Oat derived Exosome Research & Application
Overview Our Services Workflow Research Highlights Platform Advantages Deliverables Customer Feedback FAQs
Oat Vesicles: A Novel Class of Botanical Nanocarriers
Oats (Avena sativa) have long been appreciated for their nutritional and medicinal benefits. In recent years, attention has shifted to the nano-sized extracellular vesicles secreted by oat plants—oat-derived exosomes (ODEs). These vesicles, typically 30–150 nm in size, are emerging as versatile bio-nanocarriers with the potential to modulate cellular activity, influence brain function, and regulate inflammation.
At Creative Biolabs, we provide customized, research-grade oat exosome development services. Our workflows are built to support basic science exploration and industrial innovation, offering high-quality exosome suspensions for downstream experimentation. With optional profiling, characterization, and bioactivity assays, we empower researchers to push the frontiers of oat-derived nanobiology.
Specialized Solutions: Oat Exosome Production and Optional Analysis
Creative Biolabs supports tailored project development with flexible service components. Our standard service includes:
-
Custom Exosome Isolation: Extraction and purification of ODEs from oat bran or oat meal under controlled conditions.
-
(Optional) Physicochemical Characterization: Measurement of vesicle size, zeta potential, and morphology using NTA and TEM.
-
(Optional) Biomolecular Profiling: RNA, protein, and lipid cargo identification using omics-based platforms.
-
(Optional) Functional Screening: Assessing ODE impact on cell models (e.g., oxidative stress, inflammation, neuroprotection).
We align every study with client-specific objectives, emphasizing transparency and reliability in each stage of service delivery.
Isolation Pipeline: From Oat Meal to Purified Vesicles
Our established oat exosome production workflow includes:
-
Sample Processing: Homogenization of oat-derived materials in buffer solution.
-
Preliminary Clarification: Removal of large particulates through multiple low-speed centrifugations.
-
Differential Centrifugation: Progressive speed separation to concentrate nanovesicles.
-
Ultracentrifugation: High-speed spin to collect vesicle-rich pellets.
-
Purification: Optional density gradient separation in iodosanol solution for enhanced purity.
Final exosome suspensions are filtered and stored in PBS, ready for direct research use or further optional characterization.
Key Insights: Advances in Oat Exosome Scientific Research
Recent studies have expanded our understanding of ODEs and their biological significance:
|
Research Focus
|
Findings
|
|
Biodistribution of ODEs
|
Oral administration in mice revealed vesicle enrichment in brain, liver, and peripheral blood, suggesting systemic uptake and CNS bioavailability.
|
|
Brain-Targeting Potential
|
Labeled ODEs were found to localize in CD11b+/CD45+ microglia cells. Immunofluorescence confirmed uptake by Iba-1+ cells. Brain macrophage depletion studies verified selectivity for microglial targeting.
|
|
Ethanol-Induced Brain Inflammation
|
The expression of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNFα was downregulated by ODEs in regions of the brain impacted by alcohol. In vitro and in vivo models showed attenuated microglial activation and improved liver inflammation.
|
|
Neuroprotection and Memory Recovery
|
ODEs inhibited TNFα release from microglia and prevented neuronal apoptosis, contributing to memory restoration in alcohol-challenged mice.
|
|
Mechanism of Cellular Uptake
|
ODEs engage β-glucan/hippocalcin/Rab11a axis to bypass dectin-1-mediated NF-κB signaling, facilitating immune modulation and inflammation reduction.
|
These cumulative findings reveal the multifaceted potential of oat exosomes in neurological and systemic biological models.
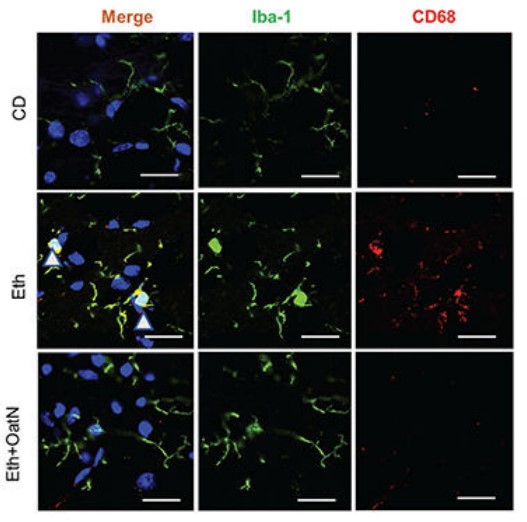 Fig.1 Oral administration of oat-derived exosomes inhibited ethanol-induced microglia activation in mouse brain.1
Fig.1 Oral administration of oat-derived exosomes inhibited ethanol-induced microglia activation in mouse brain.1
Scientific Infrastructure: Tools Enabling High-Quality Data
At Creative Biolabs, we provide a comprehensive selection of optional instruments and assays to support and advance oat exosome research.
-
Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
-
Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
-
Proteomics and RNA-seq (optional)
-
qPCR, cytokine ELISA, and inflammation profiling
-
Microglial activity assays and oxidative stress testing
Our modular testing platform allows researchers to select only the components relevant to their experimental goals.
Why Choose Creative Biolabs for Oat Vesicle Research?
|
Proprietary protocols adapted to the physicochemical properties of oat tissues.
|
-
Flexible Project Architecture
Clients select core isolation services with the option to add testing as needed.
|
|
Detailed documentation for each step of production and optional QC.
|
Our platform is optimized for preclinical and academic studies, not clinical use.
|
Project Outputs: Deliverables for Oat Exosome Studies
Standard deliverables include:
-
Process documentation and raw material sourcing records
-
Isolated oat-derived exosomes in PBS
-
Project report and procedural metadata
Optional deliverables include detailed characterization reports, transcriptomic/proteomic cargo profiles, and assay data from functional evaluations.
Client Reflections
"Collaborating with Creative Biolabs facilitated the reliable and consistent isolation of oat-derived vesicles. Their custom services gave us exactly what we needed without unnecessary extras."
— Dr. L. GraXXXX
"Our in vivo studies on dietary vesicle uptake were supported by Creative Biolabs' standardized oat exosome workflow. The quality of their output enabled high-resolution data collection in our lab."
— Prof. S. MakXXXX
With their unique bioactive composition and systemic transportability, oat-derived exosomes are attracting rising interest in the fields of nutrition, neuroscience, and cosmetics. Creative Biolabs is here to help you explore their full research potential with confidence. Reach out to Creative Biolabs today to kickstart your oat exosome research journey.
FAQs
Q: What are the key functions of oat-derived exosomes?
A: Oat-derived exosomes are known to possess several key functions including the transport of bioactive molecules, modulation of cellular processes, and stimulation of immune responses. Their lipid bilayer enables them to protect and deliver these natural compounds to targeted cells, which can enhance skin health and support cellular repair mechanisms.
Q: How are oat-derived exosomes being utilized in beauty and skincare products?
A: In the cosmetic industry, oat-derived exosomes are increasingly incorporated into formulations aimed at improving skin hydration, elasticity, and overall appearance. Their ability to convey nourishing ingredients directly to skin cells makes them valuable assets in anti-aging and skin rejuvenation products, appealing to consumers seeking natural and effective solutions.
Q: What emerging trends are we seeing in the research of oat exosomes?
A: Research into oat-derived exosomes is expanding to explore their application in various sectors beyond cosmetics. Studies are investigating their role in agricultural biotechnology, where they can enhance plant resilience and crop yield. Additionally, there is an interest in their potential use in food systems, as natural preservatives and enhancers of nutritional value.
Q: What future research directions are suggested for oat-derived exosomes?
A: Future research may focus on the comprehensive profiling of oat exosomal contents to identify novel bioactive compounds and establish their specific biological effects. Additionally, leveraging advanced delivery systems to optimize the efficacy of oat exosomes in various applications is a promising avenue for exploration. Collaborative efforts across disciplines, such as molecular biology, agronomy, and materials science, will likely enhance our understanding and utilization of these innovative biological nanocarriers.
Reference
-
Xu, Fangyi et al. "Restoring Oat Nanoparticles Mediated Brain Memory Function of Mice Fed Alcohol by Sorting Inflammatory Dectin-1 Complex Into Microglial Exosomes." Small (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany) vol. 18,6 (2022): e2105385. doi:10.1002/smll.202105385. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by extracting and using only Part G of the original image and revising the title.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Oral administration of oat-derived exosomes inhibited ethanol-induced microglia activation in mouse brain.1
Fig.1 Oral administration of oat-derived exosomes inhibited ethanol-induced microglia activation in mouse brain.1









