Wheat derived Exosome Research & Application
Overview Our Services Workflow Research Focus Platform Why Choose us Deliverables Testimonials FAQs
Wheat Nanovesicles: A Frontier in Plant-Derived Exosome Research
Wheat (Triticum aestivum), one of the world's most cultivated grains, has recently emerged as a promising source of extracellular vesicles (EVs), including exosomes. These nano-sized particles, typically 30–150 nm in diameter, naturally carry a suite of bioactive components, including proteins, RNAs, and lipids. Wheat-derived exosomes (WDEs) are increasingly recognized for their ability to facilitate intercellular communication, mediate wound healing processes, and support tissue regeneration.
At Creative Biolabs, we offer end-to-end research solutions to support the isolation, development, and functional evaluation of WDEs. Our ultracentrifugation-based workflows, optional downstream characterization services, and flexible study designs enable clients to pursue a wide range of basic research objectives in the plant nanovesicle space.
What We Provide: Tailored Wheat Exosome Development Services
Creative Biolabs specializes in customized wheat-derived exosome research services. Our standard offerings include:
-
Custom Exosome Development: Isolation and concentration of WDEs from wheatgrass tissue, optimized for experimental reproducibility.
-
(Optional) Particle Characterization: Size distribution, morphology, and charge analysis using NTA, DLS, and electron microscopy.
-
(Optional) Content Profiling: Proteomic and transcriptomic profiling of exosome cargo for functional insights.
-
(Optional) Functional Assays: Evaluation of effects on cell proliferation, migration, and oxidative stress response in mammalian or plant models.
Each project is designed in close collaboration with the client to ensure alignment with research goals and sample requirements.
Workflow: From Wheatgrass to Vesicle Suspension
Our typical isolation process for WDEs includes the following steps:
-
Raw Material Preparation: Harvesting and cleaning of young wheatgrass.
-
Tissue Disruption: Mechanical juicing to obtain cell lysate.
-
Centrifugation Steps: Sequential low-speed and high-speed centrifugation to remove large particles.
-
Chemical Precipitation: Incubation with proprietary buffer to enrich vesicle content.
-
Ultracentrifugation: High-speed isolation of nano-sized vesicles.
-
Final Purification: Resuspension in PBS and sterile filtration.
Optional steps include density gradient centrifugation for achieving higher purity, depending on the application's needs.
Highlights from Wheat-Derived Exosome Research
Recent studies have demonstrated the diverse functional roles of wheat-derived exosomes across multiple biological contexts. The following table summarizes key findings:
|
Functional Area
|
Scientific Findings
|
|
Cell Proliferation
|
WDEs stimulate growth in dermal fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and epidermal cells without compromising viability.
|
|
Cell Migration
|
Scratch assays confirm that WDEs enhance cellular motility, supporting their application in skin regeneration models.
|
|
Angiogenesis
|
Treatment with WDEs increases branch and tubule formation in endothelial cells, indicating pro-angiogenic potential.
|
|
Collagen Expression
|
Immunocytochemistry and RT-PCR analyses reveal elevated type I collagen expression in fibroblasts following WDE exposure.
|
|
Anti-Apoptotic Effects
|
Flow cytometry and Annexin V staining suggest that WDEs mitigate stress-induced apoptosis, promoting cellular survival.
|
These findings underscore the regenerative and functional versatility of wheat-derived vesicles, paving the way for expanded exploration in plant exosome science.
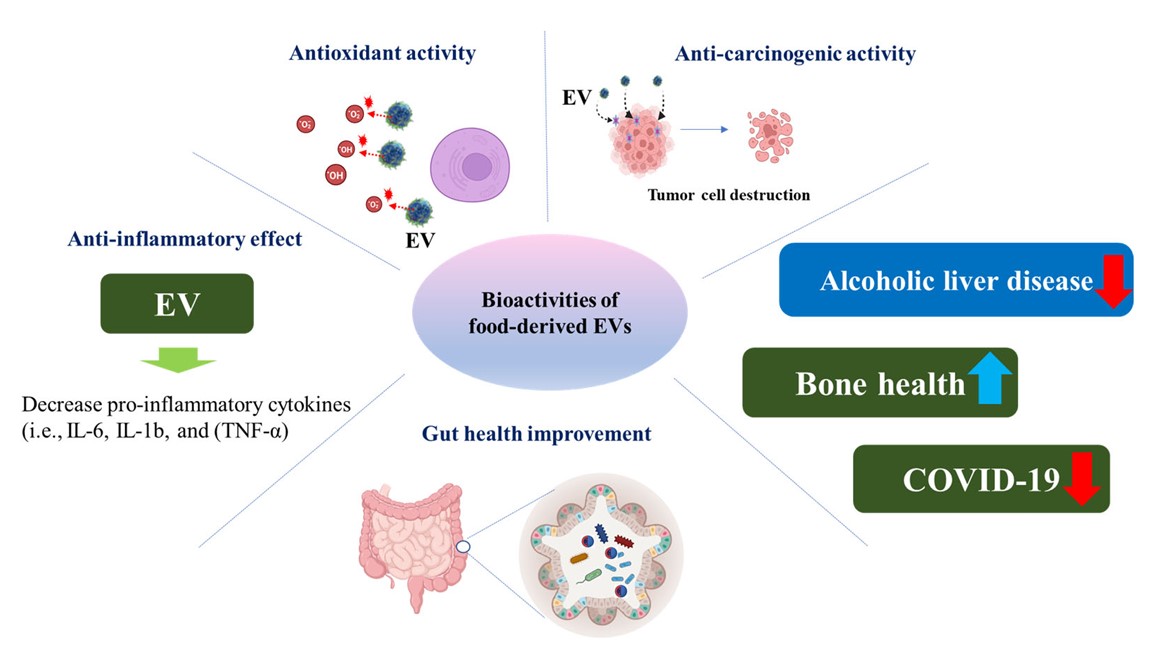 Fig.1 Various health benefits of food-derived EVs.1
Fig.1 Various health benefits of food-derived EVs.1
Technical Infrastructure: Tools to Support Quality and Insight
Our platform at Creative Biolabs includes the following (optional) analytical tools for wheat exosome characterization:
-
Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
-
Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
-
Zeta Potential Analysis
-
RNA and Protein Extraction Kits
-
RT-PCR and qPCR panels
-
Cell proliferation, migration, and oxidative stress assays
Clients can select from our menu of assays based on the research objective.
Key Advantages of Working with Creative Biolabs
-
Source-Optimized Protocols
Isolation protocols refined for wheatgrass-derived vesicles.
|
Flexibility to meet specific experimental goals and delivery formats.
|
|
Reliable reproducibility ensured through rigorous SOPs and quality checks.
|
Ongoing communication with Creative Biolabs scientists during all project phases.
|
Standard Project Deliverables
A basic wheat-derived exosome research project with Creative Biolabs includes:
-
Documented isolation protocol and raw material source
-
Exosome suspension in PBS
-
Summary of yield and process parameters
(If requested, optional reports include detailed particle characterization, bioactivity assays, and molecular profiling.)
What Researchers Are Saying
"Creative Biolabs' wheat exosome services were instrumental to our wound healing study. Their isolation was clean, reproducible, and delivered on schedule."
— Dr. F. LeXXXX
"Thanks to Creative Biolabs, we were able to explore the angiogenic potential of plant vesicles for the first time. Their guidance made a complex workflow simple."
— Prof. T. KuXXXX
Wheat-derived exosomes represent a growing area of interest for plant scientists, food technologists, and regenerative biology researchers alike. Creative Biolabs offers expert support at every step to help you explore this exciting vesicle class. Contact us today to begin your wheat exosome research project.
FAQs
Q: What are exosomes derived from wheat, and what are their purposes?
A: Wheat-derived exosomes are nano-sized extracellular vesicles secreted by wheat cells. These exosomes are believed to be involved in various biological processes, including stress response, nutrient transport, and signaling pathways. Because of their special makeup, they can interact with other cells and possibly affect how plants and other organisms function physiologically.
Q: How can wheat-derived exosomes be utilized in the field of skincare and cosmetics?
A: Wheat-derived exosomes show great potential in skincare due to their regenerative properties and ability to enhance skin barrier functions. Research indicates that they may contain bioactive compounds that can improve hydration, reduce inflammation, and promote skin cell regeneration. Consequently, they are being explored as natural ingredients in cosmetic formulations aimed at anti-aging, skin repair, and overall skin health enhancement.
Q: Are there any research studies demonstrating the benefits of wheat-derived exosomes in agricultural applications?
A: Yes, several studies have explored the role of wheat-derived exosomes in promoting plant growth and resistance to environmental stressors. According to research, these exosomes can improve plant resistance to illnesses and unfavorable environments while also facilitating nutrient uptake. Such findings underscore their potential as a natural approach to improving crop yield and sustainability.
Q: What are the challenges researchers face when studying wheat-derived exosomes?
A: One of the significant challenges in studying wheat-derived exosomes is the complexity of isolating and characterizing these vesicles. The variability in exosome composition based on the wheat variety and environmental conditions adds another layer of difficulty. Additionally, comprehensively understanding the mechanisms through which these exosomes exert their functions requires advanced research methodologies and technologies.
Q: What future applications are being considered for wheat-derived exosomes beyond skincare and agriculture?
A: Beyond skin care and agricultural applications, wheat-derived exosomes are being investigated for their potential in food technology, such as enhancing the nutritional profile of food products and as natural preservatives. Additionally, their biocompatibility and ability to deliver bioactive molecules make them promising candidates for research in nanotechnology and biomaterials, particularly for developing smart packaging solutions and functional foods.
Q: How can researchers contribute to the knowledge base of wheat-derived exosomes?
A: Researchers can contribute by conducting interdisciplinary studies that explore the biogenesis, composition, and functional characterization of wheat-derived exosomes. Collaborating to share findings across various fields—such as plant biology, food science, and materials science—will enhance our understanding and open up new avenues for practical applications.
Reference
-
Yeo, JuDong. "Food-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Multi-Bioactive Complex and Their Versatile Health Effects." Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 12,10 1862. 13 Oct. 2023, doi:10.3390/antiox12101862. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Various health benefits of food-derived EVs.1
Fig.1 Various health benefits of food-derived EVs.1









