DHMEQ-Expressed Exosome Modification Service
Overview Services Features FAQs
DHMEQ (Dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin) can be used as a pretreatment for systemically administered exosomal agents, facilitating in vivo circulation and delivery of exosome carrier systems by down-regulating macrophage phagocytosis and digestion of exosomes. Creative Biolabs has a comprehensive exosome research platform that provides exosome functional investigation services to help DHMEQ intervention-induced exosome evasion phagocytosis.
DHMEQ Induces Exosome Evasion of Phagocytosis
DHMEQ, a novel anti-inflammatory drug, can exert anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway as well as modulating macrophage-mediated phagocytosis. DHMEQ down-regulates macrophage-mediated phagocytosis mainly in the following ways.
-
Inhibition of macrophage phagocytosis: DHMEQ can inhibit macrophage phagocytosis by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway, reducing the phagocytosis and digestion of microorganisms and waste by macrophages. Unlike other NF-κB inhibitors that target the phosphorylation level of IκBα, DHMEQ has been identified to target the nuclear translocation of p65, a component of NF-κB, by covalently modifying specific cysteine residues in p65 and other Rel homologous proteins in a 1:1 stoichiometric ratio.
-
Inhibition of macrophage surface receptor expression: receptors on the surface of macrophages are important for the phagocytosis of microorganisms and cellular waste. DHMEQ can inhibit the expression of macrophage surface receptors, which in turn affects phagocytosis. For example, DHMEQ can reduce the expression of Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) and Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) in macrophages, weakening their response to external stimulation.
-
Reduced cytoskeleton stability: DHMEQ can reduce the stability of the macrophage cytoskeleton, which in turn affects the phagocytic function of the cells. DHMEQ can reduce the stability of the cytoskeleton by inhibiting the polymerization of microtubule proteins, which in turn reduces the phagocytic function of macrophages.
 Fig.1 Molecular design of DHMEQ.1
Fig.1 Molecular design of DHMEQ.1
Services
-
Isolation and Purification: We isolate exosomes from various cell types and purify them to ensure high-quality samples for downstream analysis.
-
DHMEQ Loading: We utilize cutting-edge techniques to load exosomes with DHMEQ, a potent inhibitor of NF-κB, to modulate their circulating properties.
-
Characterization: We employ advanced methods such as electron microscopy, nanoparticle tracking analysis, and Western blotting to thoroughly characterize DHMEQ-loaded exosomes.
-
Functional Assays: Through a variety of in vitro and in vivo assays, we assess the phagocytosis evasion performance of DHMEQ-expressed exosomes.
Features
-
Customization: Tailored protocols to meet specific research needs, ensuring optimal experimental outcomes.
-
Expertise: Our team consists of experienced scientists proficient in exosome biology, guaranteeing reliable and accurate results.
-
State-of-the-Art Facilities: Access to cutting-edge equipment and technologies for precise characterization and analysis of exosomes.
-
Data Analysis: Comprehensive data analysis and interpretation, providing valuable insights into the phagocytosis evasion mechanisms of DHMEQ-expressed exosomes.
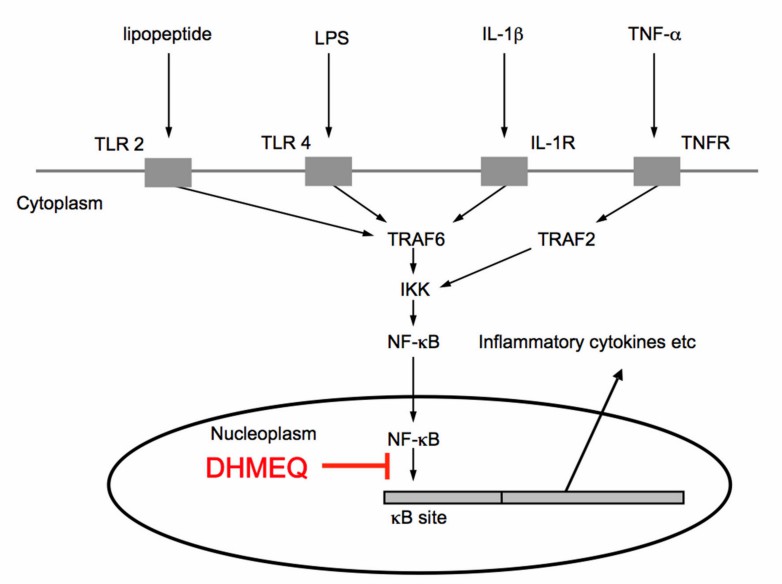 Fig.2 Signaling pathway for NF-κB activation and inhibition by DHMEQ.1
Fig.2 Signaling pathway for NF-κB activation and inhibition by DHMEQ.1
DHMEQ can down-regulate macrophage-mediated phagocytosis through various mechanisms including inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway, reduction of macrophage surface receptor expression, and reduction of cytoskeleton stability. This effect may be beneficial for improving the targeted delivery performance of systemically administered exosome therapies and has potential applications. Creative Biolabs provides research services on DHMEQ treatment-induced exosome evasion phagocytosis, contributing to enhancing the application utility of exosome delivery platforms. Please contact us for a customized solution.
FAQs
Q: What cell types can be used for exosome isolation?
A: We can isolate exosomes from various cell types, including but not limited to cancer cells, immune cells, and stem cells.
Q: How is DHMEQ loaded into exosomes?
A: DHMEQ loading into exosomes is achieved through a series of specialized protocols, ensuring efficient and stable encapsulation of the inhibitor.
Q: Can DHMEQ-expressed exosomes be used for in vivo studies?
A: Yes, DHMEQ-expressed exosomes are suitable for in vivo studies to investigate their effects on immune responses and tumor progression.
Q: What types of assays are available to assess the effects of DHMEQ-expressed exosomes?
A: We offer a range of assays, including cytokine profiling, cell proliferation assays, and cell viability assays, among others, to evaluate the properties of DHMEQ-expressed exosomes.
Reference
-
Ma, Jun, et al. "Inhibition of cellular and animal inflammatory disease models by NF-κB inhibitor DHMEQ." Cells 10.9 (2021): 2271. Under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Molecular design of DHMEQ.1
Fig.1 Molecular design of DHMEQ.1
 Fig.2 Signaling pathway for NF-κB activation and inhibition by DHMEQ.1
Fig.2 Signaling pathway for NF-κB activation and inhibition by DHMEQ.1









