Advantages Applications Our Services
Bispecific antibodies (BsAbs) are engineered antibody-derived proteins with two or more distinct binding specificities within one molecule, mainly produced by quadroma technology, chemical conjugation, or genetic approaches. A vast array of formats of BsAbs have been generated by different technologies to cater to research and clinical uses, including applications in diagnostics.
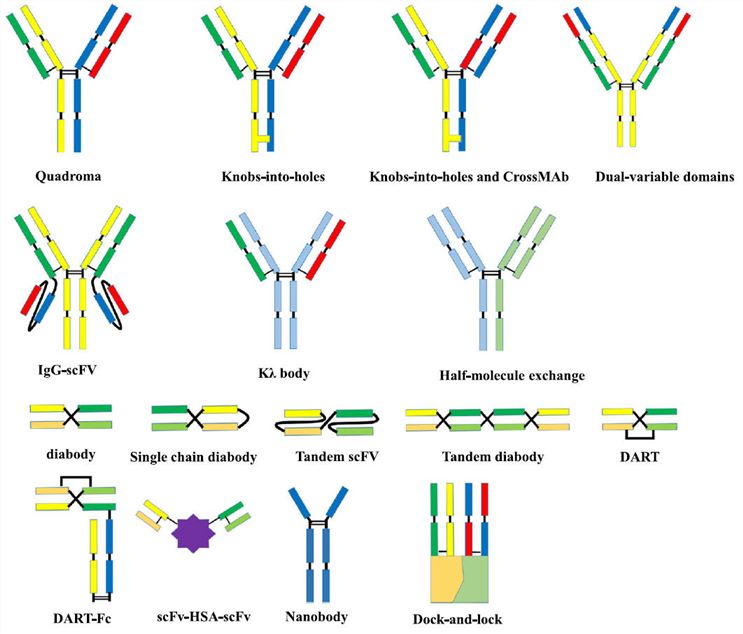
Fig. 1 Molecular formats of BsAbs.1
Advantages of BsAbs for Diagnostic
Owing to the potential of concurrent detection of multiple antigens or combining assay markers with antigen-binding sites, along with the flexibility and convenience in design, BsAbs have been considered as promising diagnostic immunoprobes with several remarkable advantages.
-
Simplified Detection: Functioning as cross-linkers to simultaneously bind antigens and reporters, BsAbs simplify the detection by omitting the chemical conjugation of the antibody with the detection sites, which eliminates the possibility of aggregations and/or inactivation of the molecule during chemical conjugation.
-
Enhanced Safety, Specificity, and Efficiency: Compared to conventional reagents, BsAbs also cause fewer harmful effects and reduce false-positive reactions, making detection more safe, specific, and rapid.
-
Optimized Purification: BsAbs for diagnostic applications are purified along with tagging, which makes the production more convenient.
-
Better Quality Control: BsAb reagents are uniform, homogenous, and have reproducible high specific activity. These features can effectively reduce batch-to-batch variations.
Application of BsAbs in Diagnostic
BsAbs have been widely used for the detection of viral or bacterial infectious diseases and in cancer diagnosis. They can participate in pre-targeting strategies in clinical diagnosis and provide better imaging for the early detection and diagnosis of tumors.
For instance, BsAbs that target human red blood cells (RBCs) and hepatitis B virus surface antigen (HBsAg) show encouraging diagnostic performance with high sensitivity (97.7%) and specificity (100%) in the detection of HBsAg in blood samples without special equipment or training. Furthermore, it is demonstrated that BsAbs targeting Lipoarabinomannan (LAM) and horseradish peroxidase (HRPO) significantly reduce the time required for detection of tuberculosis bacteria, from 2-6 weeks (traditional laboratory culture) to less than 2h, also ensuring high specificity (100%) and sensitivity (64%).
In medical imaging for cancer and potential lesions, pre-targeted detection based on BsAbs and small radiolabeled molecules exhibits high binding specificity, sensitivity, and safety, which compensates for the limitations of 18F fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) in recognizing small tumors (less than 1 cm) and inflammatory or infectious lesions.
Our Services
With our high-caliber BsAbs development platforms, Creative Biolabs is dedicated to providing customers with qualified and reliable one-stop services related to BsAbs, from design, engineering, purification to analysis, and manufacturing. We are here to assist your research for both scientific and clinical purposes. Please do not hesitate to contact us for more detailed inquiries.
Reference
-
Fan, Gaowei, et al. "Bispecific antibodies and their applications." Journal of hematology & oncology 8 (2015): 1-14. (Under open access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.)
Our products and services are for research use only, and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Welcome! For price inquiries, we will get back to you as soon as possible.
To order, please email
INQUIRY





