Stem Cell-derived Exosomes and Therapeutic Application
- Native Form
Overview Services Features FAQs
Exosomes from different native stem cells have been used to treat conditions like cardiovascular disease, neurocentral diseases, and immunological regulation since they have been demonstrated to have regenerative potential both in vivo and in vitro. Creative Biolabs lists the characteristics of donor stem cells from a variety of exosomes and their applications to provide reliable native SC-Exo (Stem cell-derived exosomes) research services.
Native SC-Exo and Applications
|
Diseases
|
SC-Exo
|
Applications
|
|
Cardiovascular disease treatment
|
Induced pluripotent SC-Exo
|
Induced pluripotent SC-Exo enriched with high concentrations of mi R-17-92 clusters (e.g. miR-19a, miR-19b, miR-20a) may have pro-angiogenic and cardiomyocyte-protective effects after myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and proteomic data identified exosomes enriched with several pro-angiogenic molecules, including bone formation protein 4, platelet-derived growth factor α embryonic tumor-derived factor 1, platelet-responsive protein 1, and vascular endothelial growth factor C.
|
|
Mesenchymal SC-Exo
|
After ischemic preconditioning, mouse bone marrow SC-Exo secrete miR-22-enriched exosomes, and their action in ischemic myocardium reduces cardiomyocyte apoptosis, and the anti-apoptotic effect of mi R-22 is mediated by direct targeting of methyl Cp G-binding protein 2. In a mouse myocardial infarction model, administration of mi R-22 by its exosomes significantly reduces infarct size and improves myocardial fibrosis.
|
|
Embryonic SC-Exo
|
Embryonic SC-Exo are enriched in mi R-290-295 cluster (especially mi R-294), which enhances neovascularization, promotes cardiomyocyte survival, and reduces post-infarction myocardial fibrosis.
|
|
Central nervous system disease treatment
|
Mesenchymal SC-Exo
|
Mesenchymal SC-Exo carry miR-26b-5p that attenuate ischemia-induced microglia M1 polarization and inflammatory responses by targeting Cholesterol-25-hydroxylase4 to inhibit Toll-like receptor signaling pathways, thereby reducing neurological injury after cerebral ischemia.
|
|
Endothelial progenitor cell exosomes
|
RNA sequencing revealed that miR-21-5p was highly enriched in exosomes and specifically inhibited the expression of receptor angiogenesis inhibitor thrombospondin-1 to alleviate cranial injury.
|
|
Dental pulp SC-Exo
|
Dental pulp SC-Exo attenuated neurological inflammation in MCAO mice by inhibiting the High mobility group Box-1/Toll-Like receptor4/Myeloid differentiation primary response88/Nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway.
|
Our Services
We specialize in providing comprehensive research services for stem cell-derived exosomes in their native form. Our offerings include precise isolation and purification of exosomes from diverse stem cell sources, and in-depth characterization through advanced techniques to analyze size, morphology, protein composition, and RNA profile. We also offer expert research consultation to guide your projects and customize services tailored to your unique needs to keep you at the forefront of exosome research.
Features of Multiple Exosome-producing Native Stem Cells
Native SC-Exo refers to the exosomes produced by different types of stem cells in natural culture. Exosomes produced by stem cells after specific culture conditions can be accessed in the extracellular environment. These exosomes contain bioactive molecules that can have important effects on surrounding cells and tissues.
-
Induced pluripotent stem cells: produced from any tissue type in vivo, long culture passages, multispectral transdifferentiation potential, no ethical controversy involved.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells: widely available, adult stem cells.
-
Embryonic stem cells: developmental totipotency and lineage transfer function, long-term proliferation always in a highly undifferentiated state.
-
Umbilical cord stem cells: low invasiveness, easier to isolate, high cell content, high efficiency of gene transfection.
-
Hematopoietic stem cells: has the capacity to develop into a variety of mature blood cell types, and they are frequently employed in allogeneic transplantation.
-
Adipose stem cells: abundant reserves in the body, convenient to obtain, and low cost.
-
Bone marrow stem cells: the earliest studied and applied, with the most proven safety and efficacy.
-
Progenitor cells: wandering, high proliferation and directed differentiation characteristics.
-
Dental marrow stem cells: the ability to induce mineralized nodules, easy to collect, high storage opportunities.
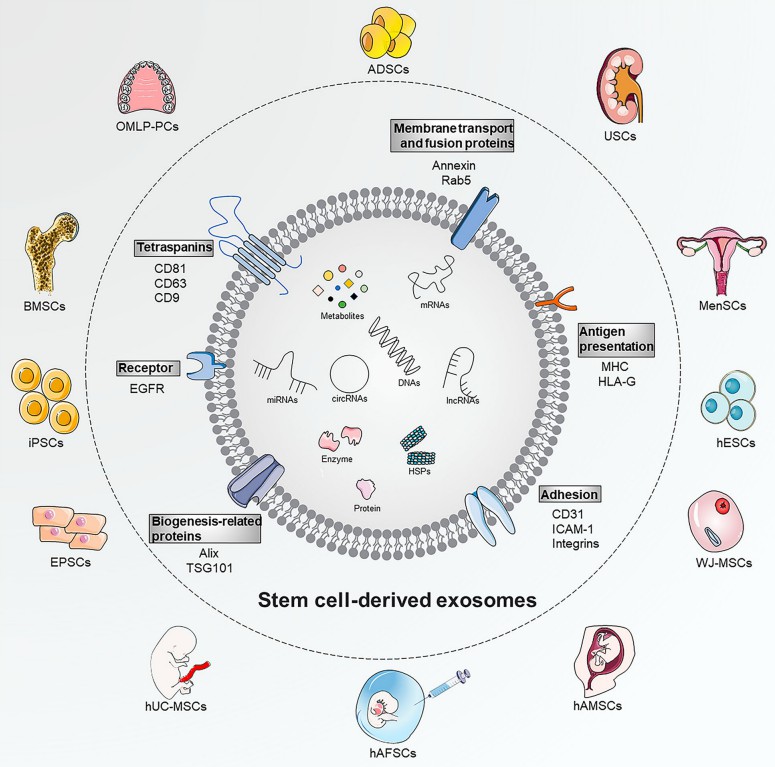 Fig. 1 The compositions, biomarkers, and source of native SC-Exo.1
Fig. 1 The compositions, biomarkers, and source of native SC-Exo.1
At Creative Biolabs, we provide professional scientific services to help scientists better understand the potential of different sources of native SC-Exo and their applications and to provide more useful information. Please contact us to learn more.
FAQs
Q: What makes native-form stem cell-derived exosomes unique in research?
A: Native form exosomes retain their natural composition and functionality, offering a more accurate representation of their biological role. This makes them ideal for studying the complex mechanisms of intercellular communication and potential applications in basic research.
Q: How is the purity of native-form exosomes ensured?
A: We employ a multi-step purification process that combines centrifugation, filtration, and immunoaffinity purification methods. Strict quality control procedures are used to guarantee high purity and low contamination.
Q: Can native-form exosomes be employed in conjunction with additional research tools?
A: Yes, native-form exosomes can be integrated with various research techniques such as proteomics, genomics, and cell culture studies to gain a more comprehensive understanding of their functions.
Q: Are there any limitations to using native-form exosomes in research?
A: While native-form exosomes offer many advantages, they may have some limitations. For instance, handling and storage circumstances can have an impact on their activity and stability. Additionally, the complexity of their composition can make analysis more challenging.
Q: How can I determine the optimal source of stem cells for isolating native-form exosomes?
A: The choice of stem cell source depends on your research goals. Different stem cell types may produce exosomes with distinct characteristics. Our experts can help you evaluate the pros and cons of various sources and choose the most suitable one for your study.
Q: Can native-form exosomes be used in comparative studies with other types of exosomes?
A: Yes, native-form exosomes can be compared with exosomes derived from other sources or modified forms to understand the differences in their properties and functions. This may offer insightful information about how exosomes function in many biological processes.
Reference
-
Zhou, Chuchao, et al. "Stem cell-derived exosomes: emerging therapeutic opportunities for wound healing." Stem cell research & therapy 14.1 (2023): 107. Under open access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig. 1 The compositions, biomarkers, and source of native SC-Exo.1
Fig. 1 The compositions, biomarkers, and source of native SC-Exo.1









