Plant-derived Exosome Isolation and Development Service
Overview Services Features FAQs
Creative Biolabs has launched an innovative customized production service for plant-derived exosomes, capable of providing pilot study services for short-batch isolation and expanding to large-scale manufacturing development services.
Overview
Fruit-derived exosomes
-
Mainly found in the pericarp, pulp, and other parts of the fruit
-
Their generation is regulated by plant growth stage, environmental conditions, and other factors.
-
Rich in antioxidants, vitamins, hormones, signaling molecules, and other substances, with antibacterial, antioxidant, promote cell proliferation and immune regulation, and other biological activities.
Vegetable-derived exosomes
-
Generally found in tissues such as leaves, roots, and seeds.
-
Rich in nutrients, such as vitamins, alkaloids, dietary fiber, etc. as well as various bioactive substances, such as antioxidants, anticancer substances, and immunomodulatory substances.
-
Possess positive effects on human health in multiple ways, such as the prevention of chronic diseases, improvement of digestive system function, and regulation of the immune system.
Medicinal plant-derived exosomes
-
Mainly distributed in roots, stems, leaves, and other parts.
-
Rich in active ingredients, such as alkaloids, flavonoids, saponins, volatile oils, and so on.
-
With pharmacological activity and biological activity, exosomes are not only an important source of extracted active ingredients, but also of significance to the in-depth understanding of the pharmacological effects and mechanisms of medicinal plants.
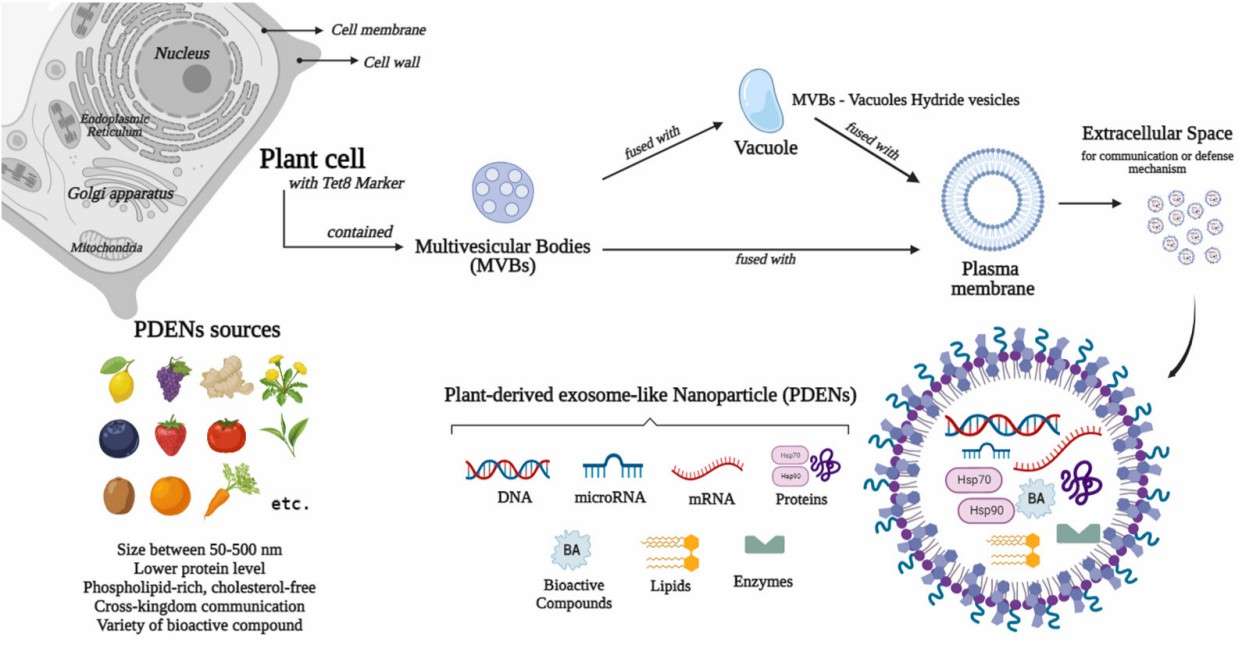 Fig.1 Sources, biogenesis, and contents of plant-derived exosomes.1
Fig.1 Sources, biogenesis, and contents of plant-derived exosomes.1
Plant Exosome Development Services
At Creative Biolabs, plant exosome production services start with pilot studies of exosome isolation and functional validation from small batches of plant samples, and if the pilot results meet client's expectations, further expansion to large-scale manufacturing development, or even GMP manufacturing, is possible.
Pilot Study
PART 1 Exosome isolation from small batches of plants
-
Plant sample preparation: pre-treated samples of native plants provided by the customer or specified plant types provided by the supplier
-
Plant exosome isolation: by pretreatment + filtration and concentration + ultracentrifugation
-
Plant exosome characterization: detection of particle size and morphology (by NTA and TEM)
-
Cell experiments:
-
Cellular uptake of exosomes assay
-
Cell migration assay
-
Cell scratching assay
PART 2 Exosome quality control
-
Mycoplasma assay (By PCR).
-
Sterility assay, PCR assay to identify bacteria, and sequencing to identify fungi.
-
Endotoxin assay (By Gel Clot LAL).
-
Endotoxin removal. Perform endotoxin removal to a limited sensitivity value for single samples in single runs.
PART 3 Animal experiments
-
Rat skin wound modeling.
-
Exosome administration.
-
Wound healing assay.
-
H&E histology analysis.
-
Routine pathological analysis.
If pilot study results meet requirements, then expand to large-scale manufacturing.
-
Determine output rates
-
Scientific grade manufacturing
Our Plant Exosome Service Features
-
Advanced Isolation Techniques:
-
Ultracentrifugation: Separates exosomes by density through multiple centrifugation rounds.
-
Precipitation-Based: Selectively precipitates exosomes using reagents like polyethylene glycol.
-
Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC): Separates exosomes by size using appropriate column pore sizes.
-
Density Gradient Centrifugation: Separates exosomes based on density differences through gradient centrifugation.
-
Immunoaffinity Capture: Selectively isolates exosomes using antibodies specific to exosomal surface markers.
-
Customized Development:
Whether you require plant exosomes for drug delivery, diagnostics, or research purposes, we can design a solution that meets your requirements.
-
Quality Assurance:
We ensure that the exosomes isolated are of the highest quality and suitable for the intended applications.
FAQs
Q: What plant sources do you work with for exosome isolation?
A: Our proficiency lies in the isolation of exosomes from diverse plant sources, encompassing fruits, vegetables, herbs, and medicinal plants, among others.
Q: What downstream applications are your plant-derived exosomes suitable for?
A: Our plant-derived exosomes have extensive purposes including drug delivery, nutraceutical development, agricultural biotechnology, and biomedical research.
Creative Biolabs' plant-derived exosome isolation and development services offer cutting-edge solutions for extracting exosomes from plant sources and harnessing their potential for various applications. To find out more about how we may help you with your research, kindly contact us.
Reference
-
Sarasati, Andari, et al. "Plant-Derived Exosome-like Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications and Regenerative Therapy." Biomedicines 11.4 (2023): 1053. Under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. The image was modified by revising the title.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Sources, biogenesis, and contents of plant-derived exosomes.1
Fig.1 Sources, biogenesis, and contents of plant-derived exosomes.1









