Trypanosoma cruzi-derived Exosome Research and Application
Trypanosoma cruzi is the protozoan parasite that causes Chagas disease, and the exosomes it releases play a crucial role in the interaction between the pathogen and the host, including enhancing parasite invasion, immunomodulation, and disease progression. Creative Biolabs offers exosome technology services and products, aiming to provide valuable support and advanced solutions for the research of these exosomes.
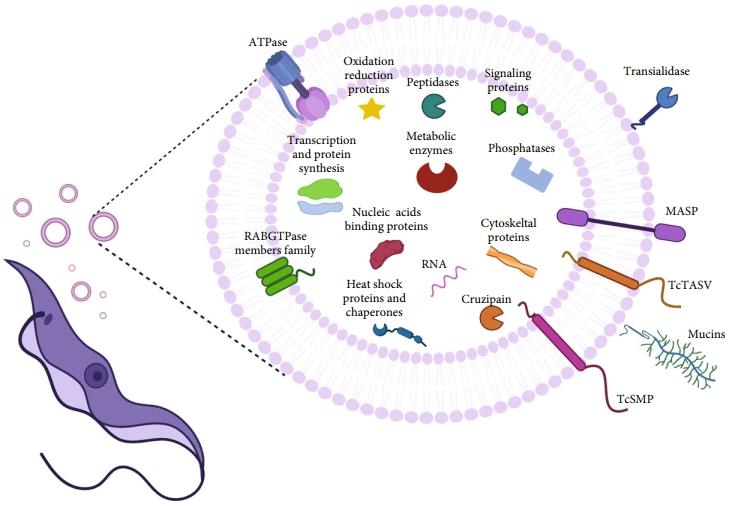 Fig.1 Schematic illustration summarizing the molecules identified in extracellular vesicles secreted by Trypanosoma cruzi trypomastigotes.1,2
Fig.1 Schematic illustration summarizing the molecules identified in extracellular vesicles secreted by Trypanosoma cruzi trypomastigotes.1,2
Key Roles of Trypanosoma cruzi-derived Exosomes
-
Enhancing Parasitic Capacity and Invasiveness
Trypanosoma cruzi-derived exosomes can increase the cardiac parasite load and enhance the infection rate of host cells. This is achieved by promoting the adherence and invasion of the parasite into host cells. In studies, Trypanosoma cruzi exposed to normal human serum can selectively form phenotypes with higher resistance to the complement system, which are more dominant in entering host cells and immune evasion.2
-
Immunosystem Regulation and Escape
By forming immune complexes with host immunoglobulin G, the antigens contained in Trypanosoma cruzi-derived exosomes can target host cells and modulate the host's immune response. These complexes may play different roles in the immune response during the acute and chronic phases.3
-
Affecting the Physiological Function of Host Cells
Trypanosoma cruzi-derived exosomes can induce changes in the permeability of host cell membranes, affect intracellular calcium mobilization, disrupt the actin cytoskeleton, thereby aiding the invasion of Trypanosoma cruzi and increasing the parasitic rate of host cells. Moreover, these exosomes can cause host cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1 phase, preventing the DNA synthesis required for cell division.4
-
Regulating Cell Signaling and Cell Death
Trypanosoma cruzi-derived exosomes affect intracellular signaling pathways, such as downregulating the expression of molecules in the Rho-GTPases pathway, which are crucial for cell movement and morphological changes.5
Potential Summary of Trypanosoma cruzi-derived Exosomes
Based on the findings above, we have reason to believe that the exosomes released by Trypanosoma cruzi have great application prospects. These exosomes not only play a key role in the interaction between the pathogen and the host but also show unique importance in regulating immune responses, promoting virus invasion, and as potential therapeutic efficacy biomarkers. More importantly, their potential application in future vaccine development and therapeutic strategies may pave new ways to combat Chagas disease.
-
Biomarkers and Therapeutic Efficacy Monitoring: In terms of therapeutic response and disease outcome indication, the development of Trypanosoma cruzi-derived exosomes as biomarkers is promising. In particular, analyzing the concentration and composition of exosomes in patient fluids can provide valuable information for the diagnosis and prognosis of Chagas disease. Additionally, specific proteins in these exosomes, such as MASP and TS family members, as well as TcTASV-C, are being studied as potential biomarkers for monitoring the efficacy of Chagas disease treatment.
-
Disease Prevention and Vaccine Development: Vaccination with Trypanosoma cruzi-derived exosomes has shown a certain degree of protection against Chagas disease in animal models, although further research is needed to identify the specific molecules responsible for the protective effect. Therefore, due to their role in host cell invasion, Trypanosoma cruzi-derived exosomes have the potential to be developed as new antigens in Chagas disease vaccine development, and they may become a favorable target in vaccine research.
Creative Biolabs is fully committed to exploring the potential of exosome technology in collaboration with clients. We have carefully constructed a research and development platform focused on microorganism-derived exosomes. No matter what technical challenges you face in the field of exosome research, we look forward to discussing with you and exploring solutions together. Please feel free to contact us.
Microorganism-derived Exosome Isolation and Identification
In Vitro Functional Discovery of Microorganism-derived Exosomes
In Vivo Functional Discovery of Microorganism-derived Exosomes
References
-
Cortes-Serra, N.; et al. Extracellular vesicles in Trypanosoma cruzi infection: immunomodulatory effects and future perspectives as potential control tools against chagas disease. Journal of Immunology Research. 2022, 2022:5230603.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Schematic illustration summarizing the molecules identified in extracellular vesicles secreted by Trypanosoma cruzi trypomastigotes.1,2
Fig.1 Schematic illustration summarizing the molecules identified in extracellular vesicles secreted by Trypanosoma cruzi trypomastigotes.1,2









