Celery derived Exosome Research & Application
Overview Our Services Workflow Research Insights Platform Key Features Our Advantages What You Get Customer Voices FAQs
Natural Vesicles from Celery: A New Chapter in Plant Exosome Research
Celery (Apium graveolens) is widely known for its high nutritional content and functional properties in health foods. Beyond its use as a food crop, recent research has uncovered celery as a rich source of plant-derived exosomes, offering a compelling tool for biomedical and molecular studies. These nanovesicles, naturally secreted by plant cells, encapsulate bioactive molecules including proteins, lipids, RNAs, and metabolites, serving as stable and biocompatible delivery systems.
At Creative Biolabs, we specialize in isolating and characterizing vegetable-derived exosomes. Our scientific platform enables researchers to unlock the diverse potential of celery-derived exosomes (CDEs), from cargo analysis to cellular assays, with high reliability and experimental reproducibility.
Tailored Exosome Services
-
Raw Material Processing – Selection and preparation of high-quality celery to maintain biomolecule integrity.
-
Exosome Isolation – Ultracentrifugation-focused protocols for high-purity vesicle enrichment.
-
Lipidomic & Proteomic Profiling (Optional) – Deep characterization of exosomal content using LC-MS/MS and GC-MS.
-
Bioactivity Evaluation (Optional) – In vitro functional assays examining anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory properties.
-
Drug Delivery Assessment (Optional) – Model systems to study encapsulation and controlled release from celery exosomes.
With Creative Biolabs' full-stack technical support, researchers can pursue advanced studies into vesicle biology and intercellular communication.
From Plant to Vesicle: Our Optimized Workflow
-
Tissue Preparation – Thorough washing and blending of fresh celery tissue.
-
Filtration – Sequential filtering to eliminate large plant debris.
-
Differential Centrifugation – Low-speed spins to remove bulk contaminants.
-
Ultracentrifugation – High-speed isolation of nano-sized vesicles.
-
Gradient Purification (Optional) – Sucrose-based density gradient for exosome refinement.
-
Final Wash & QC – Resuspension in PBS, followed by particle size and concentration assessment.
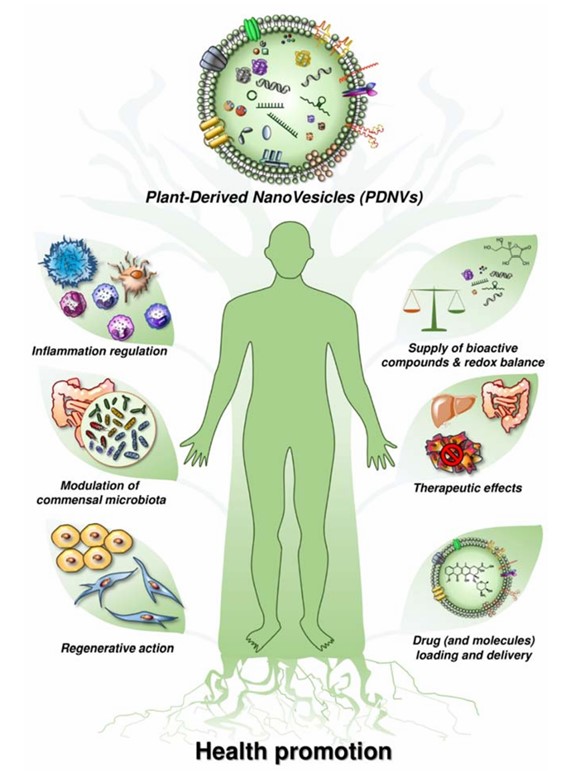 Fig.1 Beneficial effects of plant-derived nanovesicles on human health promotion.1
Fig.1 Beneficial effects of plant-derived nanovesicles on human health promotion.1
Current Research Highlights on Celery-Derived Exosomes
Summarized below are the recent findings by the broader scientific community:
|
Focus Area
|
Scientific Insights
|
|
Physical Profile
|
Celery exosomes are spherical vesicles sized 50-200 nm with a well-dispersed peak diameter near 140 nm (NTA analysis).
|
|
Lipid Content
|
Rich in phosphatidic acid, diacylglycerol, and anti-inflammatory fatty acids, suggesting roles in membrane dynamics and immune modulation.
|
|
Biocompatibility
|
High cellular uptake with minimal cytotoxicity confirmed via fluorescent tracking and viability assays.
|
|
Drug Vehicle Function
|
Demonstrated capacity to deliver anticancer agents, reducing tumor proliferation markers (Ki67) and enhancing apoptotic signals (Caspase-3).
|
|
T Cell Immunomodulation
|
Downregulation of IL-6 and IFN-γ, decreased p-LAT and p-Lck signaling proteins, and reduced CD4+CD25+ activated T cell populations.
|
Molecular and Technical Platforms
At Creative Biolabs, we integrate a suite of advanced analytical technologies and validated experimental platforms to ensure the accurate characterization and functional assessment of celery-derived exosomes. By combining high-resolution imaging, precision particle analysis, and molecular profiling tools, our team is able to generate consistent and reproducible data that researchers can confidently rely on for further exploration of exosome structure, composition, and biological activity.
-
NTA – Particle size distribution and zeta potential analysis.
-
TEM – High-resolution visualization of exosome morphology.
-
Lipidomics & GC-FAME – Fatty acid and membrane lipid identification.
-
Western Blot & Flow Cytometry – Protein quantification and immunophenotyping.
-
Fluorescence Imaging – Tracking vesicle uptake and intracellular trafficking.
Distinct Features of Celery-Derived Exosomes
-
Nutrient-Rich Cargo – Enriched with polyphenols, vitamins, and functional lipids.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms – Suppress pro-inflammatory cytokines and signaling molecules in immune cells.
-
Oxidative Stress Protection – Capable of neutralizing free radicals and stabilizing redox balance.
-
Immunosuppressive Potency – Inhibit T cell hyperactivation, suggesting promise for immune regulation research.
-
High Yield Potential – Efficient isolation with stable physicochemical properties under physiological and storage conditions.
Why Choose Creative Biolabs?
|
Expertise centered on vegetable-derived exosomes.
|
Reliable, high-purity vesicle preparations in each batch.
|
|
Vesicle suspensions or lyophilized forms tailored to your study.
|
Comprehensive analytical reports with visual documentation.
|
Deliverables
-
Standard operating procedures
-
Size and zeta potential measurement data (Optional)
-
Optional cargo profiling results (lipids, proteins, metabolites)
-
Optional functional assay data (uptake, immunomodulation, delivery capability)
-
Optional fluorescent and EM imaging datasets
-
Custom summary reports
Researcher Testimonials
"Creative Biolabs' expertise in plant-derived exosomes provided us with valuable perspectives on the role of dietary vesicles in modulating immune cell responses. The results were delivered promptly and with exceptional accuracy."
— Dr. K. XXXX
"We were exploring exosomal delivery in phytochemical research and found Creative Biolabs' celery exosome preparation to be both stable and highly functional. Outstanding service."
— Prof. L. XXXX
Celery-derived exosomes are gaining traction in next-generation bio-nanotechnology research. Creative Biolabs provides dependable support to unlock their full potential. Contact us to discuss your celery exosome project.
FAQs
Q: What functionalities do celery-derived exosomes possess?
A: Among the many bioactive substances found in celery-derived exosomes are flavonoids, polyphenols, and antioxidants. Research suggests they play a critical role in intercellular communication, delivering molecular signals that can influence cellular behavior and promote skin health by enhancing hydration, reducing inflammation, and providing antioxidant protection. Their unique composition also supports regenerative processes in various tissues.
Q: What applications do exosomes generated from celery find in the skincare and cosmetics sector?
A: In the beauty sector, celery-derived exosomes are gaining traction as a natural ingredient in skincare formulations. Their capacity to boost hydration, stimulate cell regeneration, and strengthen the skin barrier makes them an important component of anti-aging products. Additionally, their anti-inflammatory properties may help in reducing skin conditions such as acne and rosacea, providing a holistic approach to skincare.
Q: What are the emerging applications of celery-derived exosomes beyond skincare?
A: Beyond cosmetics, celery-derived exosomes are being explored in various fields, including agriculture, where they may enhance plant resilience to environmental stressors. In the nutrition sector, research is investigating their potential as delivery vehicles for functional nutrients, improving bioavailability and efficacy. They have potential uses in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine due to their involvement in improving cellular communication.
Q: What research developments are currently ongoing regarding celery-derived exosomes?
A: Current research is focused on understanding the mechanisms by which celery-derived exosomes exert their beneficial effects on cells. Studies are investigating their biocompatibility, potential for modulating cellular signaling pathways, and interactions with other biomolecules. Advanced isolation and characterization techniques are also being developed to enhance the purity and functionality of these exosomes for various applications.
Q: Are there any challenges in the research of celery-derived exosomes?
A: Yes, several challenges exist in this field. The variability in exosome composition due to environmental factors, the need for standardized isolation protocols, and the limited understanding of their in vivo behavior and long-term stability pose hurdles.
Q: What developments may we anticipate in the study of exosomes generated from celery?
A: Future trends may include a focus on biotechnology approaches to enhance the yield and functionality of celery-derived exosomes. There is also likely to be increased interest in their role as sustainable, plant-based alternatives in cosmetics and nutraceuticals. Additionally, as research uncovers more about their mechanisms, we may see novel applications leverage these exosomes for preventative approaches in skin health and overall cellular wellness.
Reference
-
Logozzi, Mariantonia et al. "The Potentiality of Plant-Derived Nanovesicles in Human Health-A Comparison with Human Exosomes and Artificial Nanoparticles." International journal of molecular sciences vol. 23,9 4919. 28 Apr. 2022, doi:10.3390/ijms23094919. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Beneficial effects of plant-derived nanovesicles on human health promotion.1
Fig.1 Beneficial effects of plant-derived nanovesicles on human health promotion.1









