NAA Services for Anti-ATP Synthase β Chain
With Ph.D. level scientists and decades of years’ experience, Creative Biolabs has successfully established promising NAA platforms for production and application. At present, we have the ability and pleased to offer a series of anti-ATP synthase β chain biomarker services for diseases diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring based on our professional teams and abundant experience.
Background of Anti-ATP Synthase β Chain Antibody
ATP synthase (ATPases) is a membrane-bound enzyme localized in the inner membrane that catalyzes the synthesis of the energy storage molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which commonly provides energy to drive many processes in living cells. ATPases β chain is one of the subunits of soluble portion known as the F1 ATPase complex. Circulating IgA and IgM autoantibodies against the ATPases β chain have been identified and described as pathogenic roles in human diseases like coeliac disease, Alzheimer's disease, nephrotic syndrome, etc. Anti-ATP synthase β chain autoantibodies display the diagnostic value as biomarkers for clinical applications.
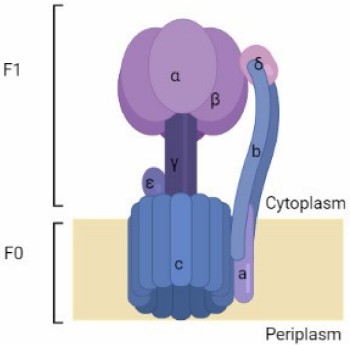 Fig.1 ATP synthase complex structure.1
Fig.1 ATP synthase complex structure.1
The Role of Anti-ATP Synthase β Chain Antibody in Celiac disease
Celiac disease is a type of autoimmune disease that primarily affects the small intestine. It is actually a problem with foods containing gluten, which is a protein triggering an abnormal immune response. This abnormity subsequently leads to inside small intestine damage and nutritional absorption disorders. Researches have been performed that several NAAs involve the immune response of the celiac disease. ATP synthase β chain has been proposed as an additional coeliac autoantigen and Anti-ATP synthase β chain of the IgA class have been identified as biomarkers with possible diagnostic utility in celiac disease patients.
The Role of Anti-ATP Synthase β Chain Antibody in Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that gradually destroys memory and other important mental functions. Increasing reports suggest that immune system and autoantibodies against a diversity of molecules have been associated with the AD. Moreover, mitochondrial dysfunction has been considered as a potential factor involved in the pathogenic process of the AD, and anti-ATP synthase β subunit exerted a pathogenetic role during the AD process, which suggested that it was a novel autoantigen as well as might be a new biomarker for the AD.
The Role of Anti-ATP Synthase β Chain Antibody in Myocarditis
Myocarditis is an inflammation and damage of the heart muscle or myocardium characterized by symptoms as an abnormal heartbeat, breath, and chest pain. Myocarditis commonly results from viral infections, bacterial infections, autoimmune disorders, and toxins. Several circulating autoantibodies induced by infections have been demonstrated to play a crucial role in the progression and induction of myocarditis. Moreover, mitochondrial function is remarkably significant to energy homeostasis, metabolism, signaling, and apoptosis in human cells particularly cardiac cell due to that cardiac contractility is strongly dependent on the mitochondria. As a key determinant of mitochondrial function, ATP synthase and anti-ATP synthase may play a predictive action as potential markers in myocarditis.
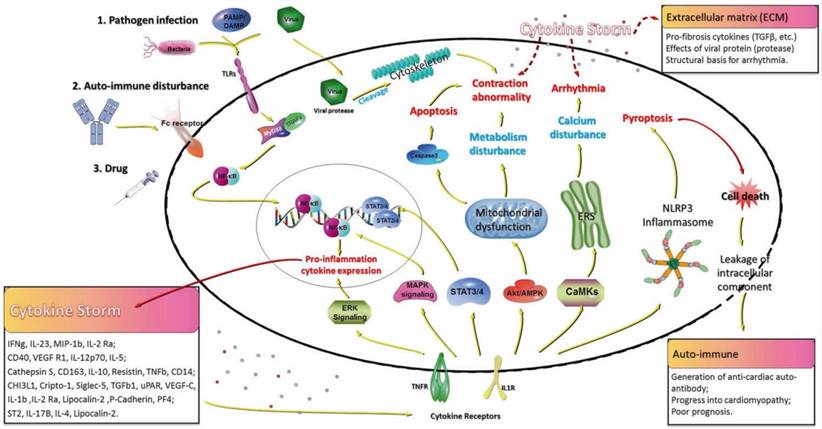 Fig.2 The role of auto-immune in fulminant myocarditis.2
Fig.2 The role of auto-immune in fulminant myocarditis.2
The Role of Anti-ATP Synthase β Chain Antibody in NAA Associated Thalassemia
Thalassemia is a genetic blood disorder characterized by the abnormal production of functional hemoglobin and red blood cells in the human body. This disorder leads to anemia and other various symptoms due to the destruction of numerous red blood cells. Thalassemia presents alpha thalassemia and beta thalassemia two types, which depend on how many of the four genes for globins are missing. Studies reported that oxidative stress was a mechanism involved in thalassemia pathology, in which anti-ATP synthase exerted a critical role during the process.
The Role of Anti-ATP Synthase β Chain Antibody in Primary Liver Cancer
Primary liver cancer is a tumor that starts in the liver, which differs from metastatic liver cancer. Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common form of primary liver cancer in adults. Risk factors such as hepatitis B/C virus infection, autoimmune hepatitis, alcoholic cirrhosis, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, and obesity/diabetes are all causes leading to primary liver cancer. According to a proteomic approach, F1-ATP synthase β subunit induced autoantibodies among patients with hepatocellular carcinoma, and anti-ATP synthase might be potential to the utility in the early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.
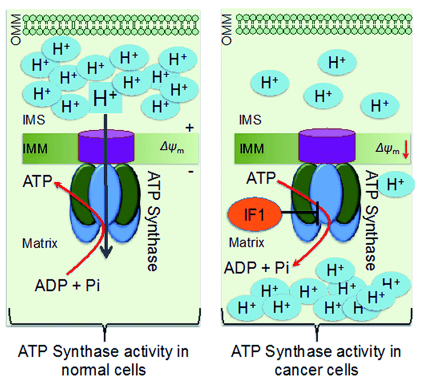 Fig.3 Schematic representation of differences in ATP synthase in normal and cancer cell mitochondria. (Wen, 2016)
Fig.3 Schematic representation of differences in ATP synthase in normal and cancer cell mitochondria. (Wen, 2016)
What We Can Do for You about NAA Services?
- Comprehensive NAA services, from NAA detection, NAA profiling, to NAA epitope mapping
- Powerful antibody research platform
- High efficiency (related diseases, products, custom services, and applications)
- Perfect after-sale service
In terms of anti-ATP synthase autoantibody, if you are interested in its detection and related studies, or you have any question. Please contact us for more information.
References:
- Mackieh, Rawan, et al. "Inhibitors of ATP Synthase as New Antibacterial Candidates." Antibiotics 12.4 (2023): 650.
- Hang, Weijian, et al. "Fulminant myocarditis: a comprehensive review from etiology to treatments and outcomes." Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 5.1 (2020): 287.
- Wen, Ru, and Shanta Dhar. "Turn up the cellular power generator with vitamin E analogue formulation." Chemical Science 7.8 (2016): 5559-5567.
Related Services:
- NAA Services for Anti-Transglutaminase 2 Antibodies (ATG2A)
- NAA Services for Anti-Transglutaminase 3 (TG3) Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-Factor XIII Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-Actin Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-Calreticulin Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-Gangliosides Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-Collagens Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-Synapsin I Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-Zonulin Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-Cardiolipin Antibody
- NAA Services for Anti-Enolase α

