Cereal derived Exosome Research & Applications
Overview Our Services Workflow Research Insights Platform Biological Benefits Why us Project Output Testimonials FAQs
Nutritional Nanocarriers: The Untapped Potential of Cereal-Derived Exosomes
Cereal crops, such as wheat, oats, corn, and buckwheat, have long been staple foods across the globe. Beyond their nutritional value, these plants produce small extracellular vesicles (EVs), also known as exosomes, that have gained increasing attention for their role in intercellular communication and molecular transport. Cereal-derived exosomes (CDEs) are nano-sized vesicles, typically 30–150 nm in diameter, and carry an array of bioactive molecules, including RNAs, lipids, and proteins derived from their parent cereal species.
At Creative Biolabs, we provide tailored research solutions for CDE investigations. Leveraging high-performance ultracentrifugation techniques and state-of-the-art analytical tools, we support scientists in uncovering the functional traits, molecular diversity, and practical applications of vesicles derived from cereal sources. Whether your study focuses on food science, cosmetic formulations, or agricultural biotechnology, Creative Biolabs' integrated platform empowers your discoveries.
Our Specialized Offerings in Cereal Exosome Research
Creative Biolabs' service portfolio includes:
-
Exosome Isolation & Purification: Reliable ultracentrifugation protocols customized to cereal species.
-
Vesicle Profiling: Particle sizing, morphology, and concentration via NTA and TEM.
-
Bioactivity Evaluation (optional): Cellular uptake, immune modulation, and oxidative stress protection assays.
-
Molecular Profiling (optional): RNA sequencing and proteomic analysis to characterize vesicle cargo.
-
Source Comparison (optional): Cross-species evaluation of vesicle content and function (e.g., corn vs. wheat).
-
Application Feasibility Studies (optional): Exploratory testing for use in cosmetics, nutraceuticals, or agro-delivery systems.
Each project is fully customizable, guided by Creative Biolabs' expert consultation and quality control checkpoints.
Streamlined Workflow: From Grain to Gradient-Purified Vesicles
Our standard CDE isolation pipeline includes:
-
Source Material Selection – Screening of cereal type and physiological maturity.
-
Mechanical Disruption – Juicing or homogenization of cereal tissue.
-
Low-Speed Clarification – Centrifugation to remove fibrous debris.
-
Filtration and Pre-Enrichment – Removal of micron-scale impurities.
-
Ultracentrifugation – High-speed vesicle pelleting from filtered extracts.
-
Density Gradient Purification – Optional step for enhanced purity.
-
Final QC and Resuspension – PBS buffer formulation, sterile filtration, and data validation.
This workflow ensures reproducible isolation of high-purity vesicles ready for downstream experimentation.
Insights from Cereal-Derived Exosome Studies
Emerging research continues to reveal the multifaceted roles CDEs can play in biological systems. Highlights from various cereal types include:
|
Cereal Source
|
Research Highlights
|
|
Wheat-derived Exosome
|
Vesicles from young wheat grasses support fibroblast and endothelial cell migration, promoting angiogenesis and wound closure.
|
|
Oat-derived Exosome
|
β-glucan-rich oat exosomes were found to regulate dectin-1 signaling and suppress microglial inflammation, protecting neuronal function in alcohol-exposed mice.
|
|
Tartary Buckwheat-derived Exosome
|
These vesicles delay starch digestion and modulate gut microbiota diversity via miRNA delivery, aiding digestive health.
|
|
Buckwheat-derived Exosome
|
Rich in phytochemicals like flavonoids and plant sterols, these vesicles may help regulate metabolism and gastrointestinal balance.
|
|
Corn-derived Exosome
|
Exosomes from corn stimulate immune cells to release TNF-α, contributing to anti-tumor responses; PEGylation boosts tissue targeting.
|
These findings suggest promising applications of CDEs in functional food science, brain health, gut microbiota modulation, and immunomodulation.
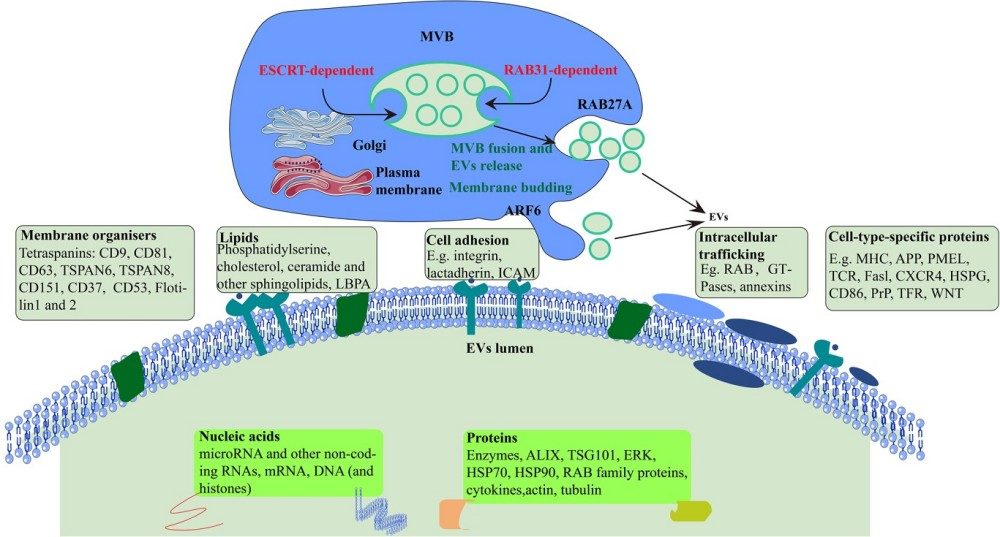 Fig.1 The release of EVs.1
Fig.1 The release of EVs.1
Our Analytical Platform: Technology That Drives Confidence
Creative Biolabs integrates the following technologies for accurate and high-throughput CDE analysis:
-
Transmission and Scanning Electron Microscopy (TEM/SEM)
-
Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
-
Zeta Potential Measurement
-
High-Throughput RNA-seq and Proteomics
-
qPCR Panels for Immune/Stress Markers
-
Uptake and Viability Assays in Human and Murine Cells
Each technique is carefully selected to support precise characterization and functional validation of cereal-derived vesicles.
Biological Signatures and Functional Advantages
-
Nutrient-Linked Cargo
β-glucan (oats), zeaxanthin (corn), and polyphenols (buckwheat) packaged into stable vesicles.
-
Immunoregulatory Activity
CDEs modulate cytokine signaling and immune cell function.
-
Neuroprotection and Gut Health
Some exosomes target inflammatory pathways in the brain and digestive system.
-
Application Flexibility
Suitable for food-grade formulations, skincare actives, and agri-delivery carriers.
-
Environmental Stability
High vesicle integrity is maintained under a variety of storage and processing conditions.
Why Partner with Creative Biolabs?
|
Proven success working with diverse cereals from lab to pilot scale.
|
Tailored plans to match specific research goals and timelines.
|
-
Confidential Collaboration
Strong IP protection and secure data handling.
|
Fast turnaround times and real-time progress reporting.
|
Deliverables
A standard cereal exosome project includes:
-
Raw material batch documentation
-
Detailed isolation procedure and quality benchmarks
-
Optional vesicle physicochemical profile (size, charge, morphology)
-
Optional cargo analysis (RNA/protein content)
-
Optional functional assay results and image records
-
Customized final report with interpretation
Voices from the Field
"Partnering with Creative Biolabs took our cereal exosome research to the next level. Their deep technical knowledge and seamless communication helped us generate high-impact data across multiple bioassays."
— Dr. H. Nguyen, Nutraceutical Development Group
"Creative Biolabs provided us with beautifully purified oat and corn vesicles, which were key to our gut-brain axis research. Their support team truly understands plant nanovesicle science."
— Prof. L. Singh, Department of Molecular Nutrition
From improving nutrition to developing bioactive ingredients, cereal-derived exosomes are a frontier with immense potential. Creative Biolabs' full-service research support helps you unlock the science behind these nanovesicles with confidence and precision. Contact us to begin your cereal exosome research today.
FAQs
Q: What types of cereal-derived exosomes are primarily studied?
A: Cereal-derived exosomes can be isolated from various sources, including wheat, corn, rice, and oats. Each type of cereal exosome can exhibit unique properties and compositions depending on the plant source, including differences in lipid, protein, and RNA contents.
Q: What uses can exosomes generated from cereals have in the skincare and cosmetics sectors?
A: There is a growing trend of utilizing cereal-derived exosomes in cosmetic formulations. Anti-aging qualities, improved skin hydration, and skin restoration are some of their possible advantages. Researchers are investigating how the rich payload of bioactive substances within these exosomes can improve skin health and address various dermatological concerns.
Q: What are some emerging trends in cereal exosome research?
A: Emerging trends include the exploration of cereal exosome applications in functional foods, nutraceuticals, and even bioplastics. Researchers are increasingly looking at how these exosomes can be harnessed to enhance food quality and provide health benefits, as well as their roles in sustainable agricultural practices.
Q: What challenges are present in cereal-derived exosome research?
A: Key challenges in this field include standardization of isolation and characterization protocols, as well as a comprehensive understanding of the interaction mechanisms between cereal-derived exosomes and target cells or tissues. Additionally, there is a need for more extensive studies to assess the safety and efficacy of exosome-based applications in various industries.
Reference
-
Fan, Shi-Jie et al. "Edible plant extracellular vesicles: An emerging tool for bioactives delivery." Frontiers in immunology vol. 13 1028418. 8 Dec. 2022, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.1028418. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 The release of EVs.1
Fig.1 The release of EVs.1









