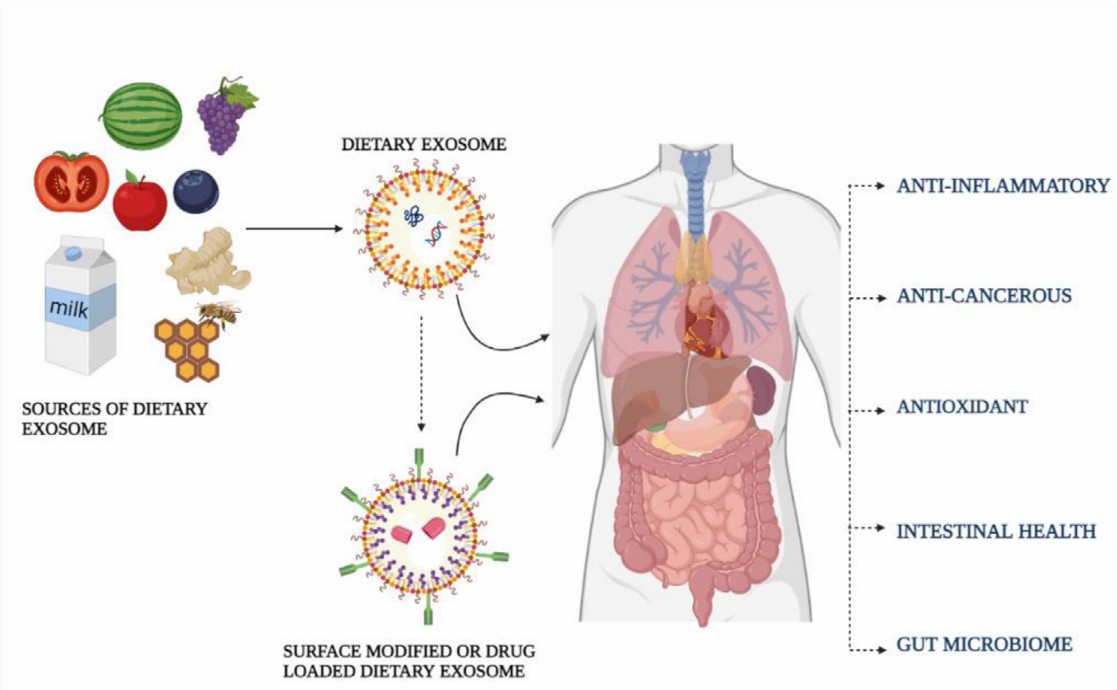 Fig.1 An overview of health benefits by consumption of dietary exosomes. (Anusha & Priya, 2022)
Fig.1 An overview of health benefits by consumption of dietary exosomes. (Anusha & Priya, 2022)
The physicochemical properties and biological functions of exosomes depend mainly on their biochemical composition and structure, which not only mediate intercellular communication but also participate in regulating various physiological processes such as angiogenesis, cell survival, inflammation, and immune response. Notably, milk-derived exosomes and edible plant-derived exosomes have the advantages of scalable preparation and low cost. They are non-toxic and convenient for oral administration, exploiting their potential for medical and biotechnological applications as carriers for specific drug delivery. Creative Biolabs has accumulated several years of professional insight and project experience in exosome research and applications, offering research services related to the preparation and application of food-derived exosomes. Please contact us with your interest.
Reference
-
Anusha, R.; Priya, S. Dietary exosome-like nanoparticles: an updated review on their pharmacological and drug delivery applications. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2022, 66(14): e2200142.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 An overview of health benefits by consumption of dietary exosomes. (Anusha & Priya, 2022)
Fig.1 An overview of health benefits by consumption of dietary exosomes. (Anusha & Priya, 2022)









