Most candidates for biotherapy will fail in the pre-clinical and clinical development stages, the so-called transitional phase of drug development. In general, protein aggregation is a well-known culprit in pharmaceutical biotechnology. Risk prediction and reduction methods for aggregation need to be applied early in the drug development cycle to facilitate early assessment and identification of potential problems, thereby reducing late-stage failure.
Protein aggregates can behave as reversible oligomers, subvisible or visible particles, or as precipitates. Protein aggregation is driven by many factors, including amino acid composition and sequence, environmental factors (such as pH, concentration, buffer/excipients and shear force in protein production), and final formulation and storage conditions. It may occur in different stages of production and development, such as fermentation, purification, preparation, filing, and storage. Studies have shown that aggregation has a significant impact on product quality and patient safety, especially because of the increased risk of the immune response. Therefore, some effective risk-recovery methods need to be applied in the early stages of drug development to facilitate early assessment and identification of potential problems and reduce failures in the later stages of development. Various in silico predictive tools have been developed in recent years in an attempt to predict the risk of aggregation in biopharmaceuticals.
The aggregation tendency of each protein seems to have evolved according to its natural abundance in the cell. Most currently available aggregation prediction tools are developed around specific aggregation pathways, such as beta-amyloid aggregation or aggregation through hydrophobic surface patches, which are suitable for detecting and redesigning specific regions of proteins that may be involved in specific types of aggregation.
In addition, some hotspot methods of aggregation have been especially applied to antibodies. The most notable tool is the Developability Index (DI) tool based on the concept of spatial aggregation propensity (SAP), which has been used to screen and arrange antibodies according to their aggregation propensity. The aggregation prediction tool can be used early in the drug development process, so as to be able to reduce the aggregation risk of guidance for sorting and selection. The application of this tool requires only the amino acid sequence of antibodies and provides a high throughput method for early screening and evaluation. The tool was used in engineering projects to screen many antibody variants targeting interferon gamma (IFNγ). It was successfully used in combination with in silico immunogenicity prediction to screen and select antibody variants with reduced aggregation and immunogenicity risks for in vitro expression and characterization. The accuracy of the model was demonstrated. It has excellent performance in predicting the aggregation risk of antibodies.
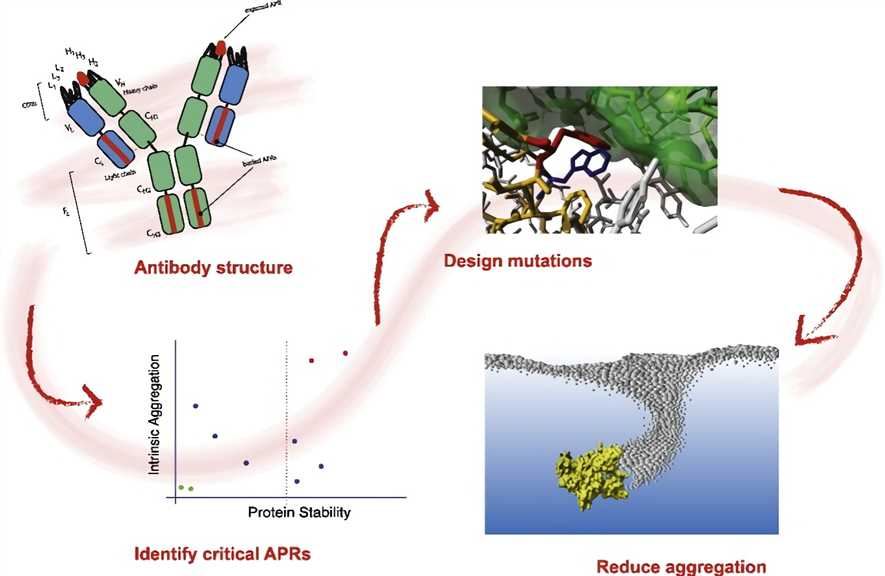 Fig.1 Prediction and reduction of the aggregation of mAbs. (van der Kant R, 2017)
Fig.1 Prediction and reduction of the aggregation of mAbs. (van der Kant R, 2017)
The application of aggregation prediction tools has been put into use as part of the workflow for evaluating the exploitability of biopharmaceuticals.
If you are interested in our services, please don't hesitate to contact us.
Reference
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.