Epitope mapping aims at identifying the binding sites of antibodies on their target antigens. It has become increasingly important in many immunological applications, including the discovery and development of new vaccines and antibody drugs. With skills and knowledge on epitope mapping, Creative Biolabs provides B cell epitope mapping services specializing in conformational and linear B-Cell epitopes.
B cells are considered to be a core component of the adaptive immune system because they provide long-term protection against infectious pathogens. They perform these functions by producing antibodies that recognize their molecular target (called antigen) by binding to a part of it (called epitope) in a highly selective manner. Thus, epitopes are binding areas on antigens. B cell epitopes are classified into two categories: linear (continuous or sequential) and conformational (nonlinear or discontinuous) epitopes. The linear B cell epitopes are made up of contiguous stretch of amino acids in antigen, whereas conformational B cell epitopes constitute the spatially folded amino acids, which lie far away in the protein sequence. 10% of the epitopes belong to the linear table, and 90% of the epitopes belong to the conformational epitope. Although the majority of B cell epitopes are conformational, most of them are composed of 1–5 linear stretches.
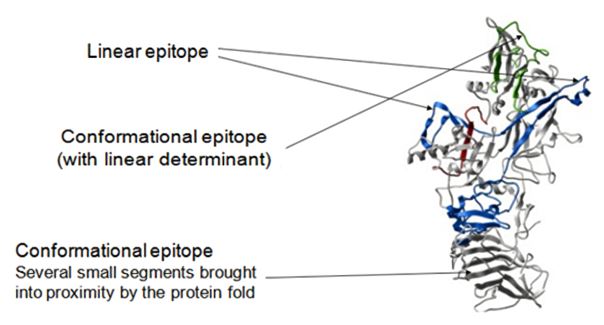 Fig.1 B cell epitope.
Fig.1 B cell epitope.
Conformational B-cell epitopes have been studied extensively due to their immunological applications, such as peptide-based vaccine development, antibody production, and disease diagnosis and therapy. Epitope mapping of an antibody will greatly facilitate antibody drug discovery and design. Experimental epitope mapping can be generally divided into structural and functional studies.
Structural approaches
The most commonly used method for structural epitope mapping is X-ray crystallography, which is used to map linear and conformational epitopes and provides information on the binding strength of antigen-antibody (Ag-Ab) complexes. However, X-ray crystallography is limited by the quality of cocrystals and electron density of the antibody. To this end, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and electron microscopy (EM) has been developed to compensate for the deficiencies of conventional X-ray crystallography. NMR provides data on the structure, kinetics and binding energy of the Ag-Ab complex and is carried out in a solution that does not require crystals. For small proteins and peptides (<25 kDa), NMR can be used for mapping, and for very large assemblies (such as whole viral particles), EM can be used to identify approximate contact areas.
Functional approaches
Methods for functional epitope mapping can be divided into four groups: competition mapping, protein fragmentation, antigen modification, and synthetic peptides or peptide libraries method. Most functional methods are based on the ability to detect binding of the antibody to antigen fragments, synthetic peptides, or recombinant antigens (including mutant variants, antigens arrayed by in situ cell-free translation, and/or expressed using selectable systems such as phage display). In the binding assay, the peptide is immobilized on a solid support and the binding of the antibody is detected by Western blot, dot blot and/or ELISA. This method does not require expensive equipment and is capable of quantifying immune responses to specific epitopes. The peptides can be synthesized on pins, on a cellulose membrane support, or on peptide microarrays. These methods simplify the processing of a large number of peptides and do not require the identification of positive peptides by sequencing or mass spectrometry. Binding assays have been successfully used to identify epitopes in several viruses, bacteria, fungi, parasites, and human diseases.

Creative Biolabs' dedicated immunologists and excellent teams can add real value to your research projects. Contact us to discuss your project and we will design an assay tailored to achieve your objectives.
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.