Liver-Targeted Exosome Modification Service
Overview Services Features FAQs
To improve the targeting of exosome carriers to the liver, Creative Biolabs provides research services for liver-targeted modification of natural exosomes using a technology platform that combines biomaterials science and molecular engineering.
Exosomes for Targeted Delivery
-
Denaturation and degradation of the carrier system in the circulation impairs the stability of drugs and molecules during delivery, being a major impediment to targeted drug release. Although non-viral carriers such as natural exosomes improve the prolonged circulation of cargo and cause lower immunogenicity and hepatotoxicity, there is still difficulty in achieving enrichment of tissue-specific exosomal carriers after systemic administration.
-
Targeted therapy is mainly a drug delivery system in which carriers selectively concentrate and localize drugs to specific target areas by local administration or systemic administration under guided polarization including magnetic fields and antibodies. It involves targeting mechanisms such as biophysical targeting, biochemical targeting, bioimmune targeting and targeting precursors.
-
Exosome targeting research is currently focused on two levels of biochemical targeting, and bioimmune targeting using membrane surface receptor/antibody specificity. With the abundant blood flow, the vascular uptake and accumulation of exosomes in the liver is high, making the liver a frequent organ of targeting in the delivery of therapeutic drugs. It is also promising to develop synthetic liver-directed drug carriers. For synthetic liver-targeted exosome carriers, displaying liver-specific ligands on their surface can achieve targeting ability to their receptors and enhance exosome enrichment in the liver.
Exosome Modifications Targeting the Liver at Creative Biolabs
Creative Biolabs provides research services in various aspects, including exosome modification for targeted liver, function and mechanism, and controlled release.
-
Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) can bind to low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptors on the membrane surface of hepatocytes, allowing the construction of ApoE-modified exosomes that can specifically accumulate in liver tissue. Several previous studies have shown that compared to bare exosomes, such surface-linked ApoE exosomes not only significantly improve the transfection efficiency of plasmid cargoes in hepatocytes, but their tumor suppressive effect after loading with antitumor drugs is also enhanced.
-
The presence of SR-B1, a specific receptor for high-density lipoprotein (HDL), was found on the hepatocyte membrane, suggesting that apo-A1, the major apolipoprotein of HDL synthesized by the liver, could serve as another potential liver-targeting peptide. It provides a new idea to confer hepatic targeting properties through the modification of apoAI-modified exosomes.
-
It has also been discovered that exosomes expressing integrin αVβ5 can interact with hepatic vitronectin and are potential targets for studying liver metastasis.
-
In addition to displaying exosomes on the surface with targeting peptides, choosing the appropriate source of cell types would also influence the hepatic tropism of exosomes. For example, exosomes isolated from hepatic stellate cells have a natural hepatic targeting and may serve as delivery vehicles for different hepatic drugs, facilitated by the homologous tissue targeting ability.
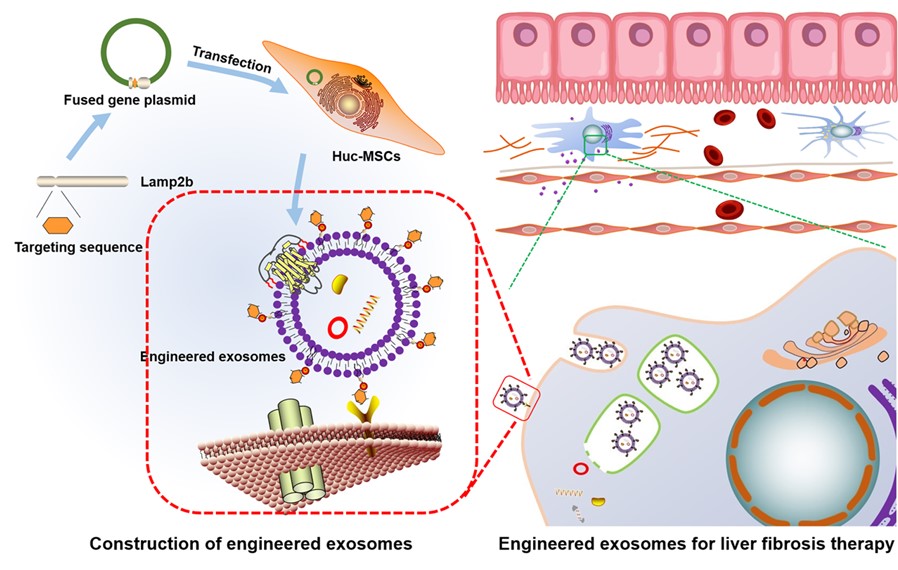 Fig. 1 Engineered exosomes for targeted therapy of liver fibrosis.1
Fig. 1 Engineered exosomes for targeted therapy of liver fibrosis.1
Features
-
Customized modification: Our service offers tailored modifications to target exosomes specifically to the liver, enhancing their ability to deliver therapeutic cargo to liver cells effectively.
-
Advanced technology: We utilize cutting-edge techniques and expertise to modify exosomes with precision, ensuring optimal targeting and delivery to the liver.
-
Increased therapeutic potential: By targeting exosomes to the liver, our service enhances the therapeutic potential of exosome-based therapies for liver-related conditions.
FAQs
Q: What types of cargo can be loaded into liver-targeted exosomes?
A: Our service is capable of loading various types of cargo that can be tailored to target specific liver cells or tissues.
Q: Is liver-targeted exosome modification suitable for all liver-related conditions?
A: Liver-targeted exosome modification is a versatile approach that can be customized to target a wide range of liver-related conditions, including liver fibrosis, hepatitis, and liver cancer. Our team will work with you to determine the most suitable modification strategy based on your specific requirements and goals.
As a leading service provider in the exosome field, Creative Biolabs is committed to providing clients with optimal modification services for targeted exosomes through surface modification and engineering edits. In addition to exosome preparation and cargo loading, we also provide research services related to exosome modification for the targeted liver to assist our clients in pursuing exosome applications. Please contact us to discuss your interest.
Reference
-
Lin, Yan, et al. "Huc-MSC-derived exosomes modified with the targeting peptide of aHSCs for liver fibrosis therapy." Journal of Nanobiotechnology 20.1 (2022): 432. Under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by extracting and using only a Part of the original image and revising the title.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig. 1 Engineered exosomes for targeted therapy of liver fibrosis.1
Fig. 1 Engineered exosomes for targeted therapy of liver fibrosis.1









