Immunomodulating Multi-antibody-modified Exosome Service
Overview Services Features FAQs
Modulation against immune checkpoints and related molecules is one of the functions of the multi-specific antibody-modified exosomes that are available at Creative Biolabs. We can control the usual immunological effects of exosome engineering by organizing and combining different antibodies to immunomodulatory molecules and altering them on exosome membranes via genetic engineering or surface coupling.
Introduction of Immunomodulating Multi-Specific Antibody-Modified Exosomes
Cancer treatment has undergone a paradigm shift thanks to immunotherapy, and several new immunomodulatory targets, including PD-L1, CD3, and OX40, have been identified. Immune checkpoint inhibitors have become increasingly significant in the treatment of cancer, dramatically enhancing prognosis and survival.
-
The interaction of PD-1 with PD-L1 has been detected in a variety of cancers, where expression of PD-1 on T cells suppresses immunity and enhances the growth of different types of PD-L1-positive tumors. In contrast, PD-1 modification on exosomes was found to compete for binding PD-L1 and to have stronger and more stable immunotoxic effects than its soluble form.
-
Anti-CD3-modified exosomes induce the proliferation of resting CD3+ T cells and increase their cytokine and chemokine levels, triggering the release of cytotoxins into cancer cells and leading to cell death.
-
OX40L-modified exosomes bind OX40 and deliver co-stimulatory signals to activate the classical NF-κB1 pathway or non-classical NF-κB2 pathway, PI3k/PKB, and NFAT pathways, thereby promoting effector T cell survival, memory T cell expansion and expression of cytokine receptor-related genes to enhance immune system response.
Immunomodulating Multi-antibody-modified Exosome Engineering Strategy
Exosomes have a different lipid composition than the plasma membrane, suggesting a different and more complex origin than simple membrane outgrowth. They contain proteins that are retained from the primary cell through biogenesis, based on which the primary cell can be genetically modified to produce the desired exosome.
Co-expression of the aforementioned immunomodulatory antibodies/ligands and antibodies to tumor-specific membrane proteins onto exosomes can specifically pull T cells and tumor cells together to develop a cutting-edge approach for therapy. In particular, considering the potential impact of individual antibody tropism on the physicochemical and biological properties of engineered exosomes, by aligning the VH and VL of these single-chain antibodies in different orientations and junctioning them with flexible peptides, these antibodies achieve the display of exosomal surface through membrane proteins as a fusion scaffold, directing the killing toxicity of immune cells.
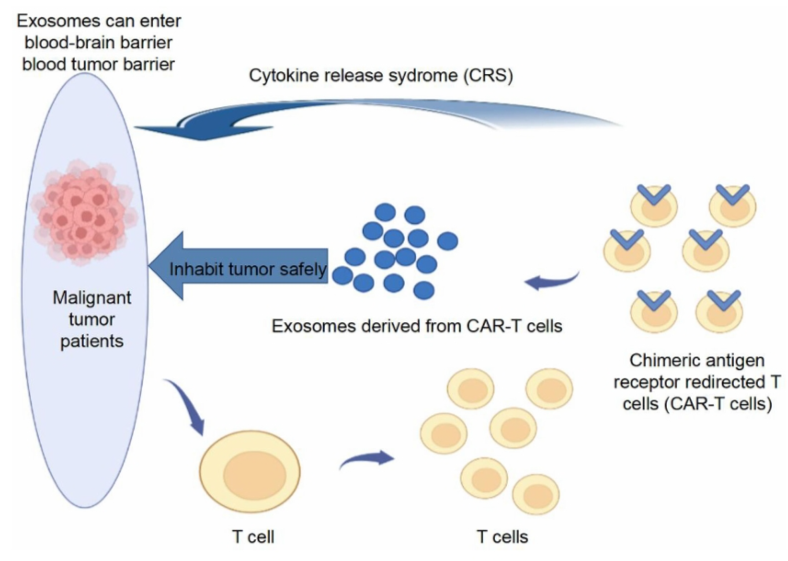 Fig. 1 CAR-T cell-derived exosomes for tumor treatment.1
Fig. 1 CAR-T cell-derived exosomes for tumor treatment.1
Features
-
Tailored Immunomodulation: Our exosome service offers personalized immunomodulation by leveraging multi-antibody modification, ensuring targeted responses for diverse immune profiles.
-
Enhanced Efficacy: Through precise antibody modification, our exosomes exhibit heightened efficacy in modulating immune responses, optimizing outcomes in various conditions.
-
Versatile Applications: These modified exosomes find utility across a spectrum of diseases, including autoimmune disorders, cancers, and inflammatory conditions, offering promise for versatile therapeutic development.
-
Minimized Side Effects: With tailored targeting and modulation, our exosomes minimize off-target effects, enhancing safety profiles and improving tolerance to interventions.
-
Advanced Delivery System: Utilizing exosomes as carriers ensures efficient delivery of therapeutic payloads, overcoming biological barriers and facilitating precise immune modulation.
Creative Biolabs provides innovative engineering modification services for the expression of antibodies to immunomodulatory molecules and antibodies to cancer cell-positive proteins on exosomes, significantly improving the degree of response to exosome-induced immunity. Please contact us to learn more.
FAQs
Q: What is the focus of research on Immunomodulating Multi-antibody-modified Exosome Service?
A: Research in this field aims to investigate the immunomodulatory properties of exosomes modified with multiple antibodies, exploring their potential for regulating immune responses in various diseases and conditions.
Q: How do Immunomodulating Multi-antibody-modified Exosomes affect the immune system?
A: These exosomes are designed to interact with immune cells and modulate their functions, such as promoting immune activation, suppressing inflammation, or inducing tolerance, depending on the specific antibodies incorporated into their structure.
Q: How are the antibodies selected for modification?
A: Antibodies are selected based on their specificity to target antigens relevant to the desired immunomodulatory response. Our experts employ rigorous screening processes to ensure optimal antibody selection.
Reference
-
Zhou, Qiujun, et al. "T cell-derived exosomes in tumor immune modulation and immunotherapy." Frontiers in Immunology 14 (2023): 1130033. Under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig. 1 CAR-T cell-derived exosomes for tumor treatment.1
Fig. 1 CAR-T cell-derived exosomes for tumor treatment.1









