Potato derived Exosome Research & Application
Overview Our Services Workflow Research Highlights Platform Key Features Why us What You Get Customer Feedback FAQs
Tiny Messengers from Tubers: A New Chapter in Plant Exosome Exploration
Potato (Solanum tuberosum), one of the most widely cultivated food crops globally, is not only a nutritional powerhouse but also a promising source of bioactive nanovesicles. In recent years, growing interest in plant-derived exosomes has led to the discovery of unique characteristics associated with potato-derived exosomes (PDEs). These naturally occurring nanoparticles carry a rich cargo of proteins, small RNAs, lipids, and metabolites and have been shown to exhibit stable physicochemical properties across various conditions.
At Creative Biolabs, we are committed to accelerating exosome research by offering precise, reproducible workflows for PDE isolation and characterization. Through our advanced plant exosome platform, we support researchers in exploring PDEs' structure, function, and potential applications across diverse scientific fields.
Customized Solutions for Potato-Derived Vesicle Research
Creative Biolabs offers a comprehensive set of service modules tailored for potato exosome research:
-
Sample Quality Control: Rigorous screening of raw potatoes to ensure only non-sprouted, contaminant-free materials are used.
-
High-Yield Isolation: Optimized ultracentrifugation-based extraction of PDEs for consistent and scalable vesicle recovery.
-
Optional Vesicle Profiling: Comprehensive analysis of vesicle morphology, size, and surface charge using NTA and electron microscopy.
-
Optional Cellular Assays: In vitro evaluation of cellular uptake, cytotoxicity, and bioactivity using keratinocytes and immune cells.
-
Optional Oxidative Stress Studies: Functional assays to test PDEs' protective capabilities under stress-induced conditions.
Our solutions are built for reproducibility and backed by Creative Biolabs' decades-long commitment to innovation in vesicle biology.
From Raw Material to Functional Nanoparticles: Our Workflow
Creative Biolabs' stepwise isolation process ensures high-quality recovery of potato-derived exosomes with minimal degradation:
-
Source Inspection – Removal of green or sprouted tubers to avoid solanine contamination.
-
Pre-Processing – Double-washing in distilled water and PBS followed by peeling.
-
Juice Extraction – Mechanical squeezing to obtain fresh potato juice.
-
Initial Clarification – Low-speed centrifugation to eliminate large particulates.
-
Filtration – Fine filtration and further clarification via differential centrifugation.
-
Ultracentrifugation – High-speed pelleting of nano-sized vesicles.
-
Resuspension & QC – Final wash and resuspension in PBS with further vesicle characterization.
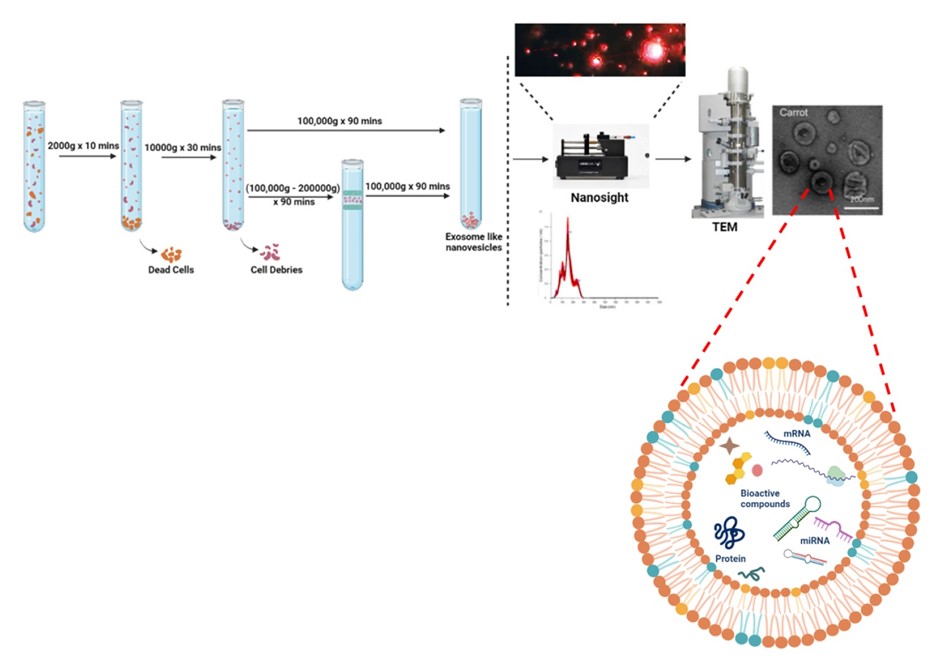 Fig. 1 The standardized protocol of edible exosomes-like nanoparticles.1
Fig. 1 The standardized protocol of edible exosomes-like nanoparticles.1
Scientific Insights into Potato-Derived Exosomes
Findings from the global research community have shed light on the distinct properties and promising functions of PDEs:
|
Research Area
|
Key Discoveries
|
|
Vesicle Properties
|
PDEs range from 50-250 nm, exhibit a bilayer elliptical shape, and are negatively charged in solution.
|
|
Cellular Uptake
|
Fluorescent microscopy and flow cytometry confirm efficient, dose-dependent uptake of PDEs by keratinocytes.
|
|
Inflammation Modulation
|
PDEs markedly decrease the expression levels of inflammatory cytokines and MMP genes in comparison to pear and citrus exosomes.
|
|
Cell Proliferation
|
PDEs enhance keratinocyte growth with negligible cytotoxic effects, according to viability assays.
|
|
Antioxidant Activity
|
Pre-treatment with PDEs rescues cells from oxidative damage induced by H2O2, showing dose-dependent ROS suppression.
|
|
Photoprotection
|
PDEs reduce photoaging markers and oxidative stress while enhancing glutathione S-transferase alpha 4 expression to protect skin cells.
|
These findings underscore the varied biological functions that PDEs may serve within cellular systems, emphasizing the need for further investigation in research environments.
Tools and Technologies that Drive Confidence
At Creative Biolabs, our specialized analytical platform integrates:
-
TEM
Visual confirmation of vesicle morphology.
-
Laser-Based NTA
High-resolution particle sizing and concentration tracking.
-
Zeta Potential Analysis
Surface charge quantification.
-
Gene Expression Assays
qPCR for inflammation and stress-response markers.
-
Functional Testing
Cell migration, viability, and uptake studies.
These platforms ensure accurate and high-throughput data generation tailored to PDE analysis.
Unique Biological Assets of Potato Exosomes
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effect – Downregulate key inflammatory genes more effectively than exosomes from other plant sources.
-
Skin Cell Proliferation Support – Promote keratinocyte expansion while maintaining safety and low toxicity.
-
Oxidative Stress Defense – Activate intracellular antioxidant responses and scavenge reactive oxygen species.
-
Photodamage Recovery – Dual action in preventing and repairing light-induced cellular damage.
-
Stable Vesicle Architecture – Robust bilayer structure and long-term solution stability under laboratory conditions.
Advantages of Choosing Creative Biolabs
-
Plant Exosome Focus
A dedicated team with niche expertise in vegetable-derived exosome research.
|
-
Methodological Precision
Consistently applied ultracentrifugation protocols for purity and performance.
|
-
Data Transparency
Clear, publication-ready results with all supporting datasets.
|
-
Responsive Support
Expert consultation throughout your project lifecycle.
|
Deliverables
-
Raw material traceability documentation
-
Isolation workflow summary and QC benchmarks
-
Particle size, zeta potential, and morphology data (Optional)
-
Optional Functional study results (inflammatory markers, oxidative stress assays, uptake efficiency)
-
Optional Imaging records (confocal, TEM)
-
Comprehensive project report
Testimonials from the Scientific Community
"Creative Biolabs' efficient workflow and technical assistance made our shift to plant exosome research seamless. Their potato-derived exosomes demonstrated reliable performance in our oxidative stress models."
— Dr. M. FXXXX
"We relied on Creative Biolabs' platform to validate the bioactivity of PDEs. Their team provided thorough data and rapid turnaround, enabling us to move forward with our formulations confidently."
— Prof. J. LiXXXX
Potato-derived exosomes are emerging as versatile tools in cellular biology, antioxidant research, and formulation science. With Creative Biolabs' comprehensive support and scientific rigor, researchers can confidently explore the expanding frontier of plant-based extracellular vesicles. Contact us to begin your customized potato exosome research journey.
FAQs
Q: What specific functions do potato-derived exosomes serve in plant biology?
A: Potato-derived exosomes play a pivotal role in mediating stress responses and enhancing plant resilience. They facilitate cell communication, allowing the plant to coordinate its defense mechanisms against pathogens and environmental stressors. They also play a critical role in ferrying key proteins and signaling entities between cells, thereby facilitating molecular communication and functional regulation within the biological system.
Q: How are potato-derived exosomes being utilized in the cosmetics industry?
A: In the cosmetics sector, potato-derived exosomes are emerging as valuable ingredients due to their potential skin-nourishing properties. They are leveraged for their antioxidant capabilities, promoting skin hydration, reducing inflammation, and enhancing overall skin health. Their natural origin also appeals to consumers seeking clean and sustainable beauty products.
Q: What new directions are being explored for potato-derived exosomes beyond skincare?
A: Beyond cosmetics, research into potato-derived exosomes is expanding into areas such as food technology, where they are explored for their potential to enhance nutritional value and shelf life of food products due to their natural bioactive components. Additionally, studies are investigating their role in sustainable agriculture as biofertilizers, aiming to improve crop yields and plant health.
Q: What challenges exist in researching potato-derived exosomes?
A: While promising, research on potato-derived exosomes faces several challenges, including the standardization of extraction and characterization methods. The complexity of exosome composition and function necessitates advanced analytical techniques to fully understand their biological roles and potential applications.
Q: What future research directions are being proposed for potato-derived exosomes?
A: Future research directions include investigating the specific molecular mechanisms by which potato-derived exosomes influence cellular processes in both plant and non-plant systems. Furthermore, exploring the synergistic effects of combining these exosomes with other natural compounds could lead to innovative formulations in various industries. Studies on their environmental impact and sustainability in application will also be crucial in driving their acceptance and utility.
Reference
-
Subudhi, P Debishree et al. "Emerging Role of Edible Exosomes-Like Nanoparticles (ELNs) as Hepatoprotective Agents." Nanotheranostics vol. 6,4 365-375. 21 Jun. 2022, doi:10.7150/ntno.70999. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig. 1 The standardized protocol of edible exosomes-like nanoparticles.1
Fig. 1 The standardized protocol of edible exosomes-like nanoparticles.1









