Stem Cell-derived Exosomes and Therapeutic Application
- Engineered Form
Overview Services Features FAQs
Exosomes have a dual identity as both a mediator of intercellular communication and a regulator of cellular metabolism. To better exploit the advantages of SC-Exo (stem cell exosomes), it has been widely used to obtain engineered SC-Exo that can carry a variety of bioactive substances by exploiting their modifiable properties. Creative Biolabs has the platform to engineer modified exosomes to provide customized engineered SC-Exo research services.
SC-Exo Applications
Based on the variability of SC-Exo in different tissues, their applications are also diverse. Engineered SC-Exo have a wide range of promising medical applications, both for disease interventions and as drug delivery vehicles through the modification of targeted peptides.
Engineered SC-Exo for cardiac diseases
Bone marrow MSC-derived exosomes overexpressing GATA-4 significantly increased the survival rate and mitochondrial membrane potential of cardiomyocytes cultured in vitro under hypoxic conditions, restored myocardial contractile function and reduced infarct size in a mouse model of myocardial infarction. miR-19a was subsequently found to be higher in GATA-4 overexpressing bone marrow MSC-derived exosomes by inhibiting phosphatases and dozens of homologs involved in myocardial protective effects.
Engineering SC-Exo for neural diseases
Adipose MSC-derived exosomes carrying miR-188-3p attenuate nigrostriatal damage in a mouse model of neurotoxin-induced Parkinson's disease by targeting NLRP3 and the 3' UTR of Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 to inhibit the expression of inflammatory vesicles and autophagosomes.
Highly targeted engineered SC-Exo drug vehicles
Engineered SC-Exo or their surface proteins can be labeled by fluorescent dyes to assay their biodistribution into animals or targeting efficiency after co-incubation with cell lines.
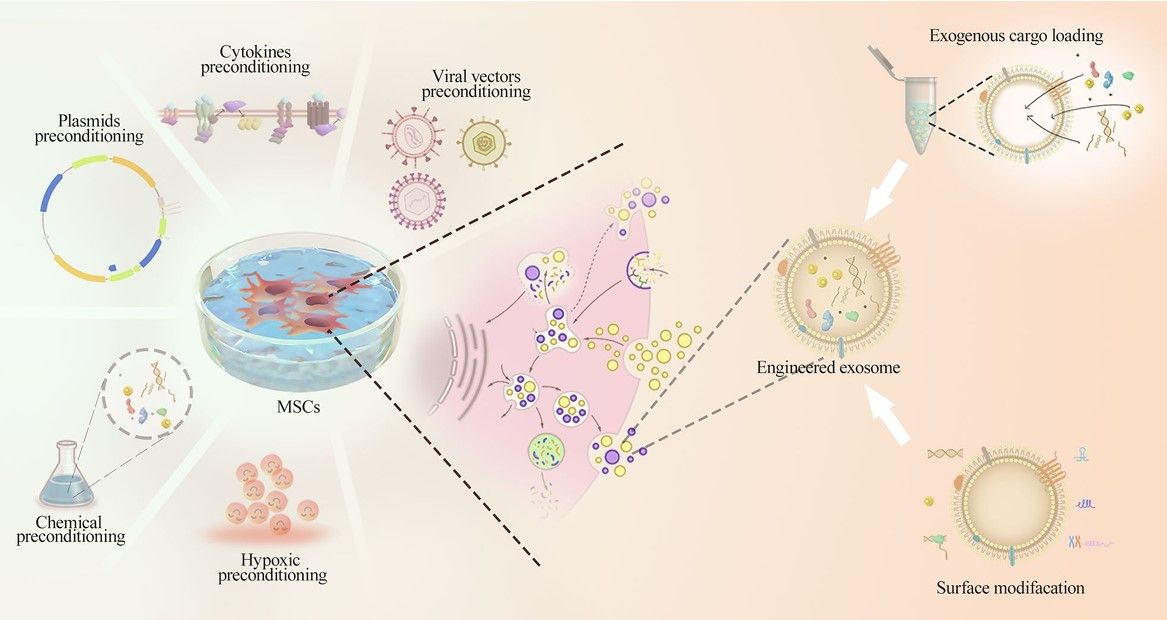 Fig.1 The avenues for the modification of exosomes.1
Fig.1 The avenues for the modification of exosomes.1
Engineering Strategies for the Modification of SC-Exo
 Fig.2 Methods of engineering SC-Exo.
Fig.2 Methods of engineering SC-Exo.
Engineered SC-Exo Features
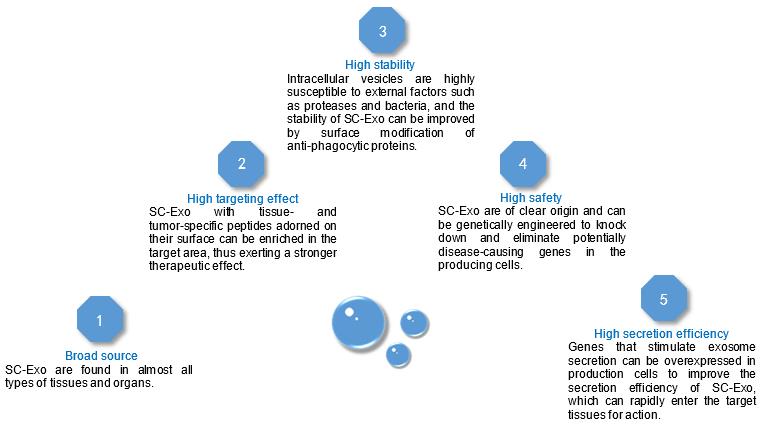 Fig.3 SC-Exo Features.
Fig.3 SC-Exo Features.
Gene-editing and chemical modification techniques are used to develop more precise and effective engineered SC-Exo for more precise and effective results. Creative Biolabs assists clients in exploring new possibilities related to engineered modified SC-Exosomes. Please contact us to discuss your project.
FAQs
Q: What are the key advantages of using stem cell-derived exosomes in therapeutic applications compared to traditional drug delivery systems?
A: Stem cell-derived exosomes offer several advantages, including enhanced biocompatibility, the ability to cross biological barriers, and natural targeting capabilities due to their origin from stem cells.
Q: How may the potential of SC-Exo be enhanced by engineering techniques?
A: Engineering techniques, such as surface modification and cargo loading, can significantly enhance the therapeutic potential of exosomes. For instance, modifying the exosome surface with targeting ligands can improve specificity towards diseased tissues, while loading them with agents can augment their functional capabilities.
Q: What difficulties lie in producing modified stem cell-derived exosomes on a big scale?
A: Challenges include maintaining consistent quality and purity during production, scaling up the isolation processes, and ensuring the stability of engineered exosomes during storage and transportation.
Q: How may SC-Exo be applied to the field of regenerative medicine?
A: Through its paracrine properties, SC-Exo can be used in regenerative medicine to promote tissue repair and regeneration. They can modulate immune responses, enhance angiogenesis, and facilitate cell survival and proliferation, making them suitable for applications in conditions such as myocardial infarction, neurodegenerative diseases, and wound healing.
Q: How can the immunogenicity of engineered stem cell-derived exosomes be minimized in therapeutic applications?
A: To minimize immunogenicity, strategies such as using autologous stem cells for exosome production, modifying exosome surface proteins, and employing immunosuppressive agents during therapy can be implemented. Additionally, thorough characterization of exosomes to ensure they are free from immunogenic contaminants is essential.
Q: What possible uses for modified SC-Exo exist in the field of cancer research?
A: Engineered SC-Exo can be applied in cancer research for targeted drug delivery, enhancing the efficacy of chemotherapeutics, and delivering RNA-based therapeutics such as siRNA or miRNA to inhibit tumor growth. They can also be used to modulate the tumor microenvironment and improve immune responses against tumors.
Reference
-
Lu, Ye, et al. "Engineering exosomes and biomaterial-assisted exosomes as therapeutic carriers for bone regeneration." Stem Cell Research & Therapy 14.1 (2023): 1-19. Under open access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 The avenues for the modification of exosomes.1
Fig.1 The avenues for the modification of exosomes.1
 Fig.2 Methods of engineering SC-Exo.
Fig.2 Methods of engineering SC-Exo.
 Fig.3 SC-Exo Features.
Fig.3 SC-Exo Features.









