NAA Services for Anti-Cardiolipin Antibody
Based on abundant experience and powerful technologies in natural autoantibodies (NAA) research, Creative Biolabs has successfully developed a series of diversified NAA platforms to provide fast and convenient NAA services for our global customers. We can provide a full range of anti-cardiolipin products, other NAA biomarkers for diseases diagnosis, and NAA detection and profiling services.
Background of Anti-cardiolipin Antibody
Cardiolipin, also termed as Diphosphatidylglycerol, is a unique phospholipid as well as an important component of the inner mitochondrial membrane. It plays a critical role in both mitochondrial function and cellular processes outside of the mitochondria, which can be almost exclusively found in the membranes of most bacteria, mammalian cells, and plant cells. Cardiolipin is essential for the functions of numerous enzymes that are involved in mitochondrial energy metabolism. Anti-cardiolipin antibody is a group of autoantibodies against cardiolipin, which can be found in several diseases including celiac disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, AIDS, etc. Anti-cardiolipin antibody is a form of anti-mitochondrial antibody that is used as a diagnostic biomarker.
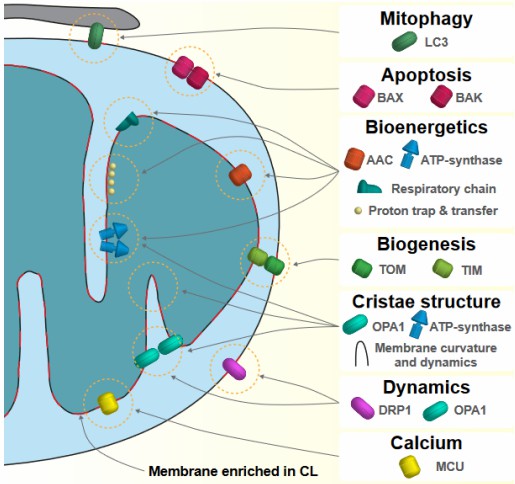 Fig.1 Main processes and proteins regulated by cardiolipin.1
Fig.1 Main processes and proteins regulated by cardiolipin.1
The Role of Anti-cardiolipin Antibody in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a kind of autoimmune multisystem disease which is characterized by multiple autoantibodies involves many parts of the body. Clinical and laboratory correlations between anti-cardiolipin antibodies and patients with SLE have been examined by plenty of studies, and high levels of IgG anti-cardiolipin are frequently found in SLE patients. It was indicated that anti-cardiolipin has predictive value in the development of thrombosis in SLE.
The Role of Anti-cardiolipin Antibody in Celiac Disease
Celiac disease is a type of autoimmune disease that primarily affects the small intestine. It is actually a problem with foods containing gluten, which is a protein triggering an abnormal immune response. This abnormity subsequently leads to inside small intestine damage and nutritional absorption disorders. Researches showed that antiphospholipid antibodies including anti-cardiolipin are significantly higher in patients with celiac disease than normal individuals, and IgA anti-cardiolipins were more frequently detected in celiac disease.
The Role of Anti-cardiolipin Antibody in AIDS
Human acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) is a type of infection immune system attack by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). The association between AIDS and autoimmunity has attracted lots of attention from clinical and pathophysiological perspectives. HIV-infected patients presented higher overall frequency of autoantibodies, which is associated with lower CD4+ cell counts. Anti-cardiolipin antibody can be frequently detected in all stages of HIV-infected patients, and considered to be a non-specific biomarker of HIV infection.
The Role of Anti-cardiolipin Antibody in NAA Associated Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a chronic disease characterized by the inside of an artery narrows due to the formation of plaque. Actually, it is also a kind of inflammatory and disorder resulting from the abnormal deposition of lipid droplets and several types of immune cells, including macrophages, T and B lymphocytes within the intima. Antiphospholipid antibodies are the hallmark of atherosclerosis. As one of the antiphospholipid antibodies, anti-cardiolipin is elevated in atherosclerosis patients and may be at least a biomarker or a risk factor for atherosclerosis.
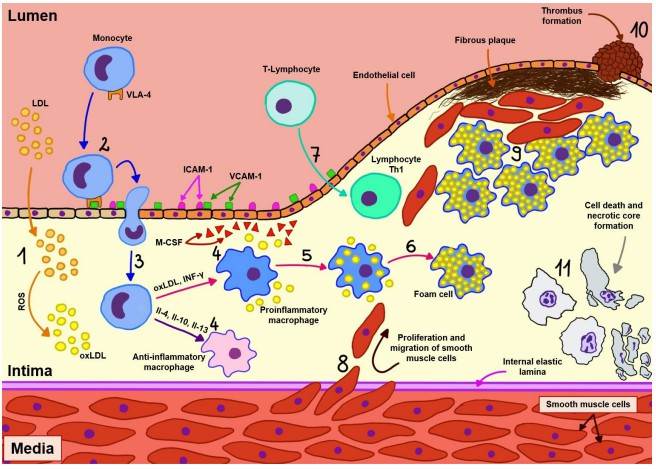 Fig.2 Pathophysiological mechanism of atherosclerosis.2
Fig.2 Pathophysiological mechanism of atherosclerosis.2
The Role of Anti-cardiolipin Antibody in Immune Thrombocytopenia Purpura (ITP)
Immune thrombocytopenia purpura (ITP) is a clinical syndrome characterized by a decreased number of circulating platelets and mucocutaneous bleeding. ITP actually is an autoimmune disease with some abnormal autoantibodies against several platelet surface antigens. Among these autoantibodies, anti-cardiolipin is increased and considered to play a critical role in the pathogenesis of in ITP.
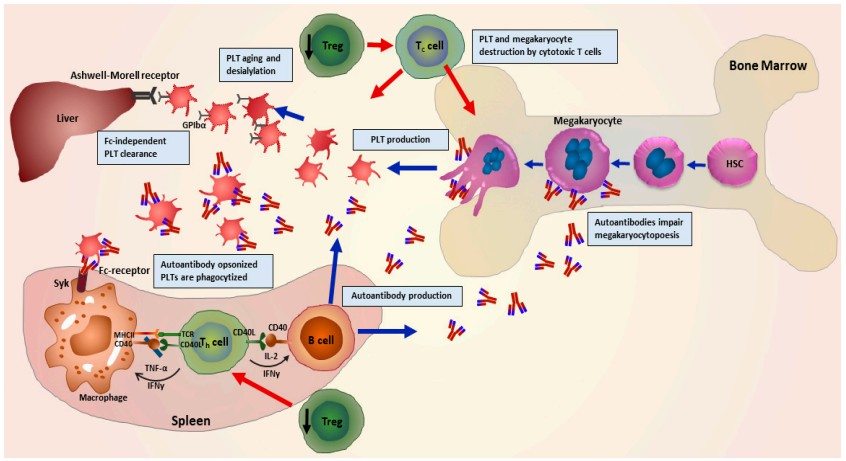 Fig.3 The pathophysiology of ITP, showing the participation of various immune cells.3
Fig.3 The pathophysiology of ITP, showing the participation of various immune cells.3
In terms of specific NAA researches like anti-cardiolipin, Creative Biolabs has successfully developed versatile NAA production and analysis platforms. Our improved platforms can provide comprehensive NAA services and custom services based on the requirements of the clients to meet the specific demand. Please contact us for more information.
References:
- Prola, Alexandre, and Fanny Pilot-Storck. "Cardiolipin Alterations during Obesity: Exploring Therapeutic Opportunities." Biology 11.11 (2022): 1638.
- Napiórkowska-Baran, Katarzyna, et al. "Molecular Linkage between Immune System Disorders and Atherosclerosis." Current Issues in Molecular Biology 45.11 (2023): 8780-8815.
- Singh, Anurag, Günalp Uzun, and Tamam Bakchoul. "Primary immune thrombocytopenia: novel insights into pathophysiology and disease management." Journal of Clinical Medicine 10.4 (2021): 789.
Related Services:
- NAA Services for Anti-Transglutaminase 2 Antibodies (ATG2A)
- NAA Services for Anti-Transglutaminase 3 (TG3) Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-Factor XIII Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-Actin Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-Calreticulin Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-Gangliosides Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-Collagens Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-Synapsin I Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-Zonulin Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-ATP Synthase β Chain
- NAA Services for Anti-Enolase α

