NAA Services for Anti-Phospholipid Antibodies
As a leader in the field of antibody research and development, Creative Biolabs is committed to providing the most comprehensive NAA services for our global clients. Based on the abundant experience accumulated in the successful completion of many NAA-related projects, we provide anti-phospholipid antibody marker services with the best quality and the most competitive prices.
Introduction to Anti-phospholipid Antibodies
Phospholipids are a class of amphiphilic lipid molecules that are the main component of the bilayer of cell membranes. Generally, a phospholipid molecule is composed of two hydrophobic fatty acid “tails” and a hydrophilic phosphate group “head”. Phospholipid is an essential component with multiple-functions, such as elective permeation as a membrane component, broken down for energy supply, blood clotting, etc.
However, when the autoimmune process occurs, the body can mistakenly recognize some phospholipids as foreign substances and produce antibodies against them. These antibodies are called anti-phospholipid antibodies (APLAs). The APLAs can lead to severe antiphospholipid syndrome or antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS or APLS), which is characterized by arterial and venous thrombosis, recurrent fetal loss, and thrombocytopenia.
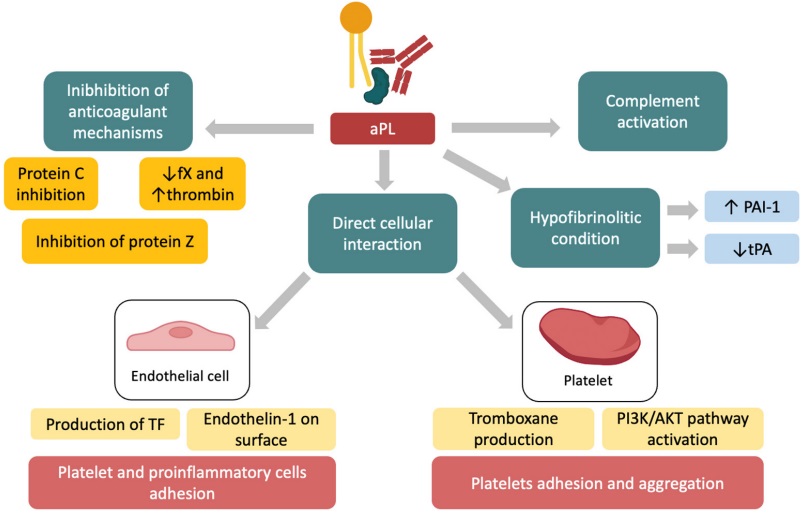 Fig.1 The aPL antibodies prothrombotic activity.1
Fig.1 The aPL antibodies prothrombotic activity.1
The Role of Anti-phospholipid Antibodies in Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common type of dementia due to a neurodegenerative disorder. As the disease progresses, patients with AD will result in severe memory loss and cognitive decline. Numbers of investigations have been conducted to reveal the associations between APLAs and neurodegenerative diseases, most of which found that the presence of cognitive deficiencies was accompanied by the rise of APLA levels in asymptomatic patients. It was suggested that APLAs might be sensitive blood biomarkers to promote early prognosis of AD.
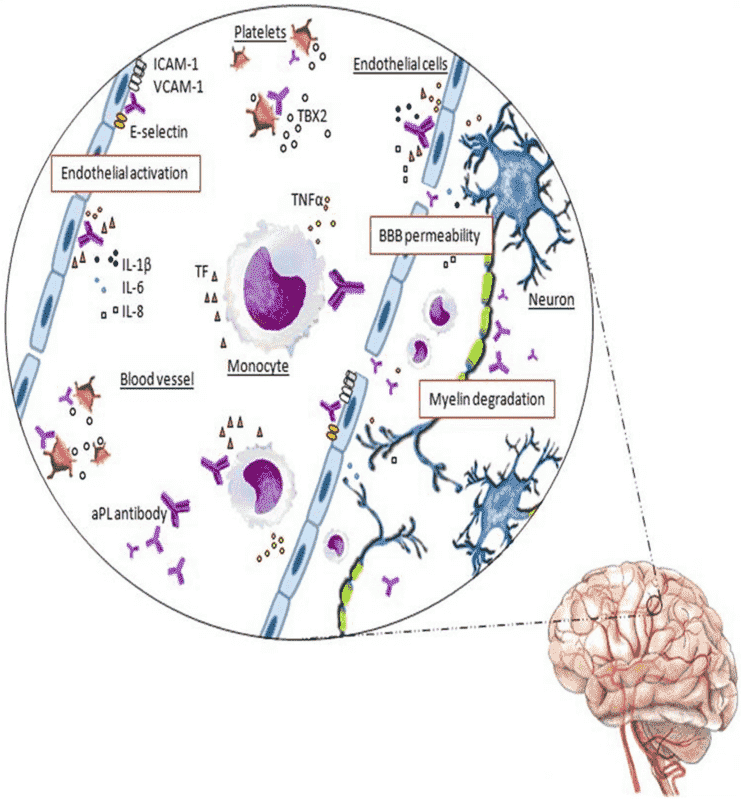 Fig.2 Neurological damage induced by aPL antibodies in the central nervous system.2
Fig.2 Neurological damage induced by aPL antibodies in the central nervous system.2
The Role of Anti-phospholipid Antibodies in Epilepsy
Epilepsy is one of the typical neurological disorder diseases. APLAs are a group of autoantibodies directed against the epitopes on anionic phospholipids on plasma membranes, including lupus anticoagulant (LA), anticardiolipin (aCL) antibodies and anti-β2-glycoprotein I (β2-GPI) antibodies. Evidence indicated that a significantly higher titer of aPLs has been observed in different neurologic disorders, in which aCL antibodies were closely associated with epilepsy in both adults and paediatric subjects. In addition, higher titers of anti-β2-GPI antibodies occur more frequently in epileptic subjects as compared to healthy controls.
The Role of Anti-phospholipid Antibodies in Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a vascular disease where the inside of an artery becomes narrowed and hardened due to the increase of plaque on the artery wall. Symptoms usually determined by the location of affected arteries, commonly including coronary artery disease, stroke, peripheral artery disease, and other related complications. APLAs have been found to be associated with clinical cardiovascular disease. Results suggested that APLAs immunoglobulin (Ig) M, IgG, and IgA and aCL IgM and IgG were presented positively in atherosclerosis patients. Besides, anti-β2-GPI IgM, IgG, IgA, and aCL IgG were positivity associated with coronary artery calcification (CAC) in patients. These data indicated that APLAs positivity during young adulthood was a risk factor for subsequent sub-clinical atherosclerosis and might play a role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis.
The Role of Anti-phospholipid Antibodies in Immune Thrombocytopenia Purpura (ITP)
ITP is a clinical disease characterized by the thrombocytopenia, symptoms including bleeding, bruising and petechiae. The IgG/IgM APLAs were found existing in ITP patients, which play a pathogenetic role in the ITP process. Besides, study results also showed an obvious decrease in platelet counts in APLAs-positive ITP patients. Thus, the persistent presence of APLAs is a crucial risk factor for the development of ITP, and the detection of APLAs is a useful strategy for the diagnosis and treatment of ITP disease.
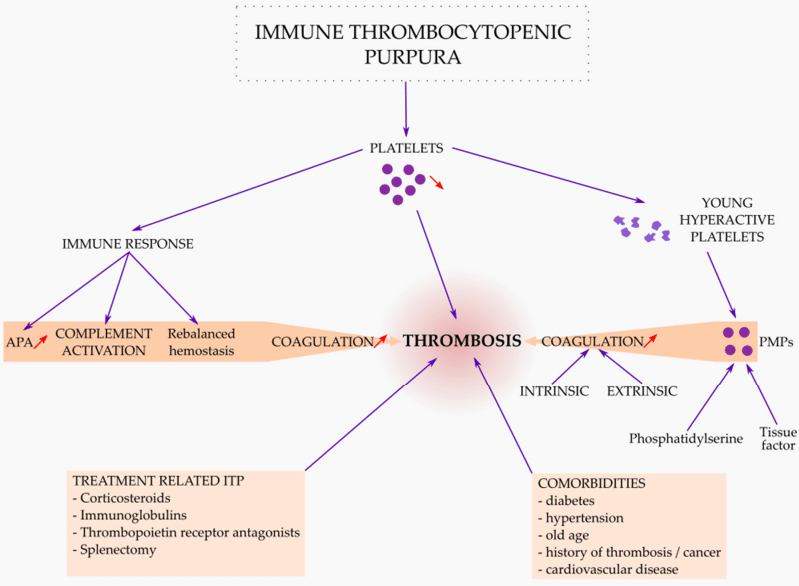 Fig.3 Thrombosis in ITP is related to antiphospholipid antibodies (APA).3
Fig.3 Thrombosis in ITP is related to antiphospholipid antibodies (APA).3
What We Can Do About NAA?
Creative Biolabs has focused on antibody detection and analysis technology for years. We have experienced scientists and experts who are able to offer high-quality NAA services for disease diagnostic against varieties of markers. Moreover, all-around NAA products are available for your choice.
If you are interested in our services, please contact us for more details. We are happy to help you to make your project a success.
References
- D’Ippolito, Silvia, et al. "Antiphospholipid Syndrome in Pregnancy: New and Old Pathogenetic Mechanisms." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24.4 (2023): 3195.
- D’Angelo, Chiara, et al. "Antiphospholipid antibodies overlapping in isolated neurological syndrome and multiple sclerosis: neurobiological insights and diagnostic challenges." Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience (2019): 107.
- Tărniceriu, Claudia Cristina, et al. "Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura as a Hemorrhagic Versus Thrombotic Disease: An Updated Insight into Pathophysiological Mechanisms." Medicina 58.2 (2022): 211.
Related Services:
- NAA Services for Anti-Aβ Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-Tau Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-Glutamate Receptor Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein (oxLDL) Antibodies
- NAA Services for Anti-AT1R
- NAA Services for Anti-5-HT

