Anti-TNFR-SF Family Members
Rich theoretical knowledge combined with our advanced antibody engineering platform, Creative Biolabs can provide agonist antibody development and customization services for the corresponding targets of the TNFR-SF family. These antibodies include, but are not limited to:
-
CD137
-
CD134
-
GITR
-
CD40
-
CD27
-
CD30
-
CD28
-
DR5
-
BTLA
-
ICOS
CD137 (4-1BB) or TNF receptor superfamily member 9 (TNFRSF9), is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor family which induced by lymphocyte activation (ILA). It was expressed on activated B cells, dendritic cells, myeloid precursors, mast cells and endothelial cells in tumors or inflammatory tissues. As a co-stimulatory immune checkpoint molecule, CD137 has aroused the interest of immunologists.
The role of CD137 in enhancing cytotoxic T cell response was established in 1997, and the anti-CD137 monoclonal antibody (mAb) as a cancer treatment was soon explored. Agonistic anti-CD137 mAb can enhance the production, proliferation and cytolysis effector function of cytokines and protect lymphocytes from programmed cell death, thereby inducing multiple immune responses on different types of immune cells. As a single therapy, anti-CD137 mAb can effectively control the growth of tumors or promote complete rejection of various transplantable rodent tumors, including sarcoma, tumor cell tumors, colon cancer and lymphoma. The mechanisms include the enhancement of cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) function and the cross-initiation of dendritic cells to tumor antigens.
In addition, another potential prospect of anti-CD137 mAb immunotherapy is to combine with other therapies. Synergistic combination with vaccines and viral therapies depends on the principle that CD137 synergistic stimuli must act on a sustained tumor-specific immune response, including CD137+ activated lymphocytes. Recently, some interesting preclinical studies have shown that anti-CD137 mAb therapy is synergistic with NK-mediated antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) induced by antibodies targeting surface antigen CD20 or human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER-2).
Pre-clinical success highlights the importance of the combination of cancer immunotherapy and CD137 in the field of cancer immunotherapy. The anti-cancer effect of the agonistic anti-CD137 mAb is one of the most promising discoveries since CD137 was identified as an immunomodulator.
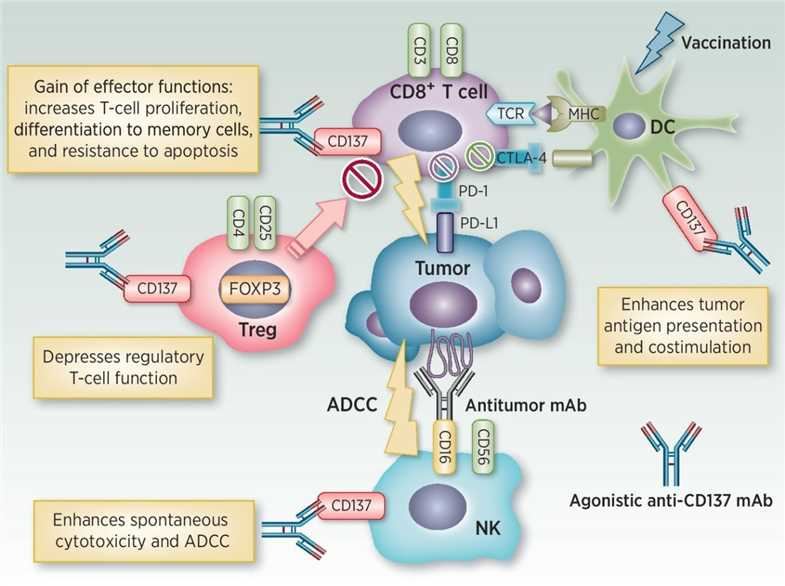 Fig.1 Immunomodulatory mechanisms of CD137. (Yonezawa, 2015)
Fig.1 Immunomodulatory mechanisms of CD137. (Yonezawa, 2015)
Reference
-
Yonezawa, A.; et al. Boosting cancer immunotherapy with anti-CD137 antibody therapy. Clinical Cancer Research. 2015, 21(14): 3113-3120.
Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 4 (TNFRSF4), also known as CD134 and OX40 receptor, is a member of the TNFR superfamily, which is not constitutively expressed on resting naïve T cells and is a secondary co-stimulatory immune checkpoint molecule. Its ligand OX40L is preferentially expressed in APCs such as B cells, dendritic cells, macrophages, as well as other cell types, suggesting that OX40/OX40L interaction may participate in many aspects of physiological responses between T cells and lymphoid and non-lymphoid cells.
In view of the involvement of OX40 to expand the T cell population, promote cytokine secretion, and support T cell memory, the anti-OX40 agonist monoclonal antibody (mAb) has been successfully applied to a variety of preclinical tumor models. In rodent tumor immunological studies, anti-OX40 mAbs have been shown to be effective in a number of tumor models, including MC303 sarcomas, CT26 colon carcinomas, SM1 breast cancer, and small B16 melanoma.
In addition, a variety of combinatorial strategies to enhance another potential prospect of anti-OX40 antibody therapy have also been proposed. Currently, anti-OX40 mAbs have been combined with other clinically relevant anti-inhibitory and costimulatory molecule mAbs to treat lymphomas and sarcomas. When used with OX40 agonists, methods with direct cell lysis capabilities, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy, have proven to be particularly effective in treating established tumors. For example, in combination with cyclophosphamide, OX40 binding not only expands anti-tumor T effector cells, but also reduces Foxp3+ regulatory T cells by promoting activation-induced cell death. In addition, considering that OX40 ligation can effectively stimulate CD4+ T cells, the use of metastatic anti-melanoma CD4+ T cells in combination with anti-OX40 antibodies and cyclophosphamide can eliminate very advanced melanoma.
Therefore, the development of anti-OX40 antibody will play an important role in the clinical treatment of various cancers.
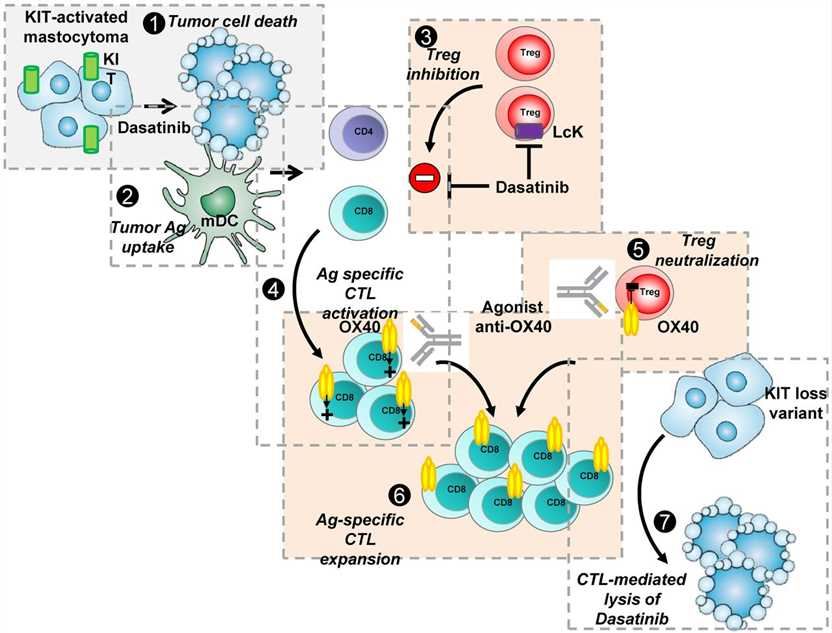 Fig.1 Potent synergy between KIT-targeted inhibitor dasatinib and agonist anti-OX40 mAb to eradicate P815 KIT-mutated mastocytoma tumors. (Marabelle, 2012)
Fig.1 Potent synergy between KIT-targeted inhibitor dasatinib and agonist anti-OX40 mAb to eradicate P815 KIT-mutated mastocytoma tumors. (Marabelle, 2012)
Reference
-
Marabelle, A.; Caux, C. Combined targeted and immunotherapy: the future of personalized medicine. Blood. 2012, 120(23): 4454-4455.
GITR (tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 18, TNFRSF18) is a protein encoded by TNFRSF18 gene in human. For a member of the TNFR family, GITR is unique in that it signals through a single TRAF5 and two TRAF2 complexes, indicating that the molecule has a non-redundant role. GITR-ligand (GITRL) binding leads to down-regulation of regulatory T cells (Tregs) function, which is considered to play a key role in dominant immune self-tolerance maintained by CD25+/ CD4+Tregs. At present, immunologists are very interested in it as a co-stimulating immune checkpoint molecule.
In animal model experiments, the preliminary study of an agonist monoclonal rat anti-mouse GITR antibody (DTA-1) showed that it could effectively stimulate effector T cells and reduce the inhibitory function of Tregs, leading to autoimmunity. Subsequently, studies have shown that DTA-1 overrides the suppressive effects of Tregs on T effector cells. Therefore, anti-GITR can potentially overcome the tolerance to itself and tumor antigens, making it an attractive target for the development of cancer immunotherapy. In fact, DTA-1 has been shown to be effective in the treatment of small established Meth-A sarcomas and lymphomas. An interesting antitumor property of DTA-1 is its ability to promote concomitant immunity, which indicates the potential of GITR-induced tumor immunity in the treatment of metastatic diseases.
In addition, it is noteworthy that DTA-1 has shown a significant enhancement of the efficacy of xenogenic DNA vaccine in the melanoma model, in which protection is marginal. Similarly, dendritic cells (DCs) designed to express melanoma antigen exhibited higher therapeutic efficacy when co-administered with DTA-1 or when DCs were designed to secrete DTA-1 or soluble GITRL.
Given the important role GITR plays in diseases, efficient development of anti-GITR agonist antibody is crucial.
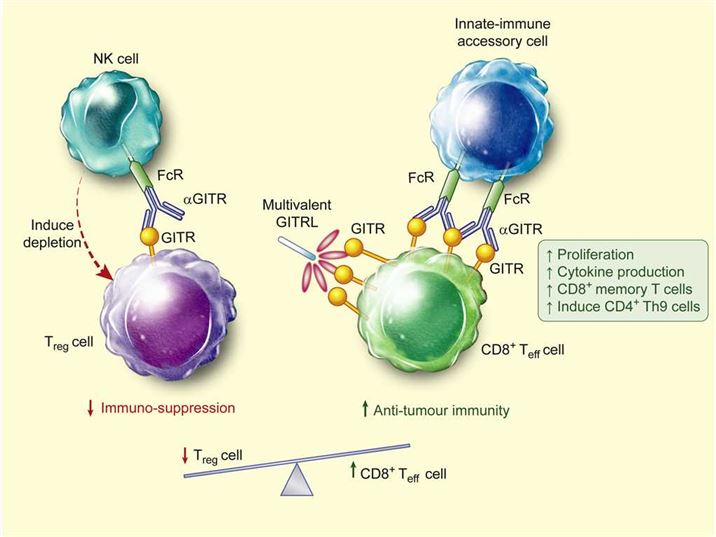 Fig.1 Model for GITR modulation of antitumour immunity. (Knee, 2016)
Fig.1 Model for GITR modulation of antitumour immunity. (Knee, 2016)
Reference
-
Knee, D.A.; et al. Rationale for anti-GITR cancer immunotherapy. European journal of cancer. 2016, 67: 1-10.
CD40 (cluster of differentiation 40) is a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily expressed on antigen presenting cells (APCs), such as dendritic cells (DCs), B cells and monocytes, as well as many non-immune cells and many kinds of tumors. The interaction between activated T helper cells and CD40 trimer ligands leads to APC activation. CD40 conjugation on DC induces co-stimulation and surface expression of MHC molecules to increase the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and enhance T cell triggering, while its junctions on resting B cells increase antigen presenting function and proliferation. The results of CD40 signal transduction are multifaceted, depending on the cell type that expresses CD40 and the microenvironment that provides CD40 signal.
The agonistic anti-CD40 monoclonal antibody (mAb) provides a new therapeutic option. It may produce anti-cancer immunity through various mechanisms, including APC activation driving anti-tumor T cells, activation of killing tumor macrophages, and induction of apoptosis in CD40+ tumor cells (such as lymphoma or some solid tumors). Studies have shown that agonistic anti-CD40 mAbs can play a role in cancer control without T cell immunity. In addition, CD40-activated macrophages can become tumoricidal, and at least in pancreatic cancer, they can also promote the consumption of tumor matrix, thereby inducing tumour collapse in vivo. For solid tumors, agonistic CD40 mAb will be most effective in combination with other modalities such as chemotherapy, radiation or vaccines; meanwhile, single-drug therapy for B-cell lymphoma remains an important possibility.
In summary, with such rich potential mechanisms and the ability of advanced technology to design the structure and function of mAbs to meet specific requirements, we will see the rapid development of agonistic anti-CD40 mAbs in the future.
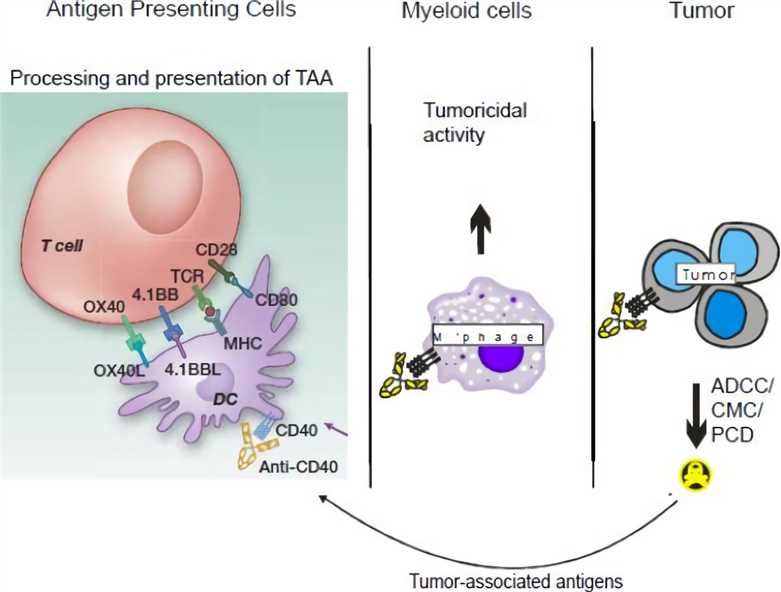 Fig.1 Potential mechanisms of action of agonistic CD40 mAb on various immune effectors. (Vonderheide, 2013)
Fig.1 Potential mechanisms of action of agonistic CD40 mAb on various immune effectors. (Vonderheide, 2013)
Reference
-
Vonderheide, R.H.; Glennie, M.J. Agonistic CD40 antibodies and cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2013, 19(5): 1035-1043.
Introduction to CD27
CD27, a costimulatory molecule on T cells and a member of the TNFR protein family, is a 120-kda disulfide bonded homodimer and type I transmembrane molecule that is constitutively expressed in subgroups of naive and activated T cells, memory B cells, and NK cells. CD27 was not considered a target of immunotherapy for many years, but as research has progressed, scientists have found that CD27 plays a key role in many immunological processes, such as T cell activation, NK cell proliferation and toxicity. Physiologically, the CD27 co-stimulus signal is regulated by the restricted expression of its specific ligand CD70, which is not expressed in resting cells, but immediately upregulated in lymphocytes and dendritic cells after activation.
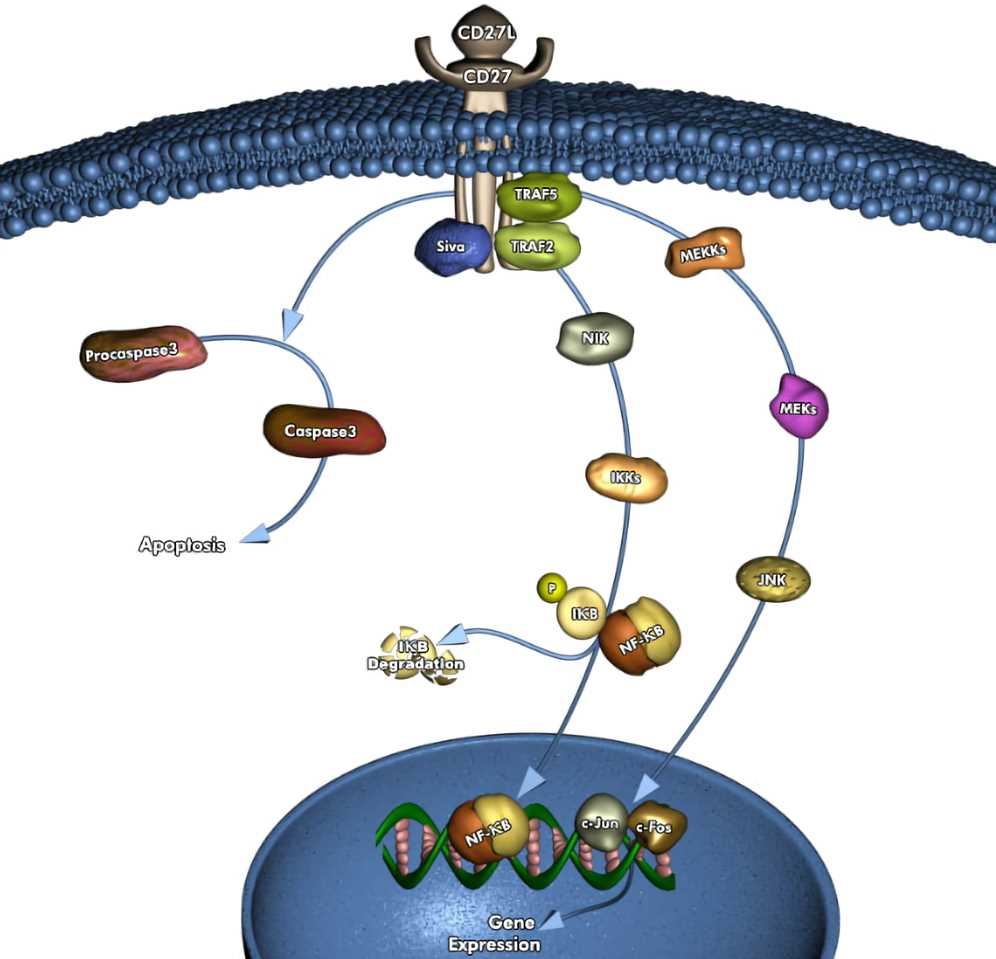 Fig.1 CD27 pathway.
Fig.1 CD27 pathway.
The therapeutic effect of anti-CD27 agonist antibodies has been confirmed in the study. In the CD40 antibody-treated tumor experiment, if the co-stimulatory pathway of CD70/CD27 is blocked, the therapeutic effect of anti-CD40 antibody in the BCL1 lymphoma model will be completely eliminated. It is indicated that the CD27 signal is necessary for the effect of the anti-CD40 antibody. This experiment made people aware of the value of CD27 as a therapeutic target and began research on it. Specific human anti-cd27 agonist antibodies have entered clinical trials. This antibody, called 1F5, blocks the binding of soluble CD70 to CD27, and can recognize and stimulate T cells expressing human CD27 in vitro, mediating anti-tumor immunity. Creative Biolabs can provide customers with CD27 agonist antibody development services, please contact us to inquire about the details of the service.
CD30 is a membrane protein of the TNFR protein family, expressed in various lymphoid and bone marrow cells. CD30 was originally recognized as an antigen on Hodgkin's disease cells and is still considered as a clinical marker for many malignant blood tumors. The soluble CD30 protein is naturally present in human serum and its expression is significantly increased in some cases such as viral infection, autoimmune disease or tumor. Studies have shown that CD30 is expressed by activated T cells or B cells, mediating signal transduction to activate nf-kappab. Therefore, it is a positive regulator of apoptosis and has been proved to inhibit the proliferation potential of autoreactive CD8 effector T cells and protect the body from the effects of autoimmune immunity.
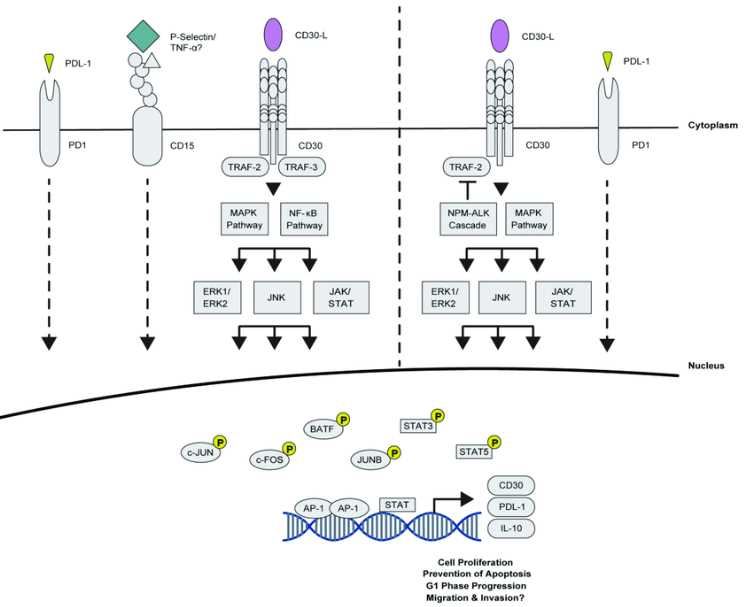 Fig.1 CD30 pathway.
Fig.1 CD30 pathway.
In the past decade, monoclonal antibodies against surface receptors have become a highly potential therapeutic option in many hematological malignancies. Due to its restricted expression in normally activated T cells and high expression on malignant cells, CD30 is an attractive therapeutic target for the treatment of Hodgkin's lymphoma and anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Over the past decade, monoclonal antibodies targeting surface receptors have become a promising treatment option for many hematologic malignancies. Due to its limited expression in normally activated T cells and high expression in malignant cells, CD30 has become an attractive therapeutic target for Hodgkin's lymphoma and anaplastic large cell lymphoma. CD30 is involved in a very complex signaling pathway that leads to different results depending on the cell environment. In addition, CD30 rapidly internalizes after cross-linking, which counteracts the effective aggregation of immune agents, but also provides opportunities for antibodies and conjugates on antibodies to metastasize to tumor cells. Creative Biolabs provides customers with the construction services of CD30 antibodies, and we can couple antibodies to specific molecules to meet your research needs, please contact us to inquire about the details of the service.
CD28 is a 44 kDa T-cell specific surface glycoprotein that constitutively expressed on most of peripheral blood T lymphocytes. It is a disulfide-linked homodimer which has been described as a cell adhesion molecule of the immunoglobulin superfamily. This protein is an important regulator of the immune system that functions as a pivotal T cell costimulatory receptor. CD28 provides cells the critical second activation signal by binding CD80/CD86 which is expressed by antigen presenting cells (APC). In addition to its co-stimulation role, this antigen exerts functions by preventing T cells from entering premature apoptotic cell death or from undergoing an anergic-hyporesponsive state.
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) with specificity for CD28 and T cell receptor complex have proved extremely useful. Neither conventional anti-CD28 mAbs or anti-T cell receptor mAbs alone by themselves suffice to fully activate T cells, while a combination of both effectively leads to T cell proliferation and cytokine release. Intriguingly, there is a subclass of CD28 specific antibodies, CD28 superagonists, capable of fully stimulating T cells without additional stimulation of T cell receptor. This anti-CD28 superagonistic antibody works not only in vivo but also in vitro as the administration of a CD28 superagonist induces a transient but significant growing in T cell numbers. At Creative Biolabs, we offer one-stop service packages of agonistic antibody development for CD28 molecule and many immune checkpoint molecules. Our custom antibodies can be humanized to reduce immunogenicity, improve the therapeutic half-life, and satisfy clients other special needs.
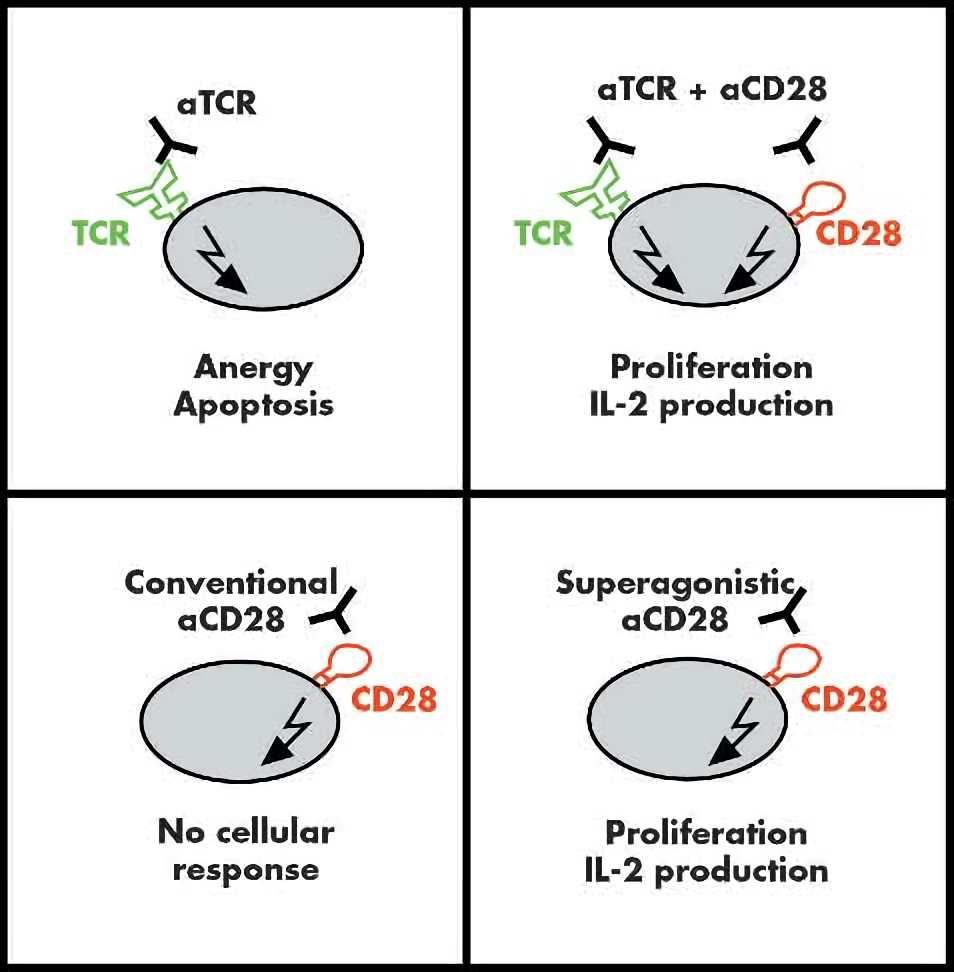 Fig.1 Two classes of CD28 specific monoclonal antibodies (mAbs): ‘‘conventional’’ and ‘‘superagonistic’’. (Beyersdorf, 2005)
Fig.1 Two classes of CD28 specific monoclonal antibodies (mAbs): ‘‘conventional’’ and ‘‘superagonistic’’. (Beyersdorf, 2005)
Reference
-
Beyersdorf, N.; et al. Superagonistic anti-CD28 antibodies: potent activators of regulatory T cells for the therapy of autoimmune diseases. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005, 64: Suppl 4.
Introduction to DR5
Breast cancer is caused by the unregulated malignant proliferation of breast tissue cells and is one of the most common malignant tumors in North American women. Death Receptor 5 (DR5) has been shown to be an important regulator of breast cancer development. It is a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNF) receptor superfamily and is a TNF receptor apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL). DR5 activates the Caspase signaling pathway through the death-inducing complex (DISC) to initiate apoptosis. In this process, the formation of DISC is important for the transmission of apoptotic signals. The mutation of DR5 affects the correct assembly of DISC and interferes with cell apoptosis.
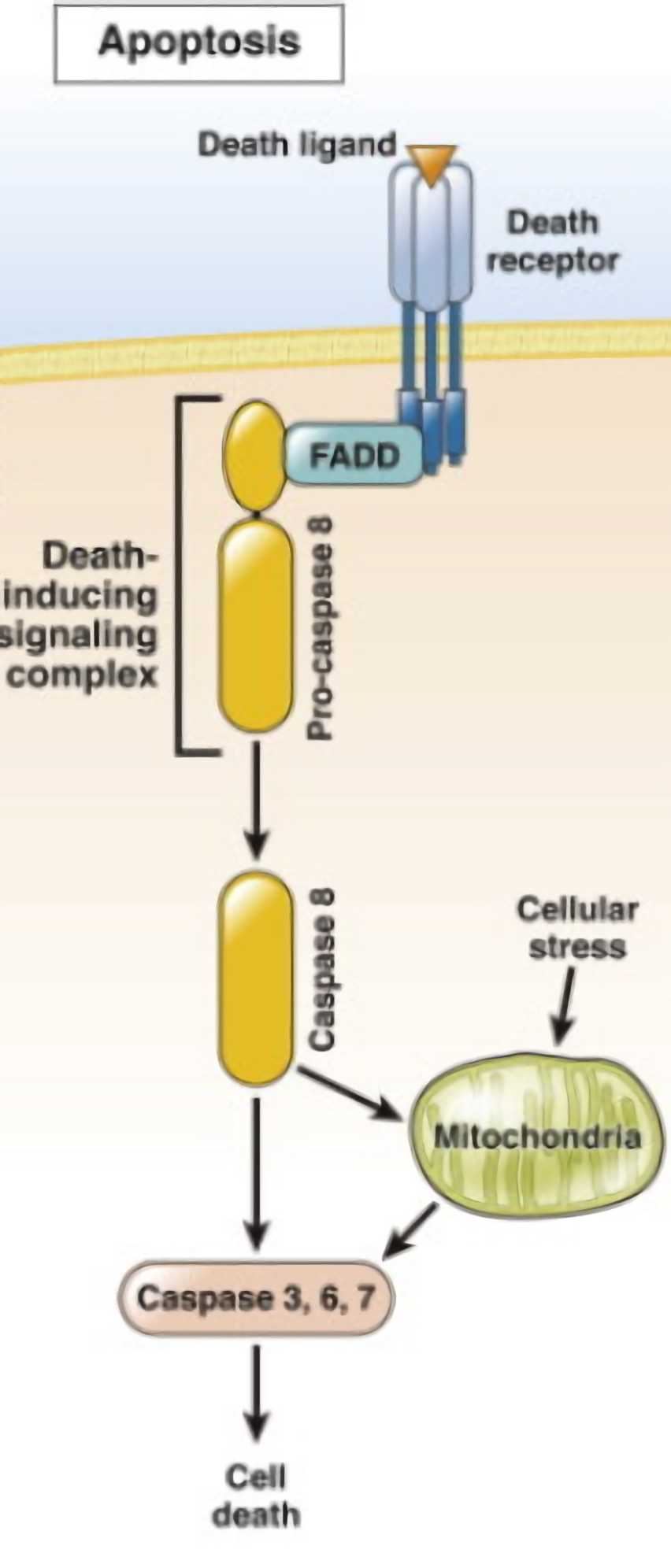 Fig.1 DR5 pathway.
Fig.1 DR5 pathway.
Compared with normal cells, the DR5 expression level in breast cancer cells is significantly increased, which provides an idea for tumor treatment, and the apoptosis inducing ability of DR5 itself makes it an ideal target for activation in cancer treatment. A TRA-8 monoclonal antibody that has been developed to specifically bind to DR5 activates it to induce apoptosis in malignant cancer cells. TRA-8 anti-DR5 antibody alone or in combination with chemotherapy and/or radiation has shown significant anti-tumor efficacy in breast cancer xenograft models. It is necessary to conduct further research and clinical trials to observe the actual therapeutic effect. Creative Biolabs provides customers with DR5 agonist antibody development services for research, please contact us to inquire about the details of the service.
Introduction to BTLA
B and T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA) is a member of the CD28/B7 protein family and its expression is detected in most lymphocytes, which have similar structures and functions as CTLA-4 and PD-1. The EBLA ligand-spreading virus entry vector (HVEM) is a member of the TNF receptor superfamily and is found in T cells, B cells, NK cells, bone marrow cells, and various tumor cells. The interaction of BTLA with its ligand blocks the activation, proliferation and production of cytokines by B cells and T cells. Carcinogenesis of cells leads to overexpression of BTLA, and a large number of T cells with reduced activity are amplified. Therefore, high levels of BTLA expression generally represent poor prognosis of cancers such as melanoma and gastric cancer. In addition, because BTLA and HVEM are involved in the synergy of multiple signaling pathways, the treatment options targeting them face many difficulties.
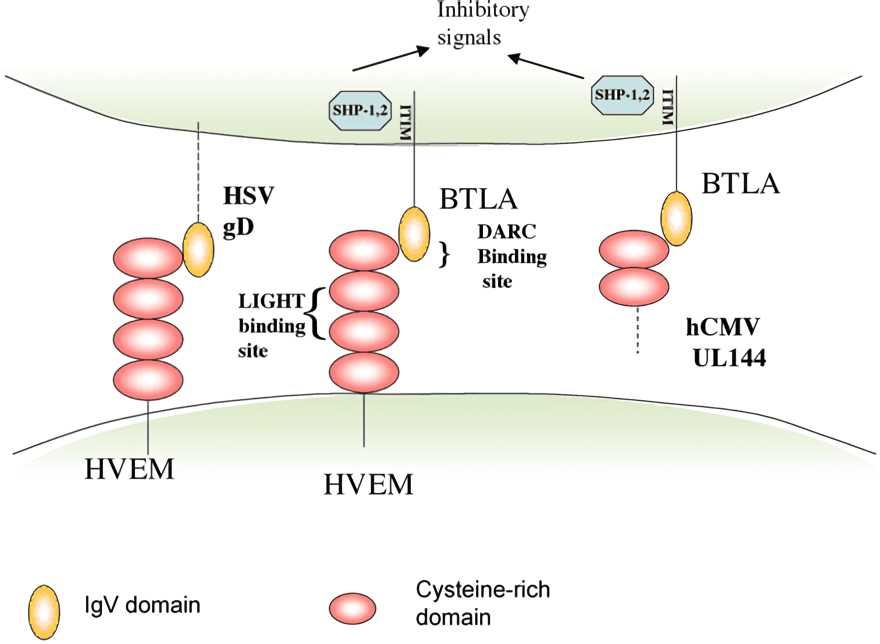 Fig.1 BTLA pathway.
Fig.1 BTLA pathway.
The use of antibodies to block immunological checkpoints is an important breakthrough in oncology and has improved health for many cancer patients. How to block the interaction between BTLA and HVEM has always been a hard work for biologists to think about. BTLA/HVEN compound crystal structure shows HVEM (26-38) amino acid residues directly involved in the combination with BTLA, after the experimental analysis results found HVEM (23 to 39) peptides can block the interaction between BTLA and HVEM, blocking ability comes from the peptides Cys residue, a finding that for the future development of the corresponding checkpoint antagonists antibody provides valuable reference information. Creative Biolabs will provide customers with antagonist antibody development services against BTLA, please contact us to inquire about the details of the service.
Introduction to ICOS
Inducible costimulatory molecules (ICOS) are the third member of the CD28/CTLA-4 protein family and are generally expressed as homodimers and expressed on activated T cells. The specific binding partner of ICOS is also known as B7-related protein-1 (B7RP-1), which is constitutively expressed on B cells. ICOS-mediated signaling primarily contributes to the regulation of T cell regulation and effector T cell function, and the potency of ICOS is enhanced after its binding to ICOS-L. In addition, ICOS plays a role in the maturation of B cells, regulation of T follicular helper cells, and maintenance of homeostasis of effector T cells and regulatory T cells.
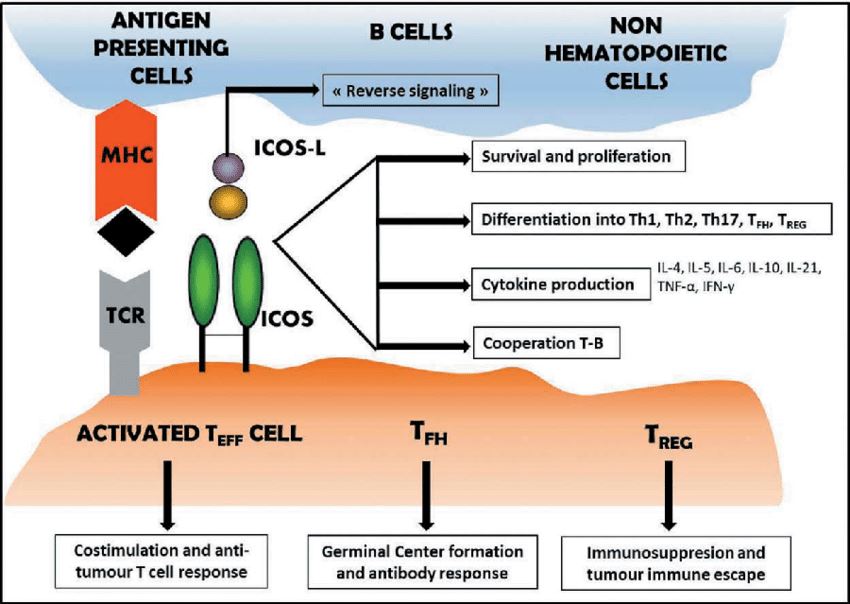 Fig.1 ICOS pathway.
Fig.1 ICOS pathway.
In the clinical treatment of tumor, it is found that the role of ICOS in tumor is bidirectional and complex. The expression of ICOS in colon cancer patients is significantly down-regulated, and the expression of ICOS in melanoma will bring higher survival rate to patients. In another aspect, selective expression of ICOS in a population of "overactivated" Treg tumors has been shown to strongly inhibit T cell responses by IL-10 mediated APC inhibition. Melanoma can provide co-stimulation by ICOS to activate and amplify Treg in the tumor microenvironment, which provides another mechanism to evade immune surveillance. In view of the complexities of ICOS, scientists will develop agonists or antagonists to cope with tumor treatment depending on the actual situation. Currently, agonist antibodies such as GSK3359609, JTX-2011 and antagonist antibodies such as MEDI-570 have entered the clinical trial stage. Creative Biolabs' technical team is ready to work with you to design new ICOS agonist or antagonist antibodies based on your requirements, please contact us to inquire about the details of the service.
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
 Fig.1 Immunomodulatory mechanisms of CD137. (Yonezawa, 2015)
Fig.1 Immunomodulatory mechanisms of CD137. (Yonezawa, 2015)