Blueberry-derived Exosome Research & Application
Overview Advantages Research Potentiality Services Products FAQs
Beyond the Superfruit: Unveiling Nature's Nanoscopic Messengers
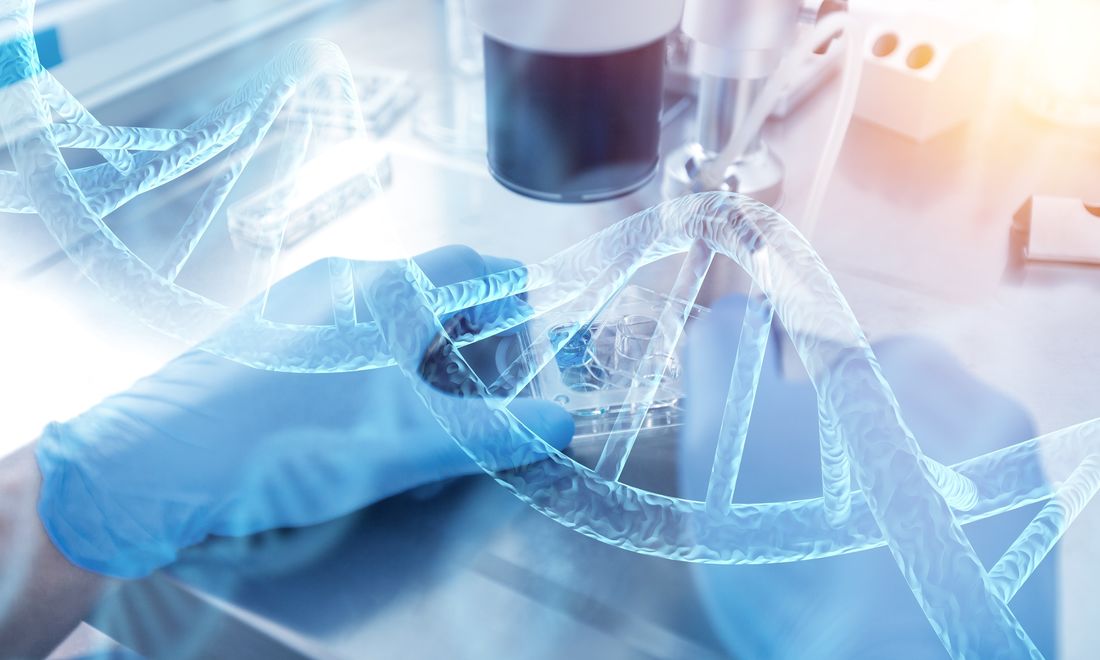
The blueberry, a fruit celebrated for its rich profile of bioactive compounds, has long been associated with significant health benefits, including potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. These properties are largely attributed to a high concentration of polyphenols, such as anthocyanins and flavonoids. In recent years, the field of intercellular communication has been revolutionized by the study of exosomes, which are nanoscale lipid bilayer vesicles that transport molecular cargo between cells. The convergence of these two fields has given rise to a compelling new area of investigation: blueberry-derived exosome.
Launch Your Blueberry Exosome Project Today. Get a Custom Quote.
The rationale for studying these plant-derived nanovesicles is multifaceted. Blueberries represent a natural, edible, and biocompatible source of nanoparticles that may encapsulate the fruit's therapeutic molecules. These exosomes could function as endogenous nanocarriers, protecting their bioactive cargo from degradation and facilitating its transport across biological barriers to target cells. Investigating blueberry-derived exosomes, therefore, is not merely an extension of nutritional science but a pioneering step into the realm of natural nanomedicine, offering a novel paradigm for developing safer and more effective therapeutic and drug delivery platforms.
The Natural Advantage: Superior Biocompatibility and Inherent Bioactivity
The unique benefits of blueberry-derived exosomes stem directly from the rich biochemical profile of their source. Naturally equipped with antioxidant and bioactive molecules, these nanovesicles hold strong potential to counter oxidative stress—a key driver of many chronic conditions. The key advantages include:
Built-in Bioactivity
Unlike synthetic liposomes, blueberry exosomes come pre-loaded with a synergistic mix of therapeutic compounds—including polyphenols and microRNAs (miRNAs)—that can deliver antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory effects.
Biocompatibility and Safety
As plant-derived vesicles from an edible source, they demonstrate excellent biocompatibility and low immunogenicity, making them a promising alternative to viral vectors or synthetic nanoparticles.
Stability and Bioavailability
Their protective lipid bilayer shields molecular cargo from enzymatic degradation in the digestive tract, offering the potential for oral delivery and improved absorption of otherwise poorly available compounds.
Natural Targeting Potential
Emerging evidence suggests that plant exosomes may carry surface ligands that support selective uptake by mammalian cells, opening opportunities for enhanced therapeutic precision.
Ready to take the next step? Connect with our exosome experts today.
Validating the Potential: A Synopsis of Groundbreaking Research
Recent scientific literature has begun to substantiate the therapeutic promise of blueberry-derived exosomes. Seminal studies have provided compelling evidence of their bioactivity across various preclinical models:
-
1. Metabolic & Liver Health
-
Significantly ameliorated nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in high-fat diet mice.
-
Reduced ROS in hepatocytes, activated the Nrf2 antioxidant pathway, and inhibited enzymes driving de novo lipogenesis.
-
2. Gut & Immune Modulation
-
Efficiently internalized by intestinal epithelial cells, delivering functional RNA cargo.
-
Down-regulated LPS-induced inflammatory genes, indicating strong anti-inflammatory potential in the gut.
-
3. Vascular Protection & Delivery Potential
-
Countered TNF-α-induced oxidative stress in endothelial cells and modulated 29 key inflammatory/metabolic genes.
-
Advanced methodologies identified Class I chitinase as a universal plant exosome marker.
-
Demonstrated high drug-loading capacity, reinforcing their promise as delivery vehicles.
Accelerate Your Research. Request a Proposal.
Harnessing the Promise: The Next Wave of Therapeutics and Delivery Systems

The convergence of inherent bioactivity, safety, and drug delivery capabilities positions blueberry-derived exosomes at the forefront of nanomedicine innovation. Their potential applications are extensive and transformative:
 Therapeutic Agents
Therapeutic Agents
As direct therapeutic agents, they hold promise for the management of chronic inflammatory and metabolic diseases, including NAFLD, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), cardiovascular conditions, and neurodegenerative disorders.
 Drug Delivery Systems
Drug Delivery Systems
Blueberry exosomes represent a next-generation platform for delivering a wide range of therapeutic payloads, such as small molecule drugs (e.g., curcumin), siRNAs, and therapeutic proteins. Their natural origin and potential for oral delivery could overcome major hurdles in modern pharmacology.
 Nutraceuticals and Functional Foods
Nutraceuticals and Functional Foods
The integration of blueberry exosomes into foods or dietary supplements could offer a highly bioavailable and effective means of delivering the health benefits of blueberries, moving beyond traditional extracts to targeted molecular delivery.
Unlock the Potential of Natural Nanotechnology. Schedule Your Free Consultation.
Accelerate Your Innovation: Our Integrated Exosome Research & Development Platform
At Creative Biolabs, we provide a comprehensive, end-to-end platform to support and accelerate research and development in the field of blueberry-derived exosomes. Our integrated service portfolio is designed to meet the rigorous standards of academic and industry research, encompassing every stage from discovery to functional validation. Our expert services include:
Utilizing state-of-the-art techniques to isolate high-purity exosome populations from blueberries.
Employing advanced analytics such as nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and mass spectrometry to define vesicle size, morphology, and composition.
Conducting detailed analysis of exosomal cargo, including exosomal RNA isolation and qPCR analysis, as well as exosomal protein isolation and profiling, to elucidate mechanisms of action.
Offering a suite of validated assays and disease models to assess the bioactivity and therapeutic efficacy of blueberry-derived exosomes in areas like antioxidant therapy, anti-inflammatory applications, and drug delivery.
Transform Your Product with Nature's Innovation. Let's Talk.
Revolutionizing Cosmetics: Premium Ingredients for Advanced Skincare
Leveraging the potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of blueberry-derived exosomes, Creative Biolabs is proud to offer these innovative nanoparticles as premium raw materials for the cosmetic and skincare industry.
Potential Benefits for Skincare Formulations:

Powerful Antioxidant Defense
Neutralizes free radicals to protect skin from oxidative stress and premature aging.

Anti-Inflammatory Action
Naturally soothes irritation and calms inflamed or sensitive skin.

Efficient Delivery System
Exosomes carry bioactive molecules deep into the skin, enhancing absorption and efficacy.
Potential Applications:
|
Anti-aging serums
|
Protective creams
|
Treatments for sensitive or inflamed skin
|
These features provide a natural, science-backed solution for next-generation cosmetics.
Harness the Power of Plant-Derived Exosomes. Ask about our custom products.
FAQs
Q: How do blueberry-derived exosomes differ from those derived from mammalian cells?
A: Blueberry-derived exosomes originate from a plant source, which makes them a unique and advantageous platform. Key differences include their innate cargo of plant-specific bioactive molecules (like anthocyanins), their potential for oral bioavailability due to stability in the GI tract, and a significantly lower risk of containing mammalian pathogens or immunogenic components.
Q: Can the molecular cargo of blueberry exosomes be customized for specific applications?
A: Yes. While blueberry exosomes have a powerful endogenous cargo, their structure makes them excellent candidates for exogenous drug loading. Creative Biolabs provides services to load these natural nanovesicles with specific small molecules, nucleic acids, or proteins, thereby creating customized, targeted therapeutic delivery systems.
Q: What quality control measures are in place for customized blueberry exosome products?
A: Creative Biolabs adheres to stringent quality control protocols. Each batch of blueberry-derived exosomes undergoes rigorous characterization to ensure consistency, purity. This includes NTA for size and concentration, TEM for morphology verification. In addition, you can choose whether to perform proteomic/RNA profiling to confirm the presence of key biomarkers and bioactive cargo.
Q: What is the expected yield of exosomes from blueberries, and how does it impact scalability?
A: The yield can vary based on the fruit's cultivar, ripeness, and the extraction method employed. To address this, Creative Biolabs offers an initial assessment service to determine the exosome yield from a specific source material. This evaluation allows us to provide clients with a reliable and accurate production quote for scalable manufacturing, ensuring a consistent supply for both research and commercial applications.
Have a Project in Mind? Let's Build a Solution Together.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:
















