Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis-based Exosome Characterization Service
Overview Services Features FAQs
Overview
Exosomes are attracting increasing attention of researches in life science and pharmaceutical industry. In order to be of assistance, Creative Biolabs has established the nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) platform for exosome characterization. Based on this advanced platform, we can provide not only the size and concentration analysis but also analysis of phenotyping of exosome services for customers.
Due to the small sizes of exosomes, their analysis and quantification are often problematic. Commonly used techniques include isolation by ultracentrifugation, purification by sucrose cushion or gradients, immunoisolation by antibodies, western blotting, absorption onto latex beads followed by flow cytometry, atomic force microscopy and electron microscopy. Flow cytometry analysis of exosomes has also been reported, but is often confounded by the typical lower detection limit of 200–300 nm in most flow cytometers, although newly developed flow cytometers can now achieve better levels of detection. Recently, nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) has been utilized to visualise and measure nanoparticles within the size range of 30 nm to 1,000 nm.
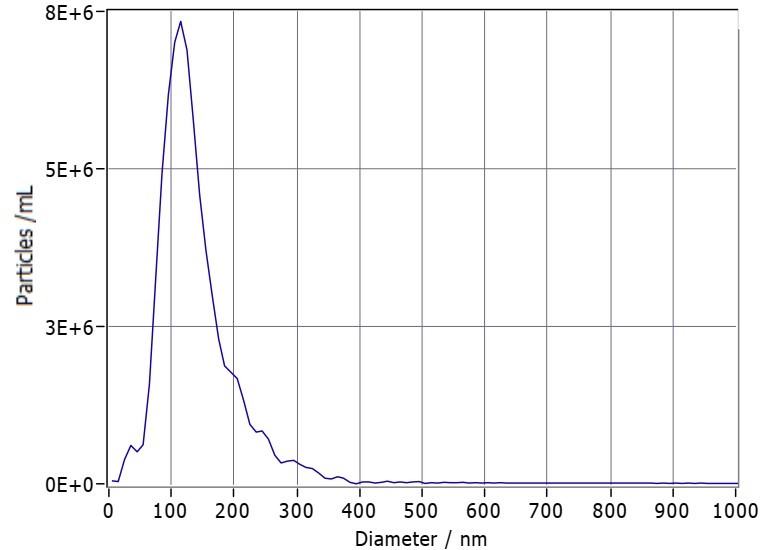 Fig.1 Presentation of particle size distribution from NTA.
Fig.1 Presentation of particle size distribution from NTA.
Services
Creative Biolabs offers robust technologies to solve the exsiting problems in exosome characterization.
-
Nanoparticle tracking analysis
Nanoparticle tracking analysis can accurately measure vesicle size and concentration. Particles move rapidly in a liquid sample under Brownian motion and act as point refractors when they pass through a laser beam. Videos can be recorded and a detailed differential particle size distribution graph can be produced using analytical software.
-
Fluorescence nanoparticle tracking analysis
Fluorescence nanoparticle tracking analysis (fl-NTA) allows for accurate sizing, counting, and phenotyping of exosome. Fluorophores (quantum dots) attached to antibodies or other biological probes, only vesicles fluorescently labeled are tracked. There are two protocols for the analysis of exosome using fl-NTA. The first protocol describes the use of the general cell membrane dye, to label exosome and their detection by fl-NTA. The second protocol is an antibody based method, for labeling exosome, with a Qdot-conjugated antibody specific for the target exosome marker, and then quantifying marker positive exosome using fl-NTA.
Features
-
Highly resolution of per particle
-
Particle count and concentration measurements
-
Skillful scientific team
-
Best after-sale service
With the help of our well-established technologies and experienced scientists, Creative Biolabs committed to develop NTA platform for exosome characterization services. We receive prepared exosome samples or exosome containing tissue samples (supported by our exosome isolation service). Based on your project purpose, you can choose nanoparticle tracking analysis or fl-NTA with different exosome labelling protocol. We are happy to make it accessible to all kinds of research and industrial customers. Besides, we are open to discussions. Please don't hesitate to contact us for more information.
FAQs
Q: Should I choose NTA or fl-NTA?
A: NTA is typically used for isolated exosomes to assess their size distribution and quantity; fl-NTA, based on membrane dyes, is generally employed for exosome quantification in cell culture supernatants or other biological fluids, whereas fl-NTA utilizing specific antibody labeling is commonly utilized for detecting the particle count of exosome subpopulations.
Q: Can fl-NTA detect multiple fluorescently labeled exosomes simultaneously?
A: Certainly. We are able to detect up to four fluorescently labeled exosome subpopulations. The project report will display the quantity and percentage of exosome subpopulations for each fluorescent label.
Q: How many exosome samples should I provide?
A:
|
Item
|
Minimum requirements
|
|
NTA
|
5μg/sample
|
|
fl-NTA
|
Inquiry
|
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:










