Exosome Mimetic-based Delivery Vehicle Feature Summary
There are still great challenges in the application of exosomes as drug delivery carriers, such as low yield, complex contents, and poor homogeneity. Currently, the solution to these deficiencies is the development and preparation of exosome mimics. Creative Biolabs summarizes research advances related to the preparation and application of exosome mimics, including cellular extrusions and exosome-liposome hybrids, and provides research services related to exosome manufacturing and profiling.
Cell Extrusions
Cell extrusions retain the natural properties of cells and have a structure and characteristics similar to exosomes. Extrusions are shaped by collecting whole cells or cell membranes and passing them sequentially through filters with progressively decreasing pore size until a particle size of 100-200 nm is observed. There is a 100-fold increase in the yield of cellular extrudates compared to the same amount of production of cell-derived natural exosomes in which exosomal marker proteins such as CD63 and TSG101 are also present. Cellular extrusions are primarily derived from a mixture of the plasma membrane and intracellular organelles, while exosomes are released by early multivesicular bodies in the endosomal pathway. This distinction makes cellular extrusions involving fewer lipid species such as sphingolipids, cholesterol, and phospholipid phosphatidylserine than in exosomes. It still deserves deeper investigation into whether this change in membrane composition affects the function and pharmacokinetics of nanovesicles. More excellently, the exosome mimics produced using endothelial cells as raw material maintain the plasma membrane protein topology exhibiting promising targeting ability to tumor sites. Therefore, these cell extrusions as drug carriers can successfully transfer chemotherapeutic drugs to tumor sites with less toxic side effects. In addition, although hand extrusion of cells with an extruder enhances production, it is necessary to better control the homogeneous quality and expand production during the manufacturing process. With the help of a centrifuge acting in centrifuge tubes containing membranes with different pore sizes, the extrusion force can be made controllable by centrifugal force, thus ensuring that centrifugation breaks down the cells into homogeneous exosome mimics. Other promising methods under development for the preparation of cell-based exosome mimics include ultrasonication, nitrogen cavitation, and stimulated cytosolic membrane vacuolization.
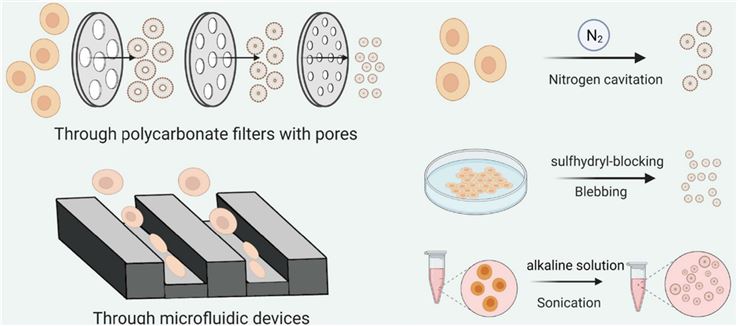 Fig.1 Top‑down strategies for generating artificial exosomes by manipulating cells. (Li, 2021)
Fig.1 Top‑down strategies for generating artificial exosomes by manipulating cells. (Li, 2021)
Exosome-Liposome Hybrids
Exosome-liposome hybrids are processed on the basis of liposomes, which can be prepared not only by freeze-thaw cycling, incubation, and co-extrusion to form hybrids directly with exosomes but also by additionally coupling proteins, chemical moieties and lipids during the lipid bilayer construction. Biohybrid assembly techniques allow for managing the biochemical and biophysical phenotype of exosome mimics by precisely and quantitatively controlling their composition. Also, the use of low complexity and well-characterized components greatly increases the pharmacological acceptability and stability of the exosome-liposome system, having lower toxicity compared to bare liposomes. The hybridization of natural exosomes with liposomes maximizes the loading capacity of large plasmids and drug encapsulation efficiency by increasing the number of particles. The application potential of such exosome-multifunctional liposome hybrids is expandable, such as responsiveness to pH, light, and heat, improved cycling and tumor enrichment.
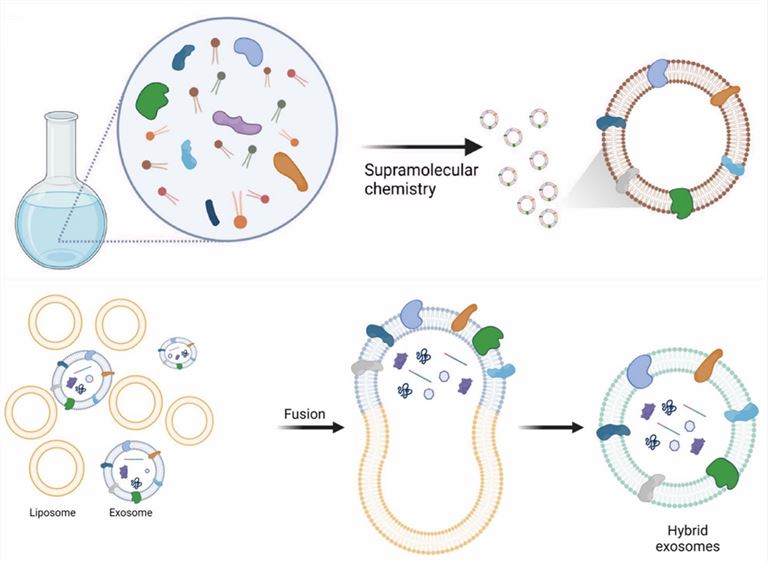 Fig.2 Bottom‑up strategies for generating fully artificial exosomes and biohybrid strategies for generating hybrid exosomes by fusing exosomes with liposomes. (Li, 2021)
Fig.2 Bottom‑up strategies for generating fully artificial exosomes and biohybrid strategies for generating hybrid exosomes by fusing exosomes with liposomes. (Li, 2021)
Considering that it is likely that not all exosome components are necessary for their proper function, the development of exosome mimics is a solution for the limited production of exosomes, showing improved drug delivery effectiveness and therapeutic potential similar to that of exosomes. Creative Biolabs' most specialized exosome scientific team is capable of providing high-quality research services for exosome isolation and profiling. Please contact us with your interest.
Reference
-
Li, Y.J.; et al. Artificial exosomes for translational nanomedicine. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021, 19(1): 242.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Top‑down strategies for generating artificial exosomes by manipulating cells. (Li, 2021)
Fig.1 Top‑down strategies for generating artificial exosomes by manipulating cells. (Li, 2021)
 Fig.2 Bottom‑up strategies for generating fully artificial exosomes and biohybrid strategies for generating hybrid exosomes by fusing exosomes with liposomes. (Li, 2021)
Fig.2 Bottom‑up strategies for generating fully artificial exosomes and biohybrid strategies for generating hybrid exosomes by fusing exosomes with liposomes. (Li, 2021)









