NAA Services for Anti-Glutamate Receptor Antibodies
As a leading provider of high-quality antibody services, Creative Biolabs has years of experience in the antibodies detection and analysis for the immunodiagnostic. We can produce a full range of diagnostic assays for various biomarkers associated with various diseases. At present, we provide high-quality anti-glutamate antibodies marker services to universal customers. With combined expertise in immunology and diseases diagnosis, our professional scientists can help you with every link of the natural autoantibody (NAA) development process, from design to validation.
Background of Anti-glutamate Receptor Antibodies
Glutamate, an amino acid, is a precursor for GABA as well as a neurotransmitter in the human body that plays essential roles in a diversity of biological processes, including excitatory transmission, synaptogenesis, cognitive functions, etc. As an abundant and important molecule, glutamate functions by binding to glutamate receptors, biochemical receptors of glutamate that mainly distribute on the membranes of neuronal and glial cells in the nervous system. Anti-glutamate receptor antibodies are essentially a class of autoantibodies produced by the immune system that directed against glutamate receptor in the body itself. According to different types of glutamate receptors, glutamate receptor autoantibodies are generally divided into anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antibody, anti-α-amino-3-hydroxyl-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionate (AMPA) receptor antibody, and anti- metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR) antibody, all of which have been indicated to be involved in several pathological mechanisms.
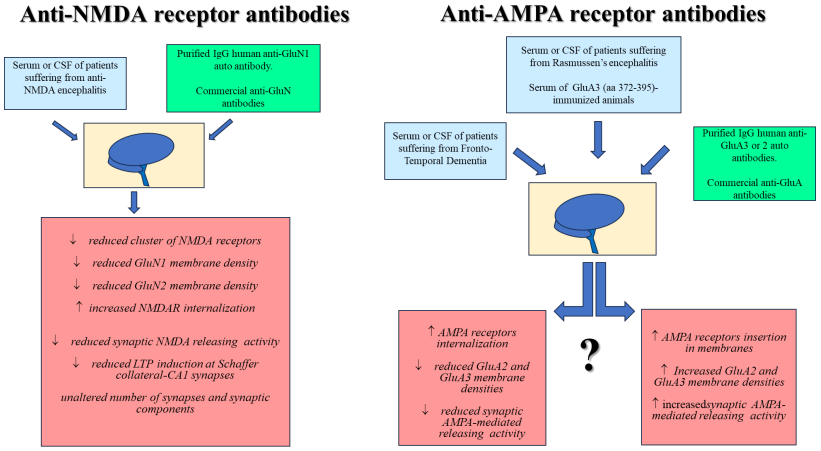 Fig.1 Role of anti-NMDA and anti-AMPA receptor antibodies on neuronal NMDA receptors (left) and AMPA receptors (right).1
Fig.1 Role of anti-NMDA and anti-AMPA receptor antibodies on neuronal NMDA receptors (left) and AMPA receptors (right).1
The Role of Anti-glutamate Antibodies in Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a worldwide age-related neurodegenerative disease that mainly affects the elderly. AD is characterized by progressive loss of memory, other typical symptoms comprise cognitive impairment, executive dysfunction, social difficulties and so forth. The pathophysiology of AD is complex and remains unclear, of which the immune system and some autoantibodies are shown inextricably linked.
In the human central nervous system, glutamate and its receptors are mainly implicated to many crucial neuronal functions, such as excitatory transmission, synaptic plasticity, ions exchange, which are associated with several autoimmune diseases and neurodegenerative diseases. Mutations of glutamate receptors genes have been observed or glutamate receptors autoantibodies have been detected were increased in the patients with AD. One of the anti-glutamate receptor antibodies, anti-NMDA receptor antibody, is directly associated with AD by influencing the NMDA receptor activity. Anti-NMDA receptor IgG antibodies can recognize the GluN1 subunit of NMDA receptor, which may interfere with the functions of the NMDA receptor in regulating synaptic plasticity and memory. More importantly, glutamate receptor autoantibodies, such as anti-mGluR1 antibodies, anti-NMDA-NR1 antibodies, anti-AMPA-GluR3 antibodies, induce cognitive abnormalities by activating glutamate receptors, subsequently inhibiting the expression of glutamate receptor and related functions.
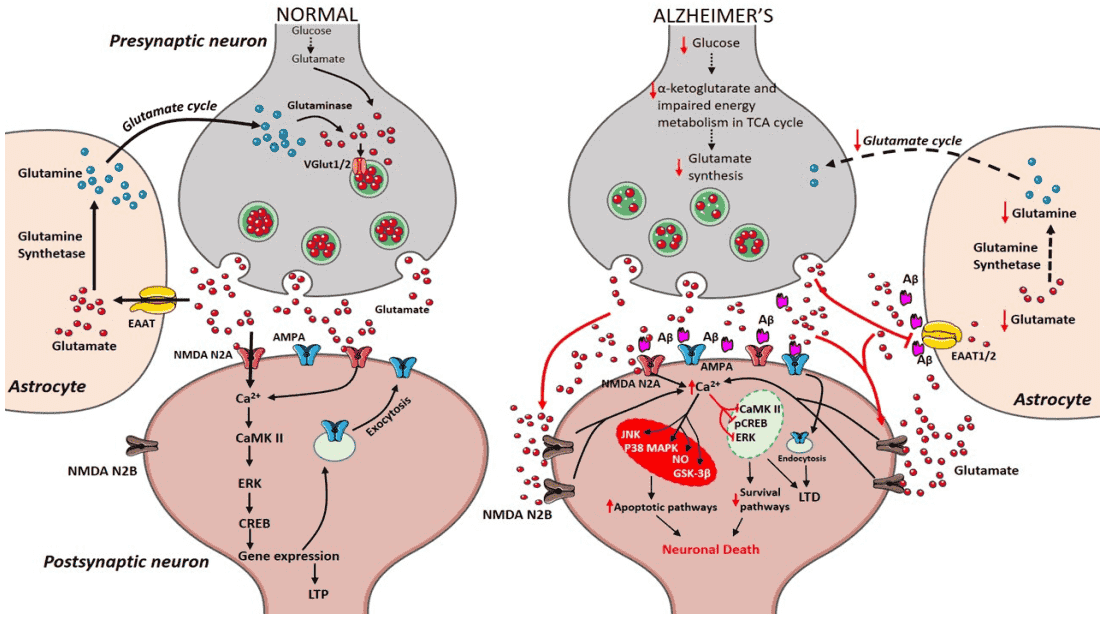 Fig.2 The dual role of glutamatergic neurotransmission in Alzheimer’s disease.2
Fig.2 The dual role of glutamatergic neurotransmission in Alzheimer’s disease.2
Creative Biolabs has long-term devoted to the development of antibodies discovery and detection. Having finished lots of projects based on our extensive experience, we are therefore confident in offering the best NAA services and products for our customers all over the world. If you are interested in our service, please do not hesitate to contact us for more details.
Reference
- Olivero, Guendalina, Alessandra Roggeri, and Anna Pittaluga. "Anti-NMDA and Anti-AMPA Receptor Antibodies in Central Disorders: Preclinical Approaches to Assess Their Pathological Role and Translatability to Clinic." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24.19 (2023): 14905.
- Bukke, Vidyasagar Naik, et al. "The dual role of glutamatergic neurotransmission in Alzheimer’s disease: from pathophysiology to pharmacotherapy." International journal of molecular sciences 21.20 (2020): 7452.
Related Services:
- NAA Services for Anti-Aβ Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-Tau Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein (oxLDL) Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-Phospholipid Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-AT1R
- NAA Services for Anti-5-HT

