Grape-derived Exosome Research and Application
Introduction Service Workflow Technology Advantages Testimonials FAQ
Introduction
Grape-derived exosomes (GEVs) represent a fascinating advancement in plant nanovesicle research. Naturally occurring, nanoscale vesicles isolated from grape juice, GEVs are rich in antioxidants and bioactive molecules that play significant roles in intercellular communication and nutrient transport. Creative Biolabs, a pioneer in plant-derived exosome research, offers an advanced portfolio of grape exosome services to support diverse basic research goals in biotechnology, molecular biology, and plant sciences.
Unlike traditional extracts, GEVs offer greater biological stability and targeted delivery capabilities. Their phospholipid bilayer protects active compounds during delivery, and their vesicular structure enables efficient penetration into cells and tissues. This makes them a valuable subject for studies on cellular communication, antioxidant action, and tissue homeostasis.
Customized Services for GEV Investigation
Creative Biolabs delivers tailored solutions to meet the evolving demands of plant-derived exosome research. Our grape exosome service platform includes:
-
Exosome Isolation & Purification: High-yield and reproducible extraction via differential centrifugation and sucrose density gradients.
-
Characterization Services: DLS, NTA, TEM, Western blot, and lipidomics for structural and biochemical profiling.
-
Bioactivity Testing: Functional assays to evaluate antioxidant properties, cellular uptake, and biological effects.
-
Molecular Profiling: Transcriptomic (miRNA-seq), lipidomic, and proteomic analyses.
-
Custom Pilot Studies: Designed to explore grape cultivar differences or evaluate novel hypotheses in exosome research.
Each project at Creative Biolabs is supported by a dedicated technical team to ensure rigorous experimental design and reliable data delivery.
From Vineyard to Vesicle: Our Standard Workflow
Our standardized yet customizable workflow ensures optimal isolation of GEVs with minimal degradation of bioactivity:
-
Selection of Grape Donors: Fresh, pesticide-free grapes are chosen for high vesicle yield.
-
Juice Extraction: Mechanical processing followed by low-speed centrifugation.
-
High-Speed Ultracentrifugation: Vesicle separation based on size and density.
-
Sucrose Gradient Refinement: Ensures high-purity exosomes.
-
Quality Control: NTA, TEM, and biochemical validation.
-
Storage: Cryopreservation to maintain stability and activity.
The entire process avoids organic solvents and harsh chemicals, preserving vesicle integrity and maximizing downstream usability.
Advanced Tools Behind Our Exosome Platform
Creative Biolabs' GEV platform is built upon cutting-edge instrumentation and methodologies:
-
Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) and Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) for particle size and concentration.
-
Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) for morphology visualization.
-
Lipidomics & miRNA Profiling to reveal unique lipid and genetic signatures.
-
Fluorescent Tracing and qPCR assays to track distribution and biological impacts.
Together, these tools enable us to deliver a deep mechanistic understanding of exosome function, laying the foundation for tailored applications in fields ranging from healthcare to agricultural sciences. Our platform's versatility ensures that we can support a broad spectrum of research, whether you're investigating therapeutic potential, nutrient delivery, or materials innovation.
Why Work With Creative Biolabs?
-
Partnering with Creative Biolabs means more than just outsourcing a service — it's about collaborating with a dedicated research partner committed to advancing your scientific goals. We stand out by maintaining exceptional quality standards across every step of our process. All our GEVs are rigorously validated for structural integrity, purity, and biological activity, ensuring consistency and reproducibility for your experiments.
-
Our scalable production streams enable us to meet diverse project needs, from small-scale discovery research to larger pilot studies. This flexibility allows clients in various industries—whether cosmetics, plant biology, or materials science—to efficiently integrate our exosomes into their workflows. Behind this is our unwavering commitment to quality control, with protocols designed to eliminate contaminants and preserve biological functionality, making our vesicles safe for a wide range of downstream applications.
-
Moreover, our team takes pride in providing responsive, personalized support. We work closely with researchers to understand their particular scientific questions and tailor our services accordingly. This collaborative approach helps streamline research, saves time, and accelerates discovery.
Researcher Experiences
"Creative Biolabs' grape exosome service allowed us to compare different grape cultivars for antioxidant activity using standardized methods. Their team was fast, communicative, and clearly very experienced in the field."
— Dr. EleXXXX
"The bioactivity data from Creative Biolabs gave us a strong foundation to explore exosomes as nanocarriers in nutrient delivery studies. We're already planning a second round of experiments."
— Dr. SamXXXX
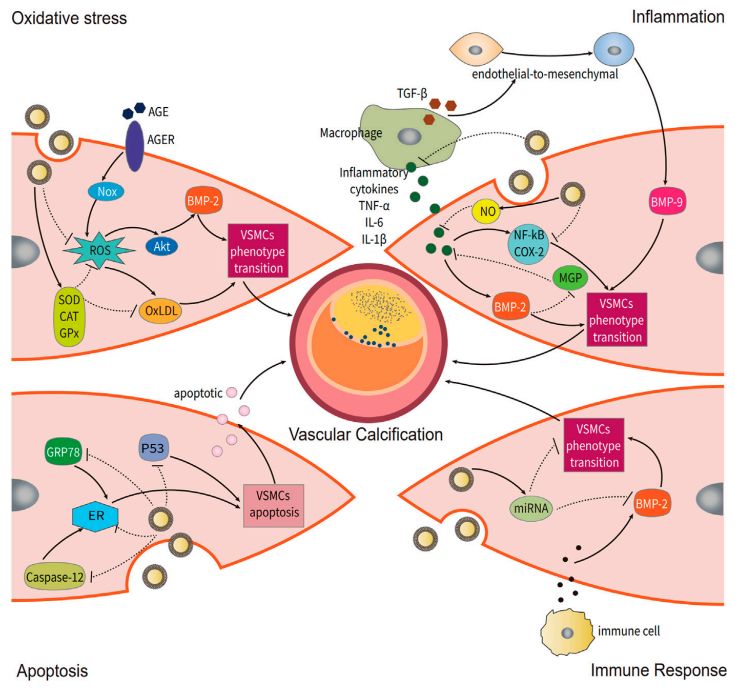 Fig. 1 Potential of grape-derived exosomes to alleviate vascular calcification.1
Fig. 1 Potential of grape-derived exosomes to alleviate vascular calcification.1
Working with Creative Biolabs offers not just a service but a partnership built on trust, expertise, and shared innovation. We look forward to helping you unlock the full potential of grape-derived exosomes for your research and development goals. Contact us today to learn how Creative Biolabs' grape exosome platform can advance your research goals in plant-derived nanovesicle science.
Common Questions Answered
Q: How can researchers validate the functions of grape-derived exosomes in scientific studies?
A: Researchers can validate the functions of grape-derived exosomes through a variety of techniques, including functional assays that measure cellular responses, transcriptomic and proteomic analyses to assess gene and protein expression changes, and in vivo studies to observe physiological effects in plants or model organisms.
Q: How do grape-derived exosomes enhance product efficacy?
A: Grape exosomes are known for their ability to carry and deliver various biomolecules, including proteins, lipids, and RNA. This delivery system enhances product efficacy by ensuring that these bioactive compounds penetrate deeper into the skin or target cells, resulting in improved bioavailability and therapeutic effects compared to conventional formulations.
Q: What are the unique benefits of grape-derived exosomes in cosmetic applications?
A: Grape-derived exosomes are rich in bioactive compounds that exhibit antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. These characteristics make them highly beneficial in skincare formulations, as they can help to improve skin barrier function, enhance hydration, and promote a more youthful appearance. Their ability to facilitate cellular communication is also key to skin rejuvenation.
Q: What potential applications do grape exosomes have beyond cosmetics?
A: Beyond their application in cosmetics, grape-derived exosomes have shown promise in various fields, including agriculture. They can be utilized as natural biostimulants to enhance plant growth and stress resistance. Additionally, their unique properties may open avenues for use in food technology, where they can potentially improve food preservation and safety.
Q: Are there specific grape varieties that produce superior exosomes for research?
A: Yes, certain grape varieties have been found to produce exosomes with exceptional properties and bioactive content. Research into different grape cultivars allows us to identify those that yield the most beneficial exosomes, providing insights for their selective use in both research and application development.
Reference
-
Teng, Yintong, et al. "Grape exosome-like nanoparticles: A potential therapeutic strategy for vascular calcification." Frontiers in Pharmacology 13 (2022): 1025768. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig. 1 Potential of grape-derived exosomes to alleviate vascular calcification.1
Fig. 1 Potential of grape-derived exosomes to alleviate vascular calcification.1









